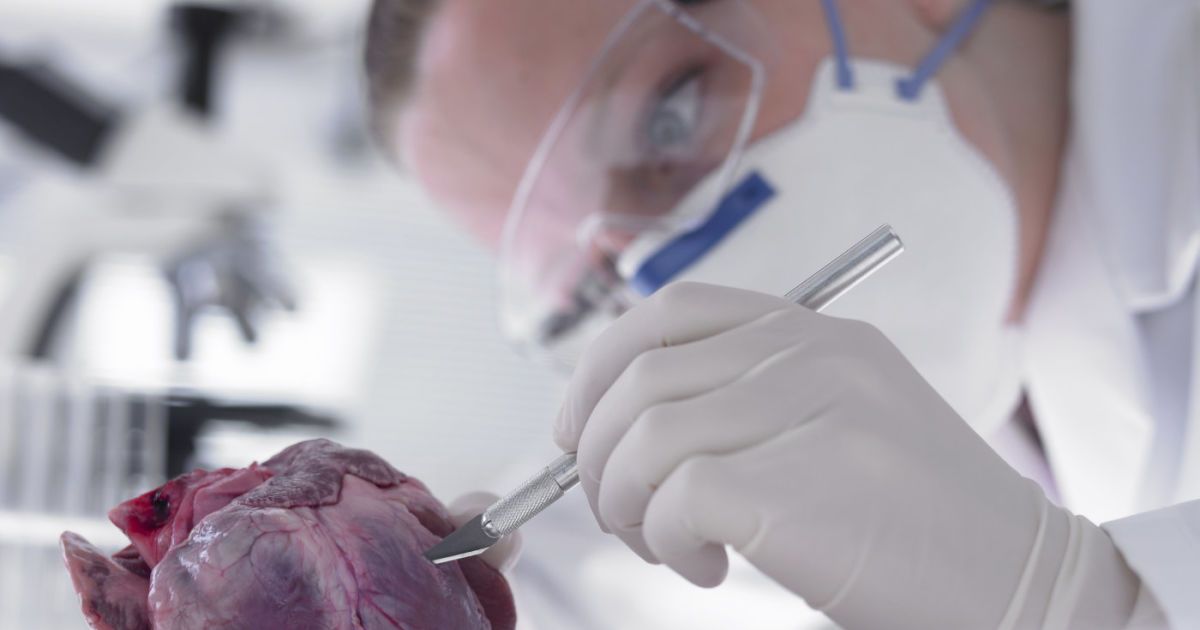
One of the latest inventions out of Tel Aviv University can patch up broken hearts. We’re talking about the real organs here, especially those damaged by myocardial infarction or heart attack. A team from the Israeli university created a “cyborg heart patch” that combines both living tissue and electronic components to replace the damaged parts of the organ. “It’s very science fiction, but it’s already here,” says one of its creators, Prof. Tal Dvir. “[W]e expect it to move cardiac research forward in a big way.” The patch can contract and expand like real heart tissue can, but it can do much, much more than that.
The electronic components allow doctors to remotely monitor their patients’ condition from afar. A physician could log into a computer and see if the implant is working as intended. If he senses that something’s amiss, he could release drugs to, say, regulate inflammation or fix the lack of oxygen. That sounds dangerous to us, since computers can be hacked. But the researchers are aiming to develop the patch further so it can regulate itself with no human intervention.
Dvir warns that the “practical realization of the technology may take some time.” For now, those suffering from cardiovascular diseases will have to rely on current treatment methods. The team is still in the midst of refining their cyborg heart patch. Plus, they’re looking at how to create bionic brain and spinal cord tissues using what they’ve learned so far to treat neurological conditions.