A new tool to address loss of proteostasis and destroy target proteins. It could potentially be used to destroy amyloids in Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, ALS, heart disease and amyloidosis which are driven by misfolded protein aggregation.
A new therapy could be the basis for addressing one of the primary reasons we age, loss of proteostasis and the resulting accumulation of Amyloidosis. Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, Amloidosis, Lipofuscin and so on could all potentially be targets for this technique.
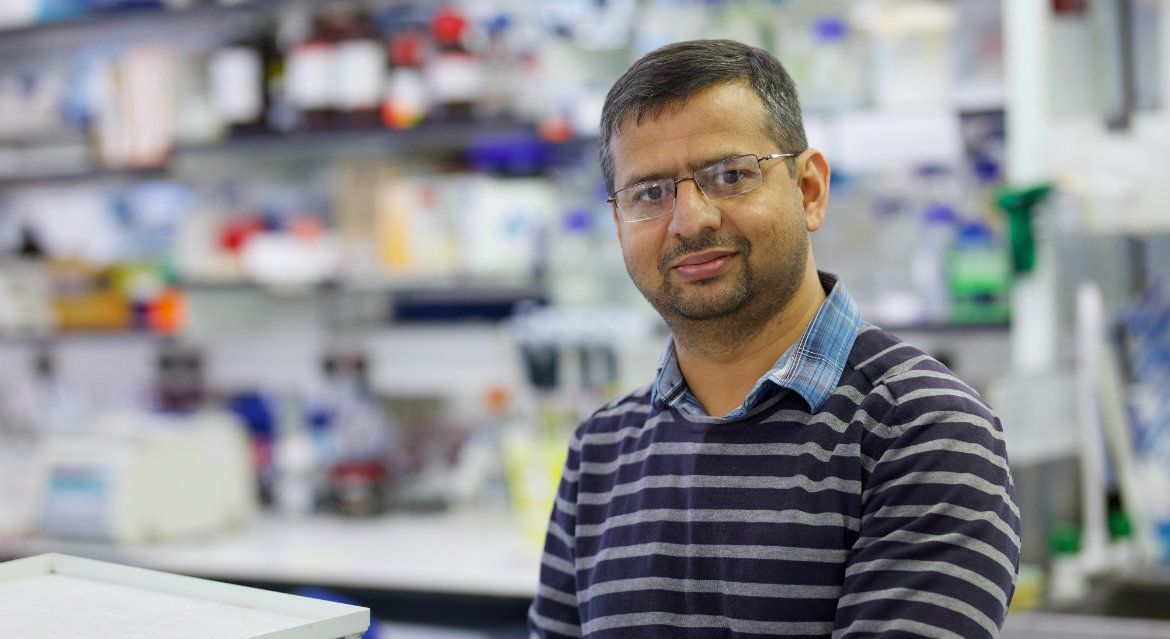
“University of Dundee researchers have shown that it is possible to rapidly target and destroy specific proteins in cells, raising the possibility of developing new ways of targeting ‘undruggable’ proteins in diseases.”