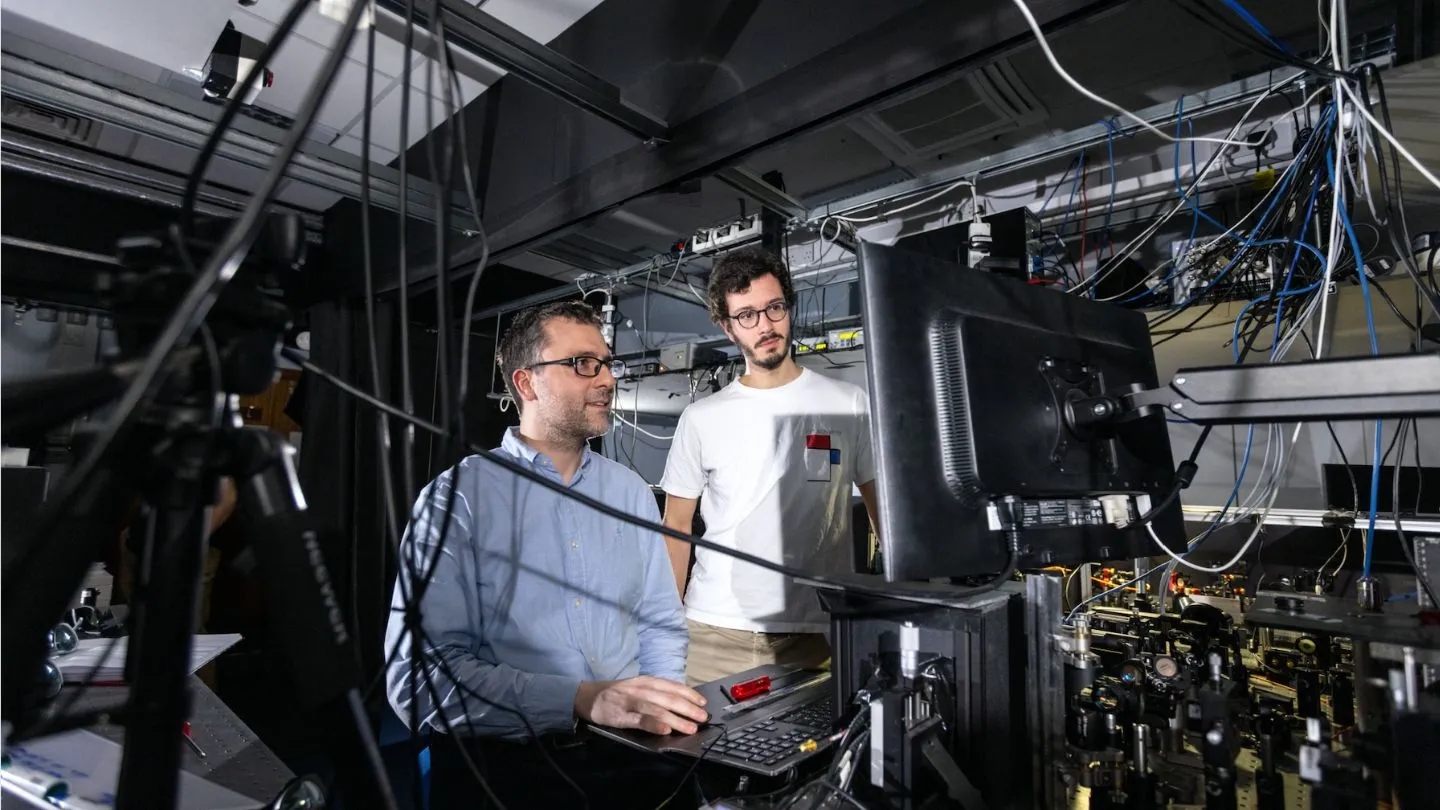
Microscopy on tissue swollen to 16 times its normal size can help unravel neural structures
We’re announcing the world’s first scalable, error-corrected, end-to-end computational chemistry workflow. With this, we are entering the future of computational chemistry.
Quantum computers are uniquely equipped to perform the complex computations that describe chemical reactions – computations that are so complex they are impossible even with the world’s most powerful supercomputers.
However, realizing this potential is a herculean task: one must first build a large-scale, universal, fully fault-tolerant quantum computer – something nobody in our industry has done yet. We are the farthest along that path, as our roadmap, and our robust body of research, proves. At the moment, we have the world’s most powerful quantum processors, and are moving quickly towards universal fault tolerance. Our commitment to building the best quantum computers is proven again and again in our world-leading results.
The significance of this experiment extends beyond telecommunications, computing, and medicine. Metamaterials like the ones used in this research could have broader applications in industries such as energy, transportation, aerospace, and defense.
For instance, controlling light at such a fine level might enable more efficient energy systems or advanced sensor technologies for aircraft and vehicles. Even black hole physics could be explored through these new quantum experiments, adding to the wide-ranging impact of this research.
As technology advances, the role of metamaterials and quantum physics will become increasingly critical. The ability to manipulate light in space and time holds the promise of reshaping how we interact with the world, offering faster, more efficient, and more precise tools across industries.
A team of 19 researchers published guidelines for the responsible use of machine learning in science. They say it could avert a crisis that’s smoldering in every field.
A new crop of artificial-intelligence models allows users to create, manipulate and learn about biology using ordinary language.
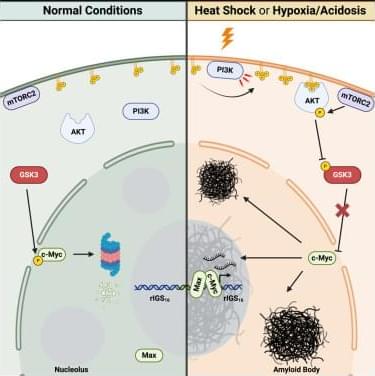
Lacroix et al. demonstrate that heat-induced activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling cascade drives the formation of functional amyloid aggregates that protect cells from harsh environmental conditions. Here, activation of PI3K and AKT represses GSK3-mediated degradation of c-Myc, leading to upregulation of nucleating noncoding RNAs that mediate this physiological amyloidogenic event.
Make sure to watch this next video about Type 1 to Type 4 Civilizations: https://youtu.be/5fTNGvuPTMU.
💡 Future Business Tech explores AI, emerging technologies, and future technologies.
SUBSCRIBE: https://bit.ly/3geLDGO
This video explores the Kardashev scale and the type 1 to type 7 civilizations. Related terms: ai, future business tech, future technology, future tech, future business technologies, future technologies, artificial intelligence, kardashev scale, type 7 civilization, type 6 civilization, type 5 civilization, type 4 civilization, type 3 civilization, type 2 civilization, type 1 civilization, etc.
ℹ️ Some links are affiliate links. They cost you nothing extra but help support the channel so I can create more videos like this.
#technology #ai
What do transgenderism, embryo design, and the erasure of religion have in common? They’re pillars of a growing transhumanist agenda.
The problem? The file was unencrypted. No password protection. No security. Just a plain text file with millions of sensitive pieces of data.
Based on his analysis, Fowler determined the data was captured by some kind of infostealer malware. A popular tool used by cybercriminals, an infostealer is designed to grab usernames, passwords, and other sensitive data from breached sites and servers. Once the criminals get their hands on the data, they can use it to launch their own attacks or peddle the information on the dark web.
After finding the database, Fowler contacted the hosting provider, which removed it from public access. Since the provider would not disclose the name of the file’s owner, Fowler said he didn’t know if the database was created legitimately and then accidentally exposed or intentionally used for malicious reasons.