Seven teeth, five hand and foot bones, and a partial femur point to a previously unknown population of early humans. Time will tell if it was truly a distinct lineage.


Scientists have taken a major step towards creating an aircraft of the future, one powered by an ion drive rather than using moving parts and fuel like conventional aircraft.
In a paper published today in Nature, a team led by Steven Barrett from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) described how they created a so-called electroaerodynamic-powered plane, one that uses solid-state propulsion, meaning no propellers or jet engines with expendable fuel.
“The future of flight shouldn’t be things with propellers and turbines,” Barrett says in the video below. “[It] should be more like what you see in Star Trek, with a kind of blue glow and something that silently glides through the air.”
;-;
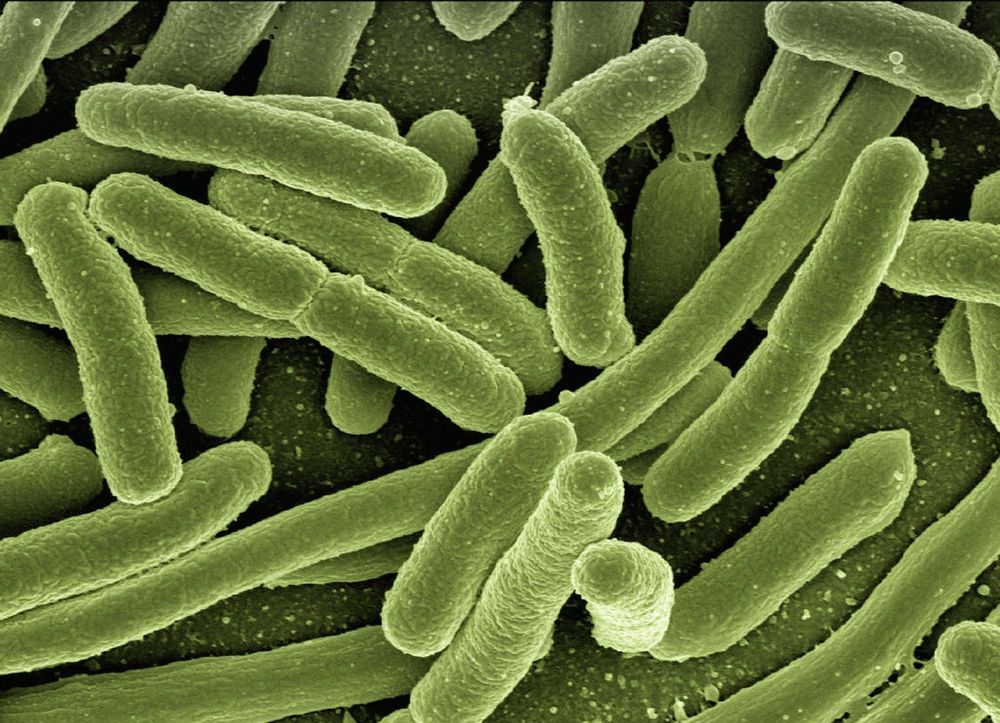
Salmonella bacteria flip an electric switch as they hitch a ride inside immune cells, causing the cells to migrate out of the gut toward other parts of the body, according to a new study publishing on April 9 in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Yaohui Sun and Alex Mogilner of New York University and colleagues. The discovery reveals a new mechanism underlying the toxicity of this common food-borne pathogen.
Salmonella are among the commonest, and deadliest, causes of food poisoning, causing over 400,000 deaths every year. Many of those deaths result when the bacteria escape the gut inside immune cells called macrophages. Macrophages are drawn to bacteria in the gut by a variety of signals, most prominently chemicals released from the site of infection. Once there, they engulf the bacteria as a regular part of their infection-fighting job. However, rather than remaining there, bacteria-laden macrophages often leave the site and enter the bloodstream, disseminating the bacteria and greatly increasing the gravity of the infection.
Tissues such as the gut often generate small electrical fields across their outer surfaces, and these electrical fields have been known to drive migration of cells, including macrophages. In the new study, the authors first showed that the lining of the mouse cecum (the equivalent of the human appendix) maintains a cross-membrane electrical field, and that Salmonella infection altered this field and contributed to the attraction of macrophages. Measurements of the polarity of the local charge indicated that the macrophages were attracted to the anode, or positively charged pole within the field. Once they engulfed bacteria, however, they became attracted to the cathode and reversed their migratory direction, moving away from the gut lining, toward vessels of the circulatory system. This switch was driven by a in the composition of certain charged surface proteins on the macrophages; the mechanism by which bacterial engulfment triggers this change is still under investigation.
