The result is sickness, starvation and death.



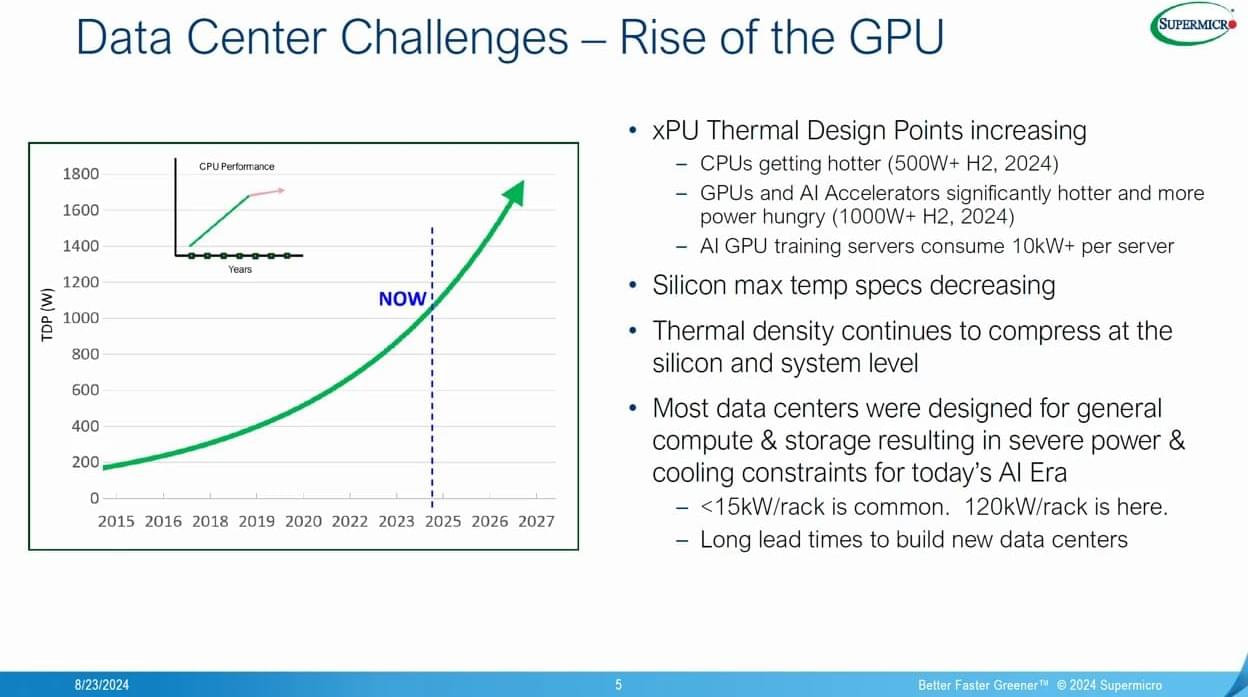
Adopting liquid cooling technology could significantly reduce electricity costs across the data center.
Many Porsche “purists” reflect forlornly upon the 1997, 5th generation, 996 version of the iconic 911 sports car. It was the first year of the water-cooled engine versions of the 911, which had previously been based on air-cooled engines since their entry into the market in 1964. The 911 was also the successor to the popular air-cooled 356. For over three decades, Porsche’s flagship 911 was built around an air-cooled engine. The two main reasons often provided for the shift away from air-cooled to water-cooled engines were 1) environmental (emission standards) and 2) performance (in part cylinder head cooling). The writing was on the wall: If Porsche was going to remain competitive in the sports car market and racing world, the move to water-cooled engines was unavoidable.
Fast forward to current data centers trying to meet the demands for AI computing. For similar reasons, we’re seeing a shift towards liquid cooling. Machines relying on something other than air for cooling date back at least to the Cray-1 supercomputer which used a freon-based system and the Cray-2 which used Fluorinert, a non-conductive liquid in which boards were immersed. The Cray-1 was rated at about 115kW and the Cray-2 at 195kW, both a far cry from the 10’s of MWs used by today’s most powerful supercomputers. Another distinguishing feature here is that these are “supercomputers” and not just data center servers. Data centers have largely run on air-cooled processors, but with the incredible demand for computing created by the explosive increase in AI applications, data centers are being called on to provide supercomputing-like capabilities.
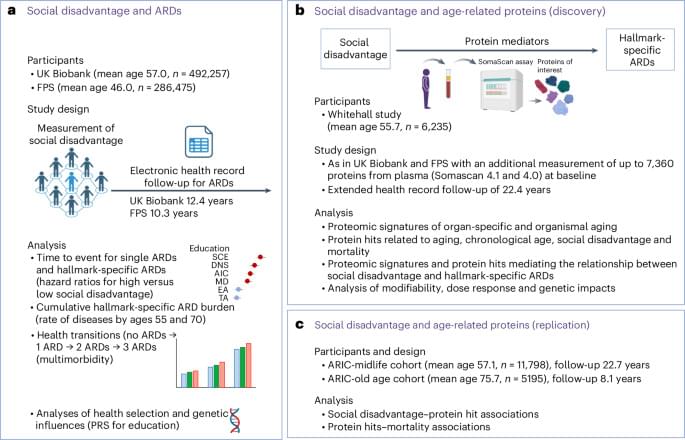
As an initial step, we selected ARDs associated with hallmarks of aging. These included a total of 83 diseases linked to one or more hallmarks of aging, based on the taxonomy put forward in ref. 4 (Supplementary Table 2). Support for this taxonomy comes from multiple sources. Analyses of electronic health records from general practice and hospitalizations identified more than 200 diseases with incidence rates increasing with chronological age6,22. Researchers linked a subset of these ARDs to specific hallmarks of aging using several approaches: mining 1.85 million PubMed abstracts on human aging, identifying shared genes in the genome-wide association study catalog, conducting gene set enrichment analysis and analyzing disease co-occurrence networks within each hallmark4.
We confirmed the co-occurrence of ARDs within each hallmark in 492,257 participants from the UK Biobank study23. The presence of one ARD increased the risk of developing another ARD related to the same hallmark, with clustering coefficients ranging from 0.76 for LOP-specific ARDs to 0.92 for SCE-specific ARDs. These findings corroborated the hallmark-specific clustering of ARDs (Extended Data Figs. 3 and 4)23.
In time-to-event analyses of UK Biobank and FPS participants without these ARDs at baseline (n ranging from 477,325 to 492,294 in the UK Biobank and from 278,272 to 286,471 in the FPS, depending on the social disadvantage indicator and ARD), social disadvantage—indicated by education and adult SES (neighborhood deprivation)—was associated with a higher risk of developing ARDs. In the UK Biobank, the age-, sex-and ethnicity-adjusted hazard ratio for developing any ARD was 1.31 (95% confidence interval (CI) 1.29–1.33) for individuals with low compared with high education. For individuals with high versus low adult SES, the hazard ratio was 1.21 (95% CI 1.20–1.23). In the FPS, the corresponding hazard ratios were 1.28 (95% CI 1.25–1.31) and 1.23 (95% CI 1.20–1.27), respectively.



