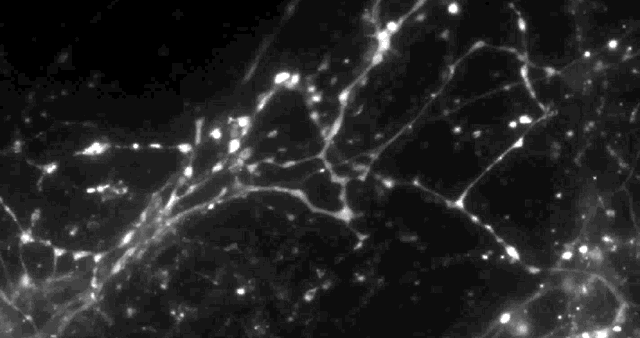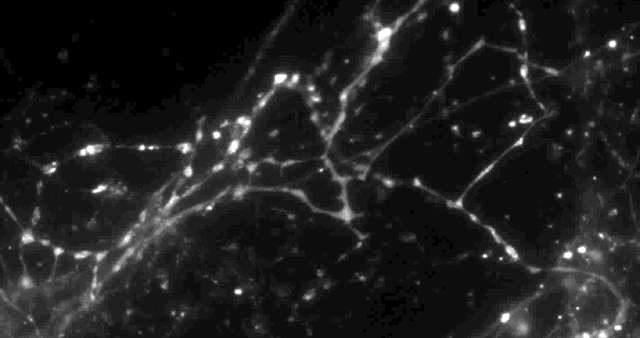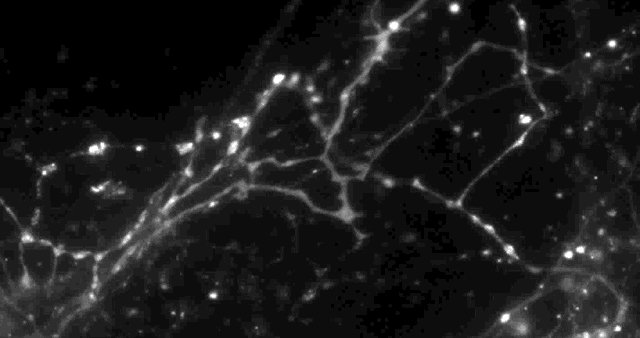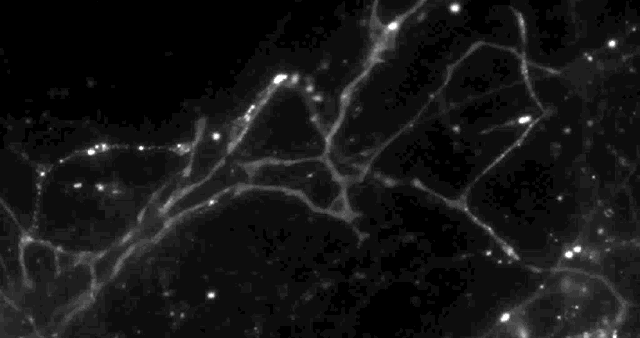
Columbia University scientists recently tested a new optical technique to study how information is transmitted in the brains of mice and made a surprising discovery: When stimulated electrically to release dopamine (a neurotransmitter or chemical released by neurons, or nerve cells, to send signals to other nerve cells), only about 20 percent of synapses — the connections between cells that control brain activity — were active at any given time.
The effect had never been noticed. “Older techniques only revealed what was going on in large groups of synapses,” explained David Sulzer, PhD, professor of neurobiology in Psychiatry, Neurology, and Pharmacology at Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC). “We needed a way to observe the neurotransmitter activity of individual synapses, to help us better understand their intricate behavior.”