This AA battery will never run out of power.



It’s a difficult choice: Go hungry or go it alone.
When soldiers are weighed down on the battlefield by food supplies and the heavy battery packs that power their communication equipment, they often choose to ditch the rations. It’s a sacrifice made to keep devices powered up and communication lines open in the field.
Smaller, longer-lasting batteries would help lighten a soldier’s load, so USC researchers are working with the U.S. Department of Defense to develop better batteries that weigh half as much as current power packs.
HIV is a sneaky virus. It can hide in the immune cells of people taking daily antiretroviral therapy (ART) drugs, waiting until they stop the therapy to come back with a vengeance.
This forces them to continue ART — and continue dealing with its many side effects — for their entire lives.
But now, researchers from the University of Pittsburgh have developed an HIV immunotherapy that not only kicks the virus out of hiding, but also kills it permanently — the first step, they say, to an HIV vaccine.

At the turn of the 20th century, scientists discovered that atoms were composed of smaller particles. They found that inside each atom, negatively charged electrons orbit a nucleus made of positively charged protons and neutral particles called neutrons. This discovery led to research into atomic nuclei and subatomic particles.
An understanding of these particles’ structures provides crucial insights about the forces that hold matter together and enables researchers to apply this knowledge to other scientific problems. Although electrons have been relatively straightforward to study, protons and neutrons have proved more challenging. Protons are used in medical treatments, scattering experiments, and fusion energy, but nuclear scientists have struggled to precisely measure their underlying structure—until now.
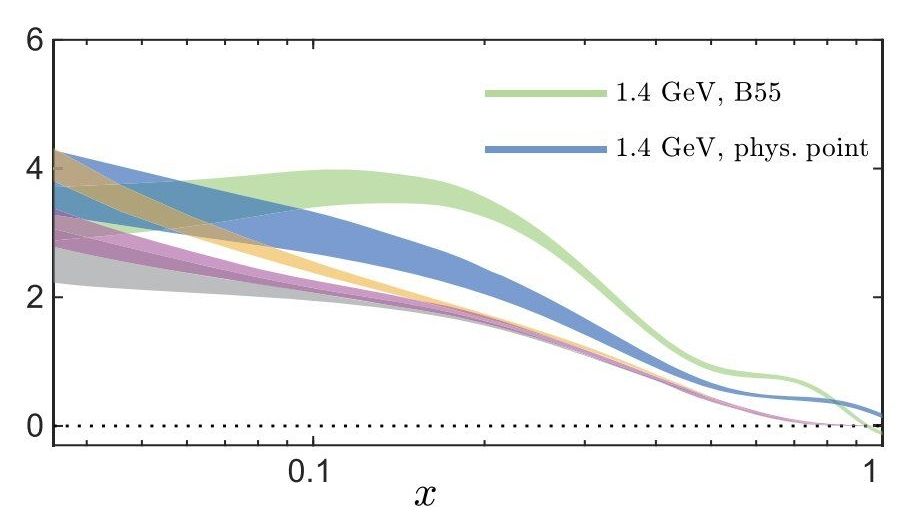
In a recent paper, a team led by Constantia Alexandrou at the University of Cyprus modeled the location of one of the subatomic particles inside a proton, using only the basic theory of the strong interactions that hold matter together rather than assuming these particles would act as they had in experiments. The researchers employed the 27-petaflop Cray XK7 Titan supercomputer at the Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility (OLCF) and a method called lattice quantum chromodynamics (QCD). The combination allowed them to map subatomic particles on a grid and calculate interactions with high accuracy and precision.
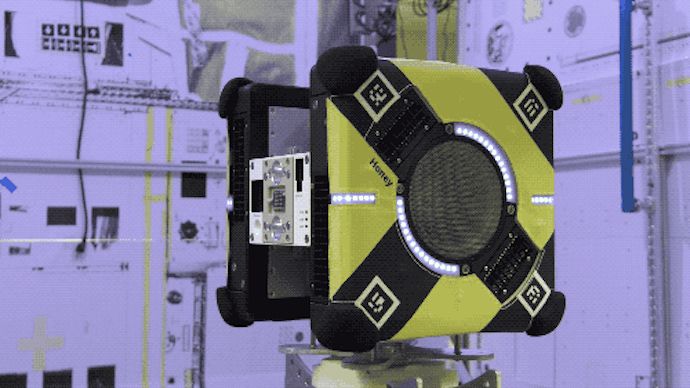
NASA’s newest International Space Station crew members are creating quite the buzz.
The agency is sending three Astrobee robots to the orbiting outpost.
The cube-shaped devices will stay “as busy as a bee” flying around the station, assisting with routine tasks like maintenance and inventory tracking.