Discovering new deposits of critical and rare earth minerals is paramount to delivering global net-zero ambitions. However, finding new ore bodies is becoming more challenging due to increasing costs and geopolitical tensions. What is more, much of the low-hanging fruit, so to speak, has already been exploited.
Could technological advances help broaden the search and speed up the process? Dr Bryony Richards, a senior research scientist with the Energy & Geoscience Institute at the University of Utah in the US, believes so.
Richards and her colleagues are incorporating NASA’s and Japan’s global Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) imagery with that of new satellite data, advances in computing power and AI. With this approach, they are developing a comprehensive first-of-a-kind method to uncover the ‘fingerprints’ of mineral deposits that could eventually provide a more cost and time-effective way of mapping minerals in remote areas.
Researchers in Utah are combining satellites, hyperspectral imaging and AI to discover mineral deposits in remote locations.

A research team led by Rice University’s Yang Gao has uncovered new insights into the molecular mechanisms of ADAR1, a protein that regulates ribonucleic acid (RNA) induced immune responses. Their findings, published in Molecular Cell March 17, could open new pathways for treating autoimmune diseases and enhancing cancer immunotherapy.
ADAR1 converts adenosine to inosine in double-stranded RNA, a process essential for preventing unwarranted immune responses, yet the molecular basis of this editing had remained unclear. Through detailed biochemical profiling and structural analysis, researchers found that ADAR1’s editing activity depends on RNA sequence, duplex length and mismatches near the editing site. High-resolution structures of ADAR1 bound to RNA reveal its mechanisms for RNA binding, substrate selection and dimerization.
“Our study provides a comprehensive understanding of how ADAR1 recognizes and processes RNA,” said Gao, assistant professor of biosciences and a Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT) Scholar. “These insights pave the way for novel therapeutic strategies targeting ADAR1-related diseases.”
Researchers have corrected a disease-causing gene mutation with a single infusion carrying a treatment that precisely targeted the errant gene.
This was the first time a mutated gene has been restored to normal.
The small study of nine patients announced Monday by the company Beam Therapeutics of Cambridge, Mass., involved fixing a spelling error involving the four base sequences — G, A, C and T — in DNA. The effect was to change an incorrect DNA letter to the right one. The result was a normal gene that functioned as it should, potentially halting liver and lung damage of patients with a rare disorder.
The small study in patients with a rare disorder that causes liver and lung damage showed the potential for precisely targeted infusions.
At GTC 2025, NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang introduced Blue, a cutting-edge AI-powered robot developed in collaboration with Disney Research and Google DeepMind. Watch as Jensen interacts with Blue and discusses this exciting partnership. While details are scarce, this brief moment showcases NVIDIA’s vision for the future of AI and robotics.
📺 Subscribe for more tech updates!
#NVIDIA #GTC2025 #AI #DisneyResearch #WaltDisneyWorld.
Thanks For Watching!
========================================================
Follow us on:
Website: http://samsdisneydiary.com/
FACEBOOK: https://web.facebook.com/SamsDisneyDiary.
…
INSTAGRAM: https://www.instagram.com/SamsDisneyDaily.
…
=========================================================