My new story for The Huffington Post on the virtue of reason and asking: Why?.

Image of the future — By Smart Gadget Technology
The human race is on the threshold of so much revolutionary change. It’s mostly due to the emerging field of transhumanism: a social movement that aims to use science and technology to radically modify the human body—and modify the human experience. I get asked all the time: What is the best way to handle such changes—like the merging of humans with machines to make cyborgs? Or spending more time in virtual reality then normal reality? Or biohacker brain implants that let us use telepathy with one another (which eventually will lead us all to be connected via a hive mind)?
Interesting Energy Animation
Posted in energy, nanotechnology
Nanotubes can self-assemble to create functional wires.
Research Paper: http://bit.ly/1SdTIVZ
Been a while since I’ve written a new article. Include my love for the Lifeboat Foundation in it!
Are we alone in the universe? Are we the first to witness the stellar bursts amongst the skies of old? Is it foretold that we were the ones destined for the stars, beginning at the Moon and then Mars? Once driving cars, do we venture far, beyond the horizon of antiquated liveliness, a surreal vibrancy-but-a-tranquillity to the origins of chaos? Without science, these imaginary realities are but dreams shuttered away in the subconscious mind. But, with this magical and logical element of human society, we are gifted with the power to envision the sleeping mind’s abstract impossibilities, transforming them into possible realities… So that we may morph the series of footsteps in waking life.
Like evolution is the guardian of change, time dictates discovery. We advance, and the nuances past become more prevalent; a new precedent set forth in every dedicated shard of time engulfed in the sublime, and rhythmic confines, of the mind. Interlinked by their commonality, the totality of the world’s abilities lays not in the futility of complacency, but in the eulogy of peaceful unity. Once we as species see the far reaches of harnessing all pieces of this puzzle [that is the international intellect], each passing day will become more perfect.
California Polytechnic State University researchers propose a 100 kilowatt space based laser system capable of probing the molecular composition of cold solar system targets such as asteroids, comets, planets and moons from a distant vantage. This system uses existing technology and only some needs refinement. All of it looks achievable in the next 3 to 5 years. They have NASA NIAC funding. They have detailed designs for a 900 kilowatt system that would use two Falcon heavy launches.
The military laser segment will be about a $5 billion per year market by 2020. There is a large multi-billion commercial laser market. Those markets will drive improvements in laser efficiency and technological improvements which will be leveraged for space based systems or ground based lasers for space beam propulsion applications.
California Polytechnic State University researchers propose a system capable of probing the molecular composition of cold solar system targets such as asteroids, comets, planets and moons from a distant vantage.
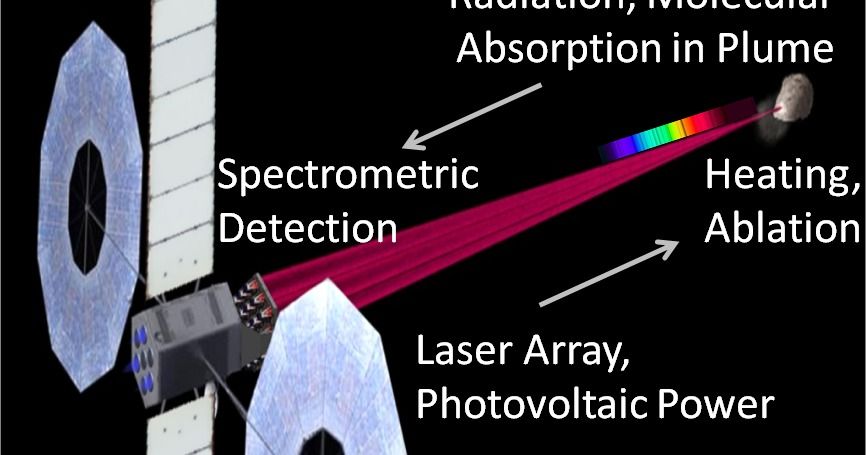
Their concept utilizes a directed energy beam to vaporize or sublimate a spot on a distant target, such as from a spacecraft near the object. With sufficient flux, our published results indicate that the spot temperature rises rapidly, and evaporation of materials on the target surface occurs (Hughes et al., 2015; Lubin and Hughes, 2015; Lubin et al., 2014). The melted spot serves as a high-temperature blackbody source, and ejected material creates a molecular plume in front of the spot. Molecular and atomic absorption of the blackbody radiation occurs within the ejected plume. Bulk composition of the surface material is investigated by using a spectrometer to view the heated spot through the ejected material. They envision a spacecraft that could be sent to probe the composition of a target asteroid, comet or other planetary body while orbiting the targeted object. The spacecraft would be equipped with an array of lasers and a spectrometer, powered by photovoltaics. Spatial composition maps could be created by scanning the directed energy beam across the surface. Applying the laser beam to a single spot continuously produces a borehole, and shallow sub-surface composition profiling is also possible.
Their initial simulations of laser heating, plume opacity, material absorption profiles and spectral detectivity show promise for molecular composition analysis. Such a system has compelling potential benefit for solar system exploration by establishing the capability to directly interrogate the bulk composition of objects from a distant vantage. They propose to develop models, execute preliminary feasibility analysis, and specify a spacecraft system architecture for a hypothetical mission that seeks to perform surface molecular composition analysis and mapping of a near-earth asteroid (NEA) while the craft orbits the asteroid.
Scientists say recent advances in laser propulsion technology could make it possible for spacecrafts to reach Mars in as little as 3 days using photon propulsion.
The concept was shared by Philip Lubin, a physics professor at the University of California, Santa Barbara at the NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) symposium. Ultimately, the method seeks to place an ultra-powerful laser in Earth’s orbit, that would use photon pressure to power a “sail-equipped” spacecraft. [ESA To Build “Moon Village” by 2030].