Bucknell has led advanced engineering teams at Chrysler and General Motors for three production high performance engine families. Was Senior Propulsion Engineer for the Raptor full-flow staged combustion methalox rocket at Space Exploration Technologies then Senior Propulsion Scientist for Divergent3D developing vehicle technologies.
In 2017, he described how high temperature (820−1000 degree celsius) nuclear power plants can solve produce synthetic fuel to replace oil.
Molten Salt reactors are being developed in China, Canada and the USA. However, those plants will run at about 700 degree celsius.



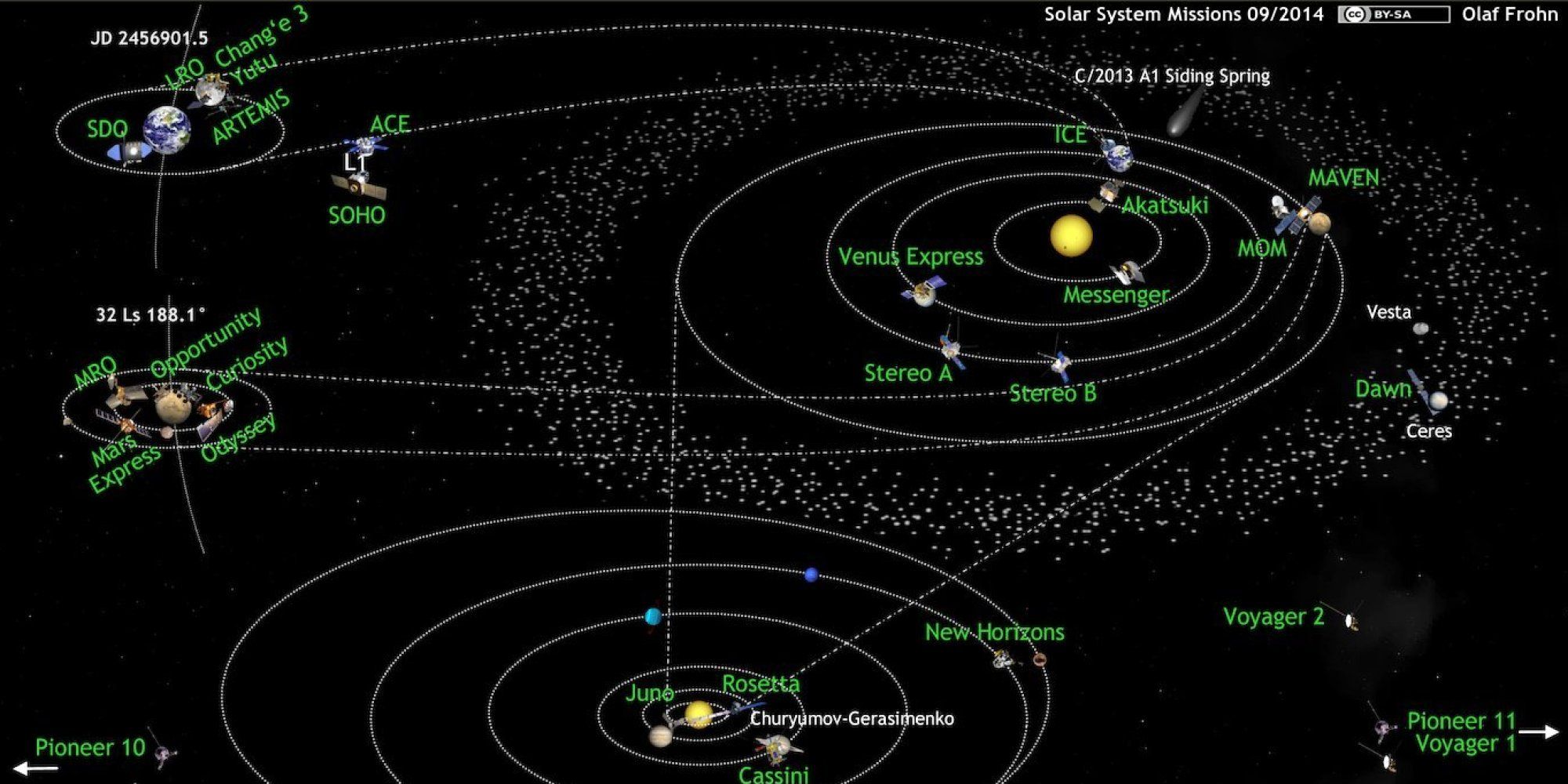
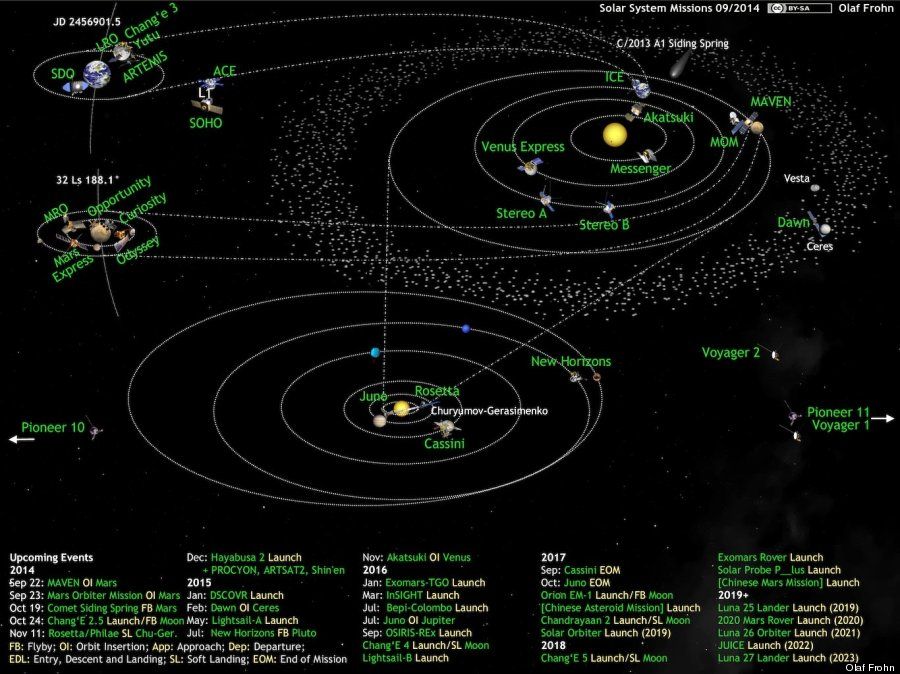 A diagram, updated once a month, of active space missions beyond Earth orbit.
A diagram, updated once a month, of active space missions beyond Earth orbit.