In episode five of The Most Unknown, astrophysicist Rachel Smith and astrobiologist Luke McKay travel to Hawaii’s powerful W.M. Keck Observatory to explore forming stars at the center of our galaxy.


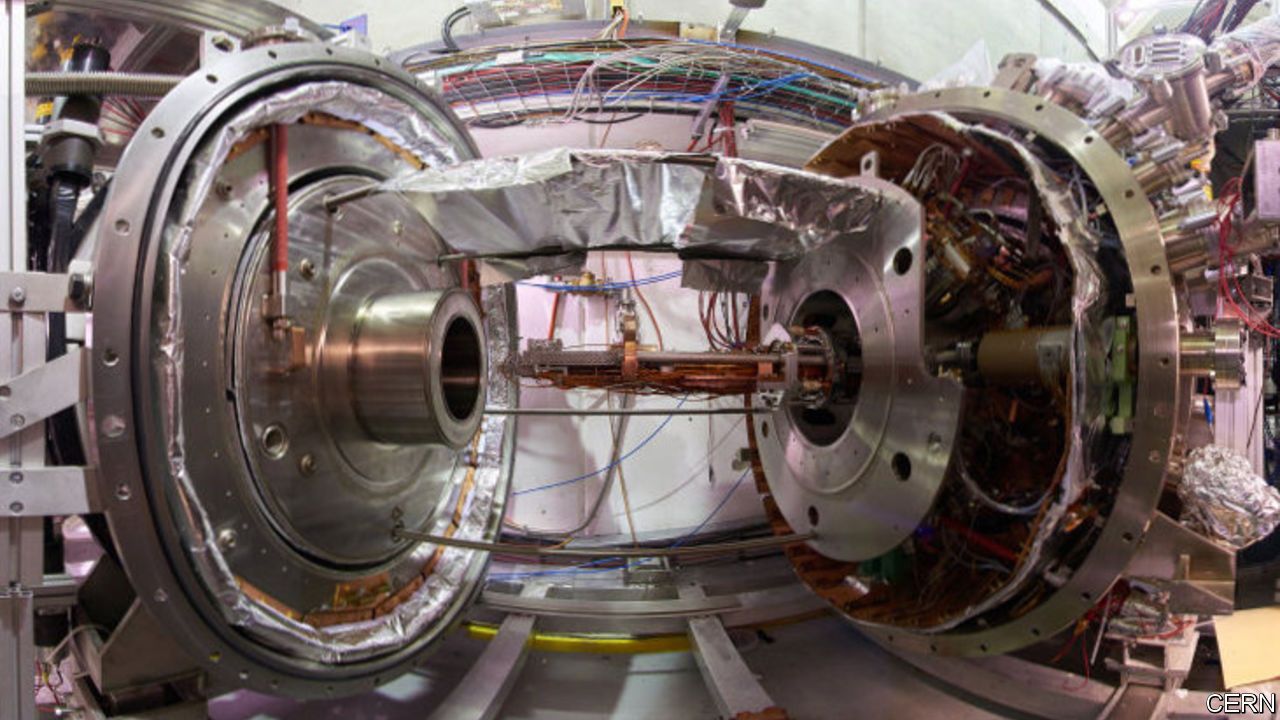
AS MISMATCHES go, it’s a big one. When physicists bring the Standard Model of particle physics and Einstein’s general theory of relativity together they get a clear prediction. In the very early universe, equal amounts of matter and antimatter should have come into being. Since the one famously annihilates the other, the result should be a universe full of radiation, but without the stars, planets and nebulae that make up galaxies. Yet stars, planets and nebulae do exist. The inference is that matter and antimatter are not quite as equal and opposite as the models predict.
This problem has troubled physics for the past half-century, but it may now be approaching resolution. At CERN, a particle-physics laboratory near Geneva, three teams of researchers are applying different methods to answer the same question: does antimatter fall down, or up? Relativity predicts “down”, just like matter. If it falls up, that could hint at a difference between the two that allowed a matter-dominated universe to form.

Australian researchers have designed a rapid nano-filter that can clean dirty water over 100 times faster than current technology.
Simple to make and simple to scale up, the technology harnesses naturally occurring nano-structures that grow on liquid metals.
The RMIT University and University of New South Wales (UNSW) researchers behind the innovation have shown it can filter both heavy metals and oils from water at extraordinary speed.

