I told folks just the other day; US Manufacturing in the next 3 to 5 years will primarily be robots, 3-/4-D printers, other AI systems, and a couple of line managers to spot check quality of the operation. Just surprised Amazon wasn’t already fully robotic.
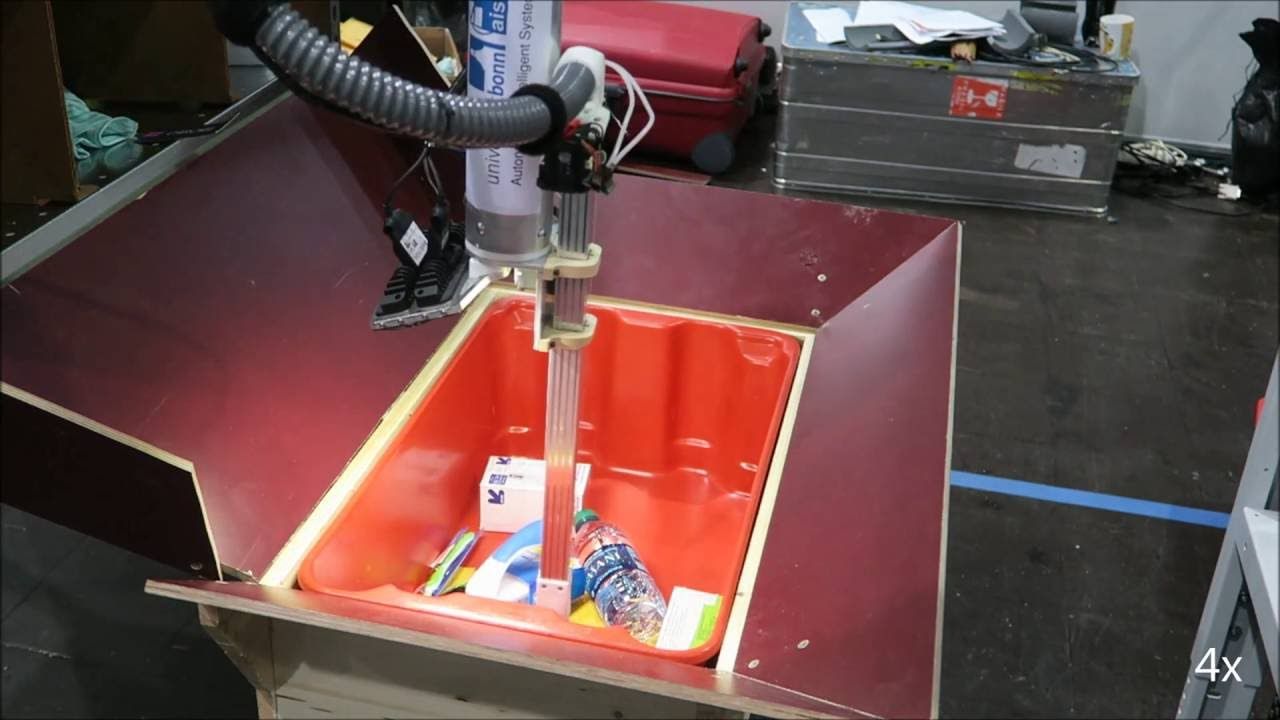
Amazon’s progress toward an army of helpful robots is one step closer: a prize for the best warehouse-working “picker” machine has gone to a robot designed by a team from TU Delft Robotics Institute and Delft Robotics, both based in the Netherlands.
The competition was held in conjunction with Germany’s Robocup in Leipzig. Announced on Monday, the winners took home $25,000, while the university of Bonn’s NimbRo won $10,000 for second place and Japanese firm PFN was awarded $5,000 for third.
The contest, in Amazon’s words, “aimed to strengthen the ties between the industrial and academic robotic communities,” and ended with slightly fewer than half of the entrants scoring more than 20 out of 40 possible points, according to a report in TechRepublic. The technology is advancing quickly: all of those contestants would have surpassed the highest scorer in the previous Picking Challenge, held just three years ago.