I have a NEW channel ► “Meet, Arnold!” — https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NsoJa2pm6Mo
If you like this video — put Thumb Up button (please) and
Okay, okay. I got to go… See You Soooooooooooooooon dudes wink
I have a NEW channel ► “Meet, Arnold!” — https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NsoJa2pm6Mo
If you like this video — put Thumb Up button (please) and
Okay, okay. I got to go… See You Soooooooooooooooon dudes wink
Join us at 7pm tonight!
Neal vanderee officiator at the church of perpetual life.
The pursuit of immortality, regeneration & longevity.
Gabriel Rothblatt will join us with his presentation: “What is Terasem? The pursuit of Joyful Immortality.”
Anand Patel will give a presentation on

After drawing both praise and skepticism, the team of astronomers who discovered NGC 1052-DF2 – the very first known galaxy to contain little to no dark matter – are back with stronger evidence about its bizarre nature.
Dark matter is a mysterious, invisible substance that typically dominates the makeup of galaxies; finding an object that’s missing dark matter is unprecedented, and came as a complete surprise.
“If there’s one object, you always have a little voice in the back of your mind saying, ‘but what if you’re wrong?’ Even though we did all the checks we could think of, we were worried that nature had thrown us for a loop and had conspired to make something look really special whereas it was really something more mundane,” said team leader Pieter van Dokkum, Sol Goldman Family Professor of Astronomy at Yale University.


Image: Business Wire
Over half of the 415 vulnerabilities found in industrial control systems (ICS) were assigned CVSS v.3.0 base scores over 7 which are designated to security issues of high or critical risk levels, with 20% of vulnerable ICS devices being impacted by critical security issues.
As detailed in Kaspersky’s “Threat landscape or industrial automation systems H2 2018”, “The largest number of vulnerabilities affect industrial control systems that control manufacturing processes at various enterprises (115), in the energy sector (110), and water supply (63).”


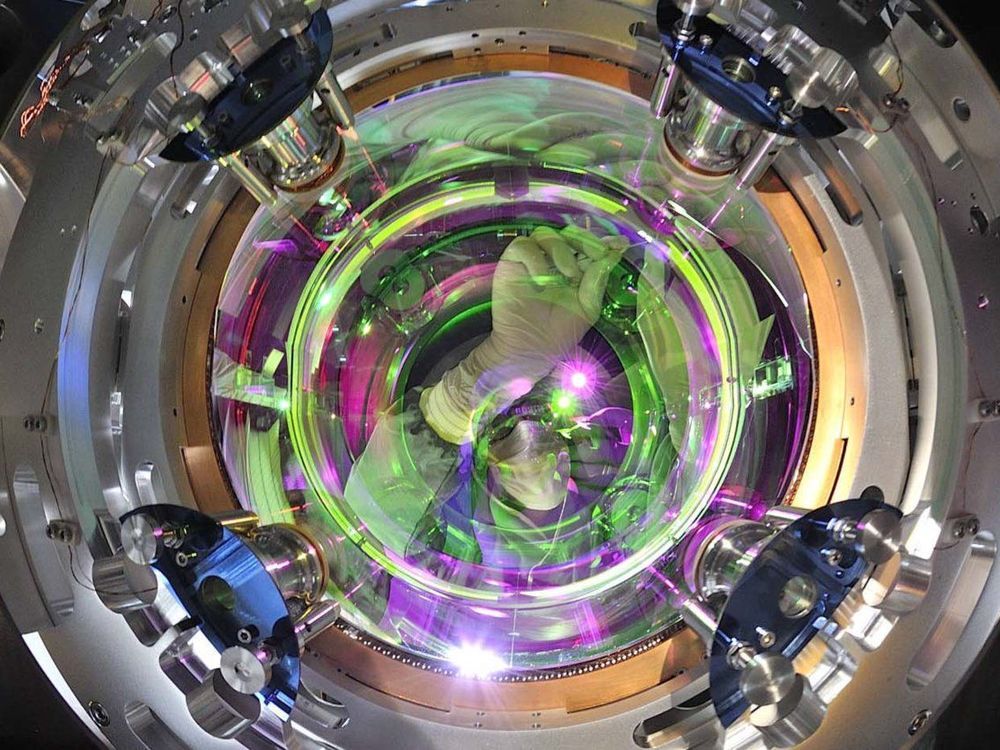
One of the most remarkable experiments in history — a pair of giant machines that listen for ripples in spacetime called gravitational waves — will wake up from a half-year nap on Monday. And it will be about 40% stronger than before.
That experiment is called the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO); it consists of two giant, L-shaped detectors that together solved a 100-year-old mystery posed by Albert Einstein.