Astrophysicists just found a planet orbiting the star HD 26965, 16 light years away from Earth. Finding exoplanets is always fun, and the fact that this one is in the star’s habitable zone (where liquid water could exist on its surface) is a bonus. But that’s not why people are particularly psyched about the announcement.
See, HD 26965 also goes by 40 Eridani A—the star orbited by Spock’s homeworld in Star Trek. That means they found Vulcan. Ok, fine, they found a real-world analog to a completely fictional world, but you can’t blame Star Trek fans for being excited.


Only a lucky handful of artists and a Japanese billionaire will take a trip on a rocketship to the moon with SpaceX. But the moonshot won’t just be televised; you’ll get to experience it from Earth in virtual reality.
That’s the message from SpaceX CEO Elon Musk on the upcoming private moon flight of entrepreneur Yusaku Maezawa, which Musk unveiled to the world Monday (Sept. 17). Maezawa will launch on a trip around the moon on SpaceX’s new Big Falcon Rocket (BFR), and he plans to take between six and eight artists along for the ride. The flight, called the Lunar BFR Mission, could launch as early as 2023, and we’ll all be able to watch it live and in VR, Musk said.
“Moon mission will be livestreamed in high def VR,” Musk announced on Twitter Tuesday (Sept. 18), “so it’ll feel like you’re there in real-time minus a few seconds for speed of light.” That speed-of-light reference is apparently a nod to the ever-so-slight time lag for a signal to cross the 238,000 miles (383,000 kilometers) between Earth and the moon. [How SpaceX’s Passenger Moon Flight Will Work].
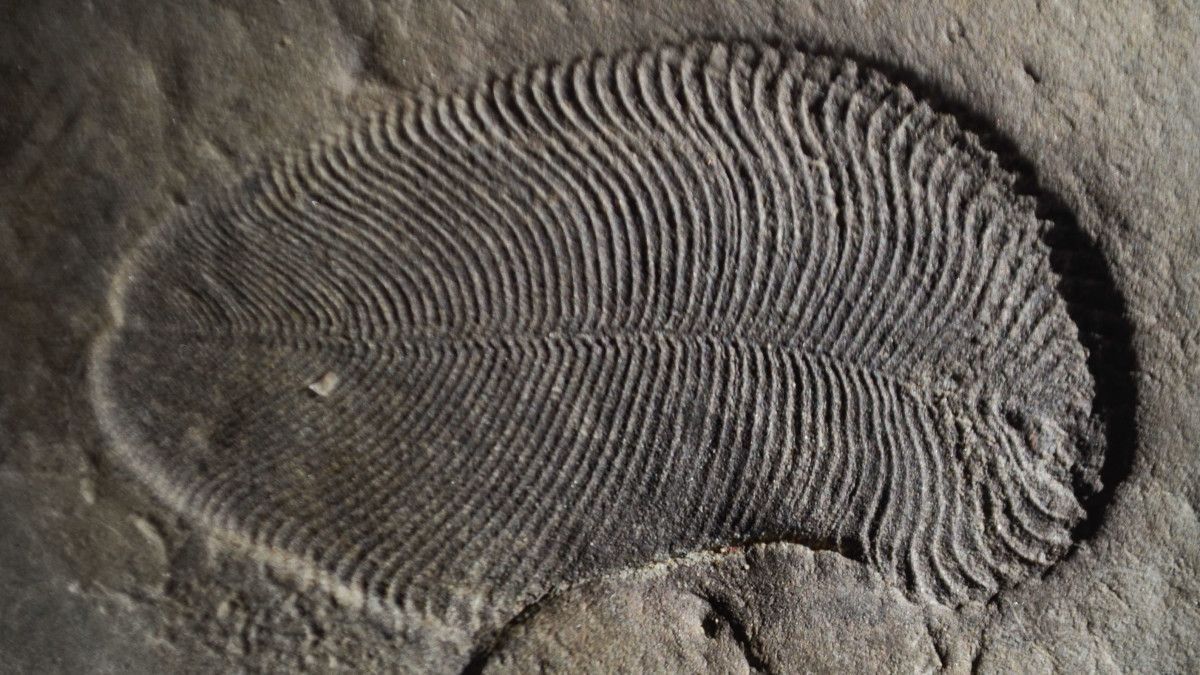

The oldest known animal in history has been discovered thanks to some well-preserved animal fat that’s been sitting in northwest Russia for the past 558 million years. The find expands the confirmed existence of animals by three million years.
The ancient animal is a Dickinsonia, which looks more like a creature from a sci-fi movie than something you’d expect to run into on Earth. Dickinsonia were oval-shaped creatures spread flat like pancakes that could grow up to four and a half feet long. Previously, the oldest macroscopic animal in the geological record was the mollusc-like Kimberella from 555 million years ago.