The following is a guest post by talented author and self-described nerd Ryan LaDue.
The Latest Wave of Sensor Tech Could be a Game-Changer for LiDAR-Equipped UAVs
Avalanche photodiode sensors are semiconductors capable of converting photons into electrons with an extremely high level of precision. The technology isn’t as new as you might think, but accessible units used for laser range finders (as part of LiDAR systems) have only been making their way into consumer markets in recent years.
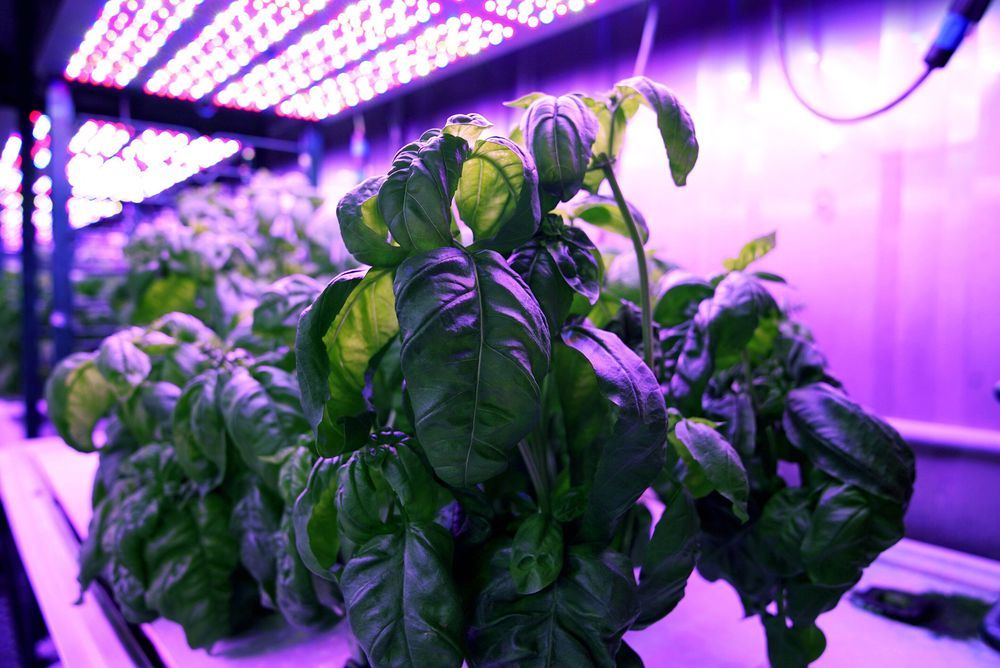

What goes into making plants taste good? For scientists in MIT’s Media Lab, it takes a combination of botany, machine-learning algorithms, and some good old-fashioned chemistry.
Using all of the above, researchers in the Media Lab’s Open Agriculture Initiative report that they have created basil plants that are likely more delicious than any you have ever tasted. No genetic modification is involved: The researchers used computer algorithms to determine the optimal growing conditions to maximize the concentration of flavorful molecules known as volatile compounds.
But that is just the beginning for the new field of “cyber agriculture,” says Caleb Harper, a principal research scientist in MIT’s Media Lab and director of the OpenAg group. His group is now working on enhancing the human disease-fighting properties of herbs, and they also hope to help growers adapt to changing climates by studying how crops grow under different conditions.


Switzerland-based energy tech startup Innolith AG announces that it is developing world’s first 1000 Wh/kg rechargeable battery.
Under development in the company’s German laboratory, the new Innolith Energy Battery would be capable of powering an electric vehicle for over 1000 km (over 620 miles) on a single charge. The Innolith Energy Battery would also radically reduce costs due to the avoidance of exotic and expensive materials combined with the very high energy density of the system.
In addition to its range and cost advantages, the Innolith Energy Battery will be the first non-flammable lithium-based battery for use in EVs. The Innolith battery uses a non-flammable inorganic electrolyte, unlike conventional EV batteries that use a flammable organic electrolyte. The switch to non-flammable batteries removes the primary cause of battery fires that have beset the manufacturers of EVs.