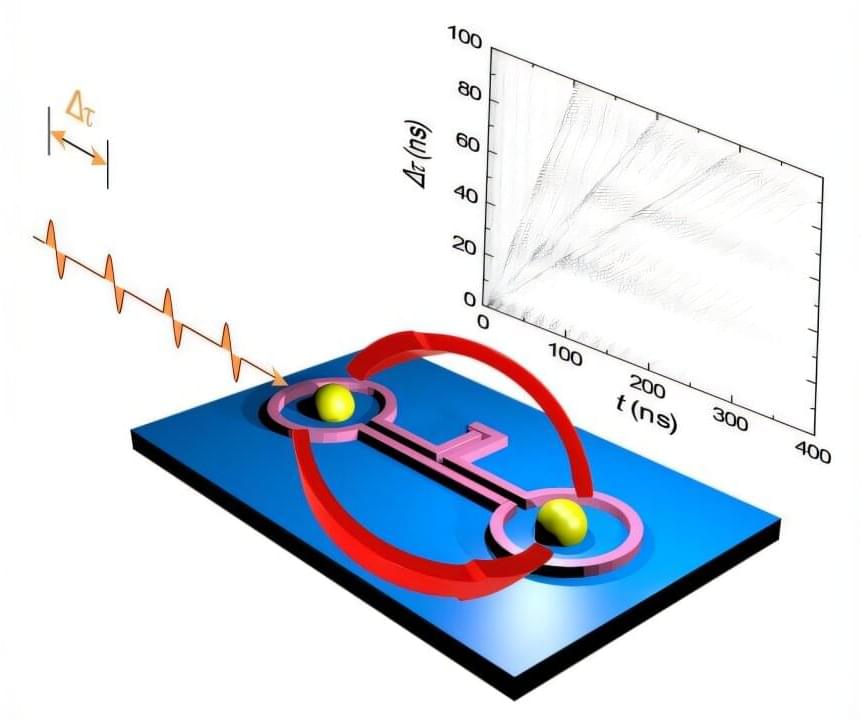
As quantum computing develops, scientists are working to identify tasks for which quantum computers have a clear advantage over classical computers. So far, researchers have only pinpointed a handful of these problems, but in a new paper published in Physical Review Letters, scientists at Los Alamos National Laboratory have added one more problem to this very short list.
“One of the central questions that faces quantum computing is what classes of problems they can most efficiently solve but classical computers cannot,” says Marco Cerezo, the Los Alamos team’s lead scientist. “At the moment, this is the Holy Grail of quantum computing, because you can count on two hands such problems. In this paper, we’ve just added another.”
Quantum computing harnesses the unique laws of quantum physics, such as superposition, entanglement and interference, which allow for information processing capabilities beyond those of classical devices. When fully realized, quantum computing promises to make advancements in cryptography, simulations of quantum systems and data analysis, among many other fields. But before this can happen, researchers still need to develop the foundational science of quantum computing.