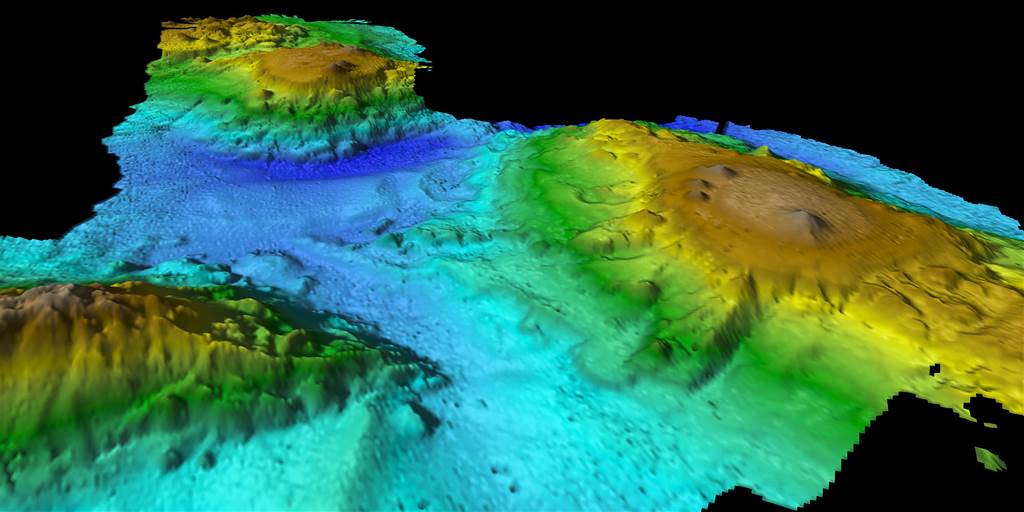
The find offers a glimpse into a previously unknown marine ecosystem — and spotlights just how little we know about the seafloor.
Scientists uncovered a chain of volcanic seamounts off the coast of the Australian island of Tasmania.


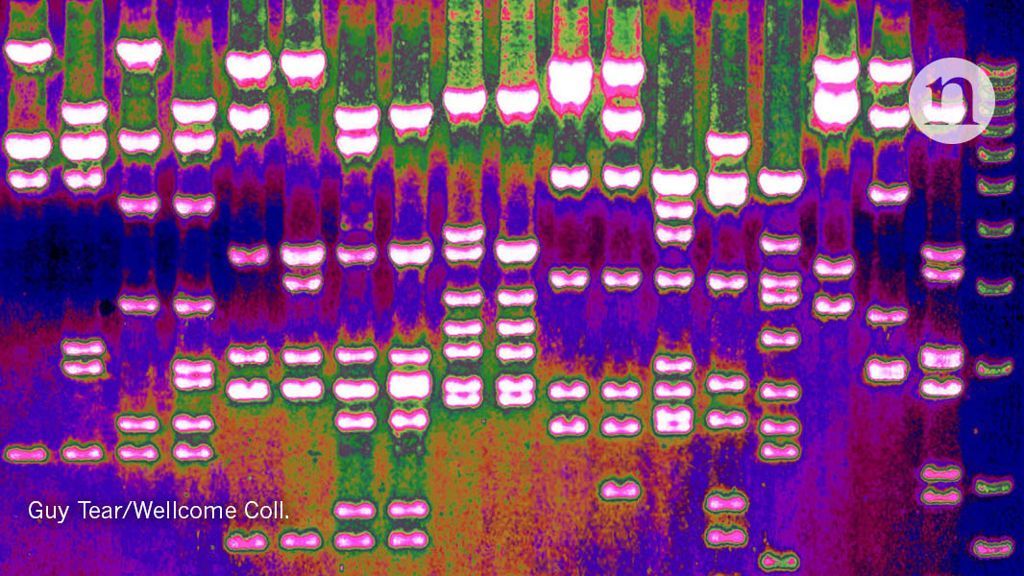
New research shows how police could use forensic DNA to track down a suspect’s relatives in genealogy databases that store a different kind of genetic data—and that were never intended for use in police investigations.
In other words, if your sibling leaves DNA at a crime scene, it could lead detectives to your door. That suggests new investigative possibilities for police—and also new concerns about genetic privacy and whether authorities who use forensic DNA in creative ways might be overstepping their bounds, says Noah Rosenberg, a professor of biology at Stanford University and senior author of a study, which appears in Cell.
“The potential to link people’s genotypes across databases has been developing for some time. It is both of interest and concerning, depending on one’s point of view,” says Rosenberg, who is also a member of Stanford Bio-X.


Scientists in Australia have for the first time demonstrated the protection of correlated states between paired photons—packets of light energy—using the intriguing physical concept of topology. This experimental breakthrough opens a pathway to build a new type of quantum bit, the building blocks for quantum computers.
The research, developed in close collaboration with Israeli colleagues, is published today in the prestigious journal, Science, a recognition of the foundational importance of this work.
“We can now propose a pathway to build robust entangled states for logic gates using protected pairs of photons,” said lead author Dr. Andrea Blanco-Redondo at the University of Sydney Nano Institute.

When fish are filleted in a seafood-processing plant, or when shrimp and shellfish are boiled, a lot of wastewater is generated. Currently, that water is simply discarded. An experimental new system, however, is able to draw much of the nutrients from it – and those nutrients could have a number of uses.