Scientists are gearing up to create supersecure global quantum networks.
Scientists have shown they can teleport matter across a city, a development that has been hailed as “a technological breakthrough”.
However, do not expect to see something akin to the Star Trek crew beaming from the planet’s surface to the Starship Enterprise.
Instead, in the two studies, published today in Nature Photonics, separate research groups have used quantum teleportation to send photons to new locations using fibre-optic communications networks in the cities of Hefei in China and Calgary in Canada.
“History “teaches us that order in international relations is the exception, rather than the rule,” Kevin Rudd, the former Australian prime minister, writes in a new report on the uncertain future of the UN.”
““A woman of firsts” is perhaps only a summary description of Dame Margaret Anstee, the first woman to serve as a United Nations Under-Secretary-General.”
“Hopes of a fast and effective response to the global refugee crisis now rest on a summit convened by Barack Obama on Tuesday in New York, after negotiations before a meeting of world leaders at the UN on Monday failed to produce any concrete measures.”
Scientists at Vanderbilt University have developed a first-ever implantable artificial kidney. The artificial kidney contains a microchip filter and living kidney cells that can function using the patient’s heart, and this bio-synthetic kidney acts like the real organ, removing salt, water and waste products to keep patients with kidney failure from relying on dialysis.
The key to this new development is a breakthrough in the microchip itself, which uses silicon nanotechnology. “[Silicon nanotechnology] uses the same processes that were developed by the microelectronics industry for computers,” said Dr. William H. Fissell IV, who led the team that developed the device.
The microchips are affordable, precise, and function as an ideal filter.
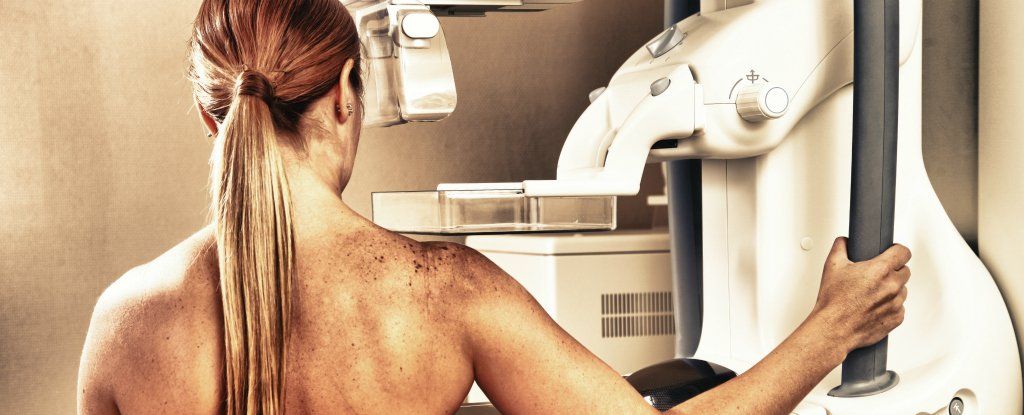
Researchers have developed machine learning software that can accurately diagnose a patient’s breast cancer risk 30 times faster than doctors, based on mammogram results and personal medical history.
The system could help doctors give better diagnoses the first time around — which means fewer mammogram callbacks and false positives.
“This software intelligently reviews millions of records in a short amount of time, enabling us to determine breast cancer risk more efficiently using a patient’s mammogram,” said one of the researchers, Stephen Wong, from Houston Methodist Research Institute. “This has the potential to decrease unnecessary biopsies.”
That brought a lot of media attention, and Giorgio got skittish. “They didn’t want to have the perception from customers that their company was developing genetically modified organisms,” says Yang. Yang is still working to perfect the anti-browning in his academic lab, but he has no immediate plans to commercialize it.
The anti-browning trait might also just be a tough sell to customers: When a Canadian apple wanted to sell a GM apple that doesn’t brown—genetically altered through conventional means—it had to battle assumptions that growers just wanted to hide bruised produce. Which is, well, true. Produce that doesn’t brown when handled does also mean less waste for stores and growers.
In Sweden, Jansson is no stranger to unease over genetic engineering. His colleagues recently returned from a conference where activists flung cow dung and eggs at scientists. The CRISPR-edited cabbage he grew he actually got from researchers outside Sweden, who did not want their names or even their country revealed, fearing backlash from environmental activists. Jansson did his cabbage stunt because he wanted people to start thinking about what CRISPR could mean for food.
Franky Zapata beat the #jetski easily! @frankyzapata #Flyboard #prowatercross Come out tomorrow for the Finals at the Flyboard World Cup Championship to see another Live demonstration in #NaplesFl!