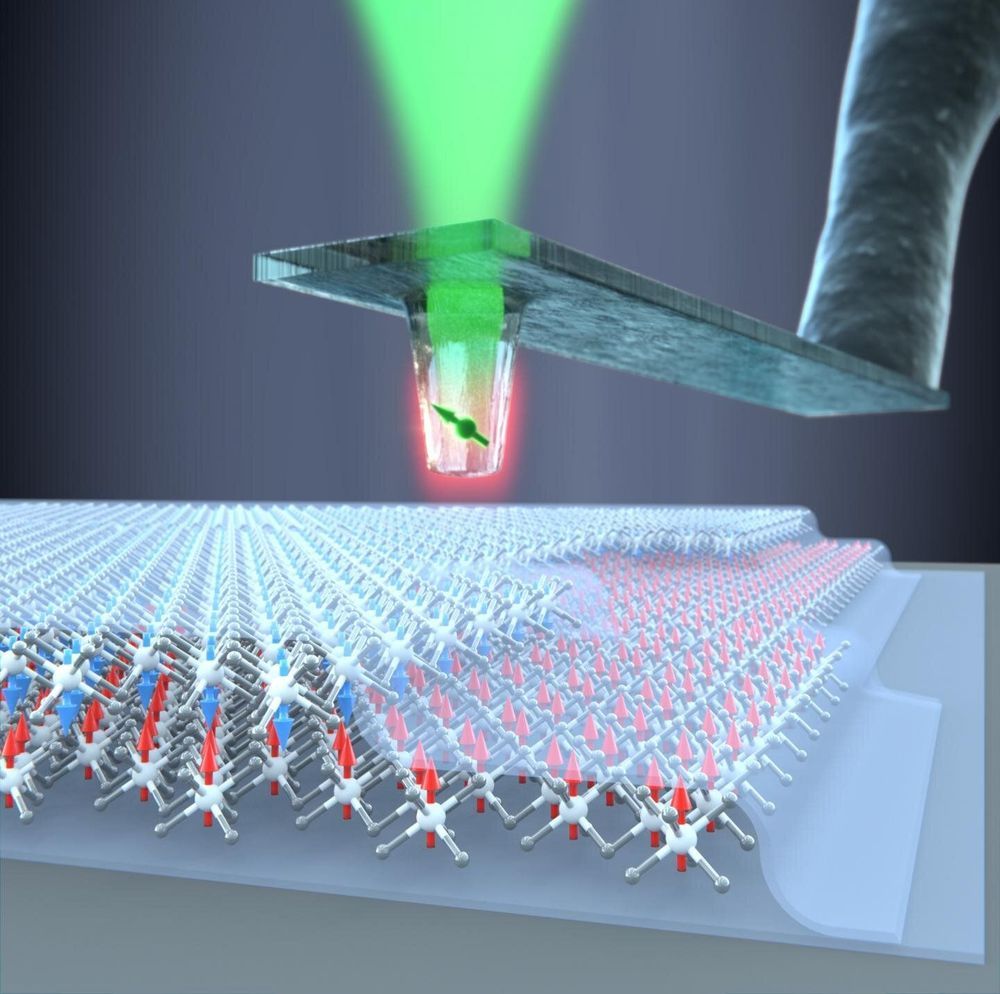
For the first time, physicists at the University of Basel have succeeded in measuring the magnetic properties of atomically thin van der Waals materials on the nanoscale. They used diamond quantum sensors to determine the strength of the magnetization of individual atomic layers of the material chromium triiodide. In addition, they found a long-sought explanation for the unusual magnetic properties of the material. The journal Science has published the findings.
The use of atomically thin, two-dimensional van der Waals materials promises innovations in numerous fields in science and technology. Scientists around the world are constantly exploring new ways to stack different single atomic layers and thus engineer new materials with unique, emerging properties.
These super-thin composite materials are held together by van der Waals forces and often behave differently to bulk crystals of the same material. Atomically thin van der Waals materials include insulators, semiconductors, superconductors and a few materials with magnetic properties. Their use in spintronics or ultra-compact magnetic memory media is highly promising.
Read more