NASA Technology
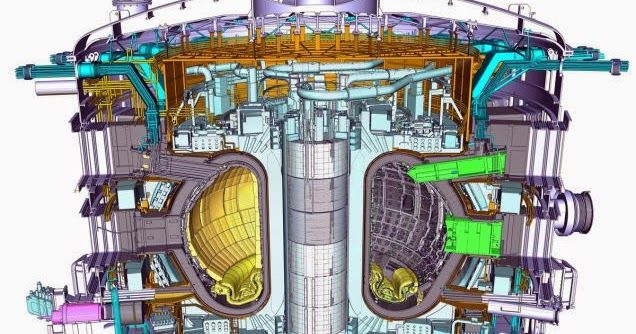
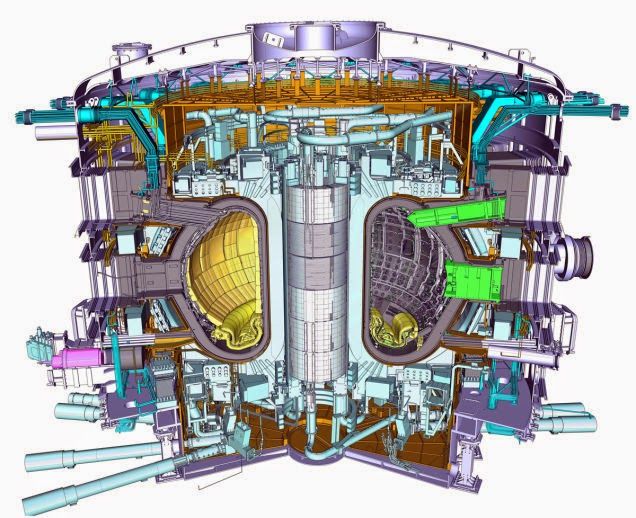
Building on work he and his companies did with Johnson Space Center’s In Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) team, Robert Zubrin has developed and commercialized technologies that could prove revolutionary in their Earth applications, such as a system that could extract millions of barrels of oil from defunct oil wells around the world and another that can harness all the natural gas currently burned off as waste at many oil drilling rigs (Spinoff 2015).
But when he’s not working to change this world or colonize others, the president of Pioneer Astronautics, Pioneer Energy, and the Mars Society enjoys a good microbrew. Now, he’s applied some of that same technology to cut costs for craft breweries that produce anywhere between 3,000 and 300,000 barrels per year.