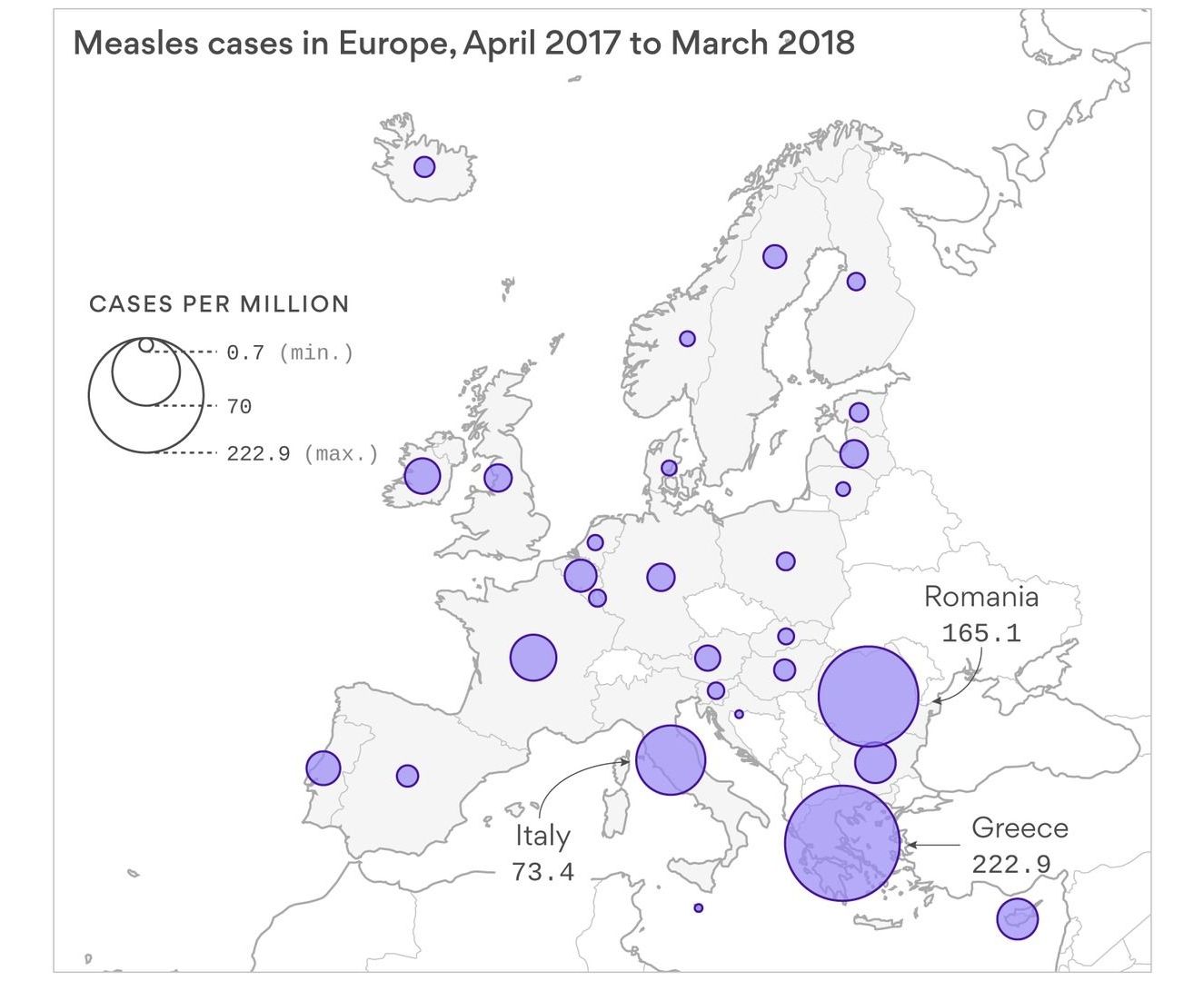
Why it matters: Measles is a killer disease. It’s estimated that more than 2 million children a year died from measles in the 1980s, but due to global vaccine programs (including Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance launched in 2000), that number has been brought under 70,000 cases. The return of measles to Europe and the Americas could suggest that some of our vaccine successes could be reversing or unraveling. In the case of Venezuela, measles outbreaks are mostly due to the effect of broad economic problems on its health care system, but for Europe and the U.S. measles outbreaks show the effects of powerful and well-organized anti-vaccine movements.
What’s next: Vaccines do not cause autism, but more advocacy is needed to counteract the false claims of anti-vaccine groups. In April 2018, the European Commission proposed activities to strengthen the EU’s capacity to vaccinate its population and address what some call “vaccine hesitancy.” In the U.S., however, there are still 18 states that allow non-medical vaccine exemptions linked to personal or philosophical beliefs.
Peter Hotez is a professor and dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, where he is also director of the Texas Children’s Hospital Center for Vaccine Development, and the author of “Vaccines Did Not Cause Rachel’s Autism.”