Awesome; could be a new track for reverse aging.
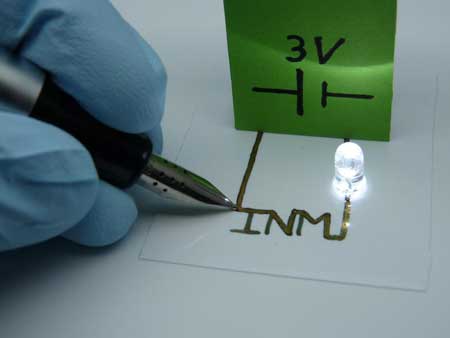
Research scientists at INM have combined the benefits of organic and inorganic electronic materials in a new type of hybrid inks. This allows electronic circuits to be applied to paper directly from a pen, for example.
The electronics of the future will be printed. Flexible circuits can be produced inexpensively on foil or paper using printing processes and permit futuristic designs with curved diodes or input elements. This requires printable electronic materials that can be printed and retain a high level of conductivity during usage in spite of their curved surfaces. Some tried and tested materials include organic, conductive polymers and nanoparticles made of conductive oxides (TCOs). Research scientists at INM – Leibniz-Institute for New Materials have now combined the benefits of organic and inorganic electronic materials in a new type of hybrid inks. This allows electronic circuits to be applied to paper directly from a pen, for example.
New hybrid inks permit printed, flexible electronics without sintering. (Image: INM)
Airforce is looking for a few good men and women for their MQ-9 program.
WASHINGTON (AFNS) —
The Air Force released basing criteria April 12 that will be used to select candidate bases for a potential new MQ-9 Reaper wing with units at up to two locations.
The Air Force is pursuing additional locations to help diversify assignment opportunities for personnel within the MQ-9 enterprise, provide increased opportunities for leadership from within the community, and provide flexibility to enhance integration with other organizations and capabilities.
The desire for additional locations for an MQ-9 wing was identified during surveys of officers and enlisted Airmen in the MQ-9 and MQ-1 Predator enterprise as part of Air Combat Command’s Culture and Process Improvement Program.
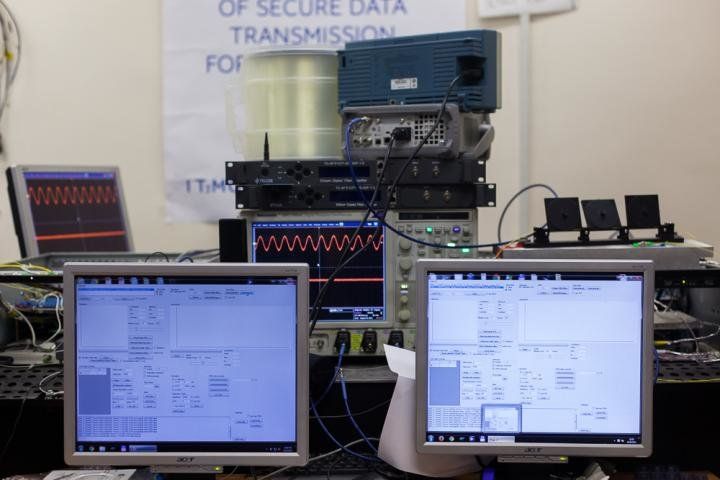
Scientists from ITMO University in Saint Petersburg, Russia have enabled the longer distance (250 Kilos) of secured data transmission occur via Quantum. Nice; and should be a wake up call to the US as well on advancing their efforts more.
A group of scientists from ITMO University in Saint Petersburg, Russia has developed a novel approach to the construction of quantum communication systems for secure data exchange. The experimental device based on the results of the research is capable of transmitting single-photon quantum signals across distances of 250 kilometers or more, which is on par with other cutting edge analogues. The research paper was published in the Optics Express journal.
Information security is becoming more and more of a critical issue not only for large companies, banks and defense enterprises, but even for small businesses and individual users. However, the data encryption algorithms we currently use for protecting our data are imperfect — in the long-term, their logic can be cracked. Regardless of how complex and intricate the algorithm is, getting round it is just the matter of time.
Contrary to algorithm-based encryption, systems that protect information by making use of the fundamental laws of quantum physics, can make data transmission completely immune to hacker attacks in the future. Information in a quantum channel is carried by single photons that change irreversibly once an eavesdropper attempts to intercept them. Therefore, the legitimate users will instantly know about any kind of intervention.
One thing about Quntum; nothing ever stays consistent. Why it’s loved & hated by Cyber Security enthusiasts as well as AI engineers.
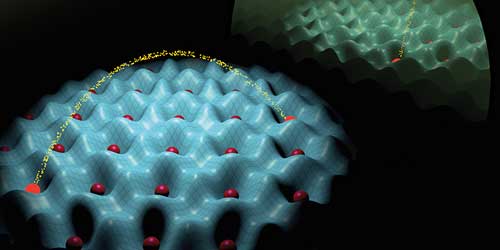
When water in a pot is slowly heated to the boil, an exciting duel of energies takes place inside the liquid. On the one hand there is the interaction energy that wants to keep the water molecules together because of their mutual attraction. On the other hand, however, the motional energy, which increases due to heating, tries to separate the molecules. Below the boiling point the interaction energy prevails, but as soon as the motional energy wins the water boils and turns into water vapour. This process is also known as a phase transition. In this scenario the interaction only involves water molecules that are in immediate proximity to one another.
An artificial quantum world of atoms and light: Atoms (red) spontaneously arrange themselves in a checkerboard pattern as a result of the complex interplay between short- and long-range interactions. (Visualizations: ETH Zurich / Tobias Donner)
The question is what does Stefano Pirandola and Samuel L. Braunstein consider “hybrid” when it comes to QC? In much of the Quantum research today only shows us things like “synthetic diamonds”, etc. are added to stablize data storage and transmissions not much else.
Physics: Unite to build a quantum Internet. Braunstein.
With 3D printers; many small mom-and-pop manufacturers are easy to set up anywhere. Which brings in some interesting challenges when thinking about regulatory compliance and safety. Imaging a neighbor who was laid off gets a 3D printer and begins building and shipping things from their home. Plus they’re stock piling chemicals and other things in their basement or garage as “bi-products” in the production of the goods that they are building with their $15K 3D printer. Question for many is — how safe is it? how can this be monitored and controlled?
Manufacturers haven’t been able to fully exploit advancements in new materials, because computer-aided design and engineering tools haven’t kept pace, says a program manager for the government agency.
Vandenbrande: Humans have reached limits of their imagination.
Could this sensor technology revolutionize how auto and other navigation technology looks in the future?
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) has awarded HRL Laboratories $4.3 million to develop vibration- and shock-tolerant inertial sensor technology that enables future system accuracy needs without utilizing GPS.
While GPS provides sub-meter accuracy in optimal conditions, the signal is often lost or degraded due to natural interference or malicious jamming.
HRL Laboratories, based in Malibu, California, is a corporate research-and-development laboratory owned by The Boeing Company and General Motors specializing in research into sensors and materials, information and systems sciences, applied electromagnetics and microelectronics.