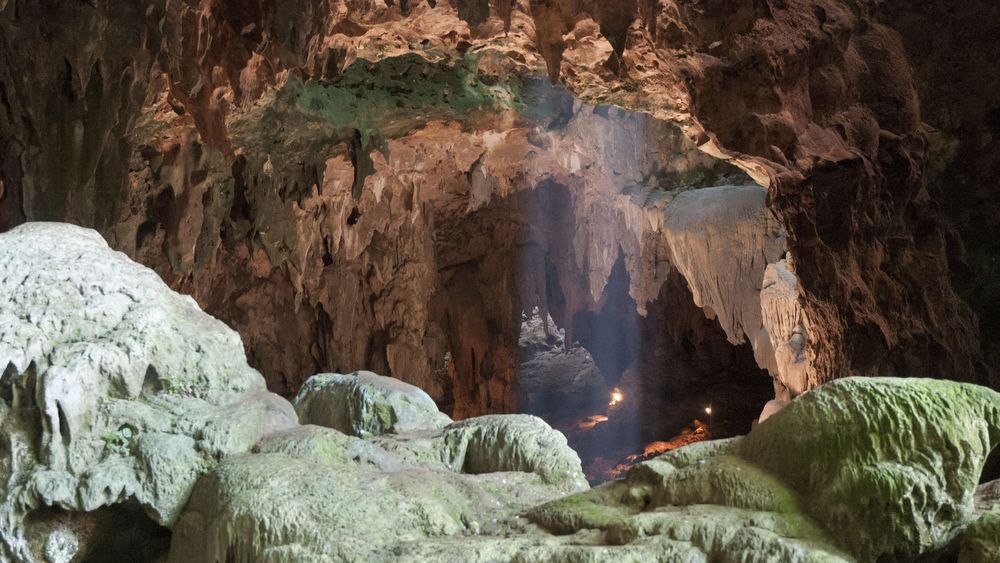
Archaeologists just pried another secret of our past from the clutches of the earth, welcoming a new human species to our growing family tree.
This discovery began with an ancient foot, or what was left of one. A foot bone, called the third metatarsal, was found in the Callao Cave on the Philippine island of Luzon back in 2007.
The oldest known Homo sapiens remains, found nearby on Palawan Island, were dated to 30,000 to 40,000 years ago. But this mysterious foot is older, dated to 67,000 years ago.


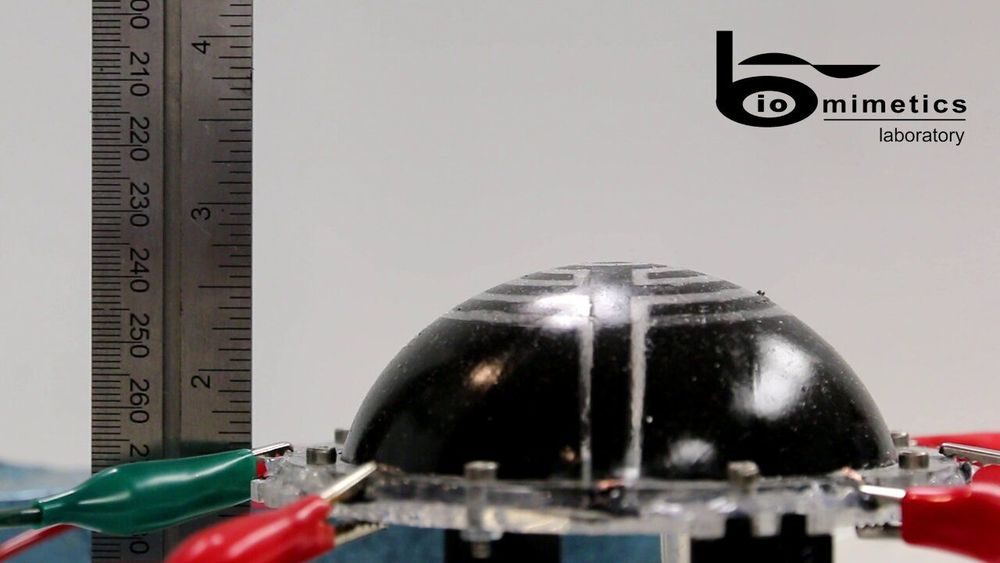
Researchers at the Auckland Bioengineering Institute and Technische Universit\xE4t Dresden have recently designed a new type of inflatable robot for space navigation. These robots, presented in a paper published in SPIE Digital Library, were created using dielectric elastomer transducers (DETs), which are essentially electrical capacitors made from soft rubbery materials.
“Current space technology is limited by its mass and volume. It takes thousands of dollars to launch even a single kilogram into orbit,” Joseph Ashby, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told TechXplore. “Our research aims to replace or augment current technology with lighter smart-material replacements combined with inflatable structures.”
If they are integrated with inflatable structures, DETs could aid the development of soft and low-mass robots, which have high packaging efficiency and are easy to deploy. In fact, DETs deform when a voltage is applied to them, due to the Maxwell stress generated by the electric field.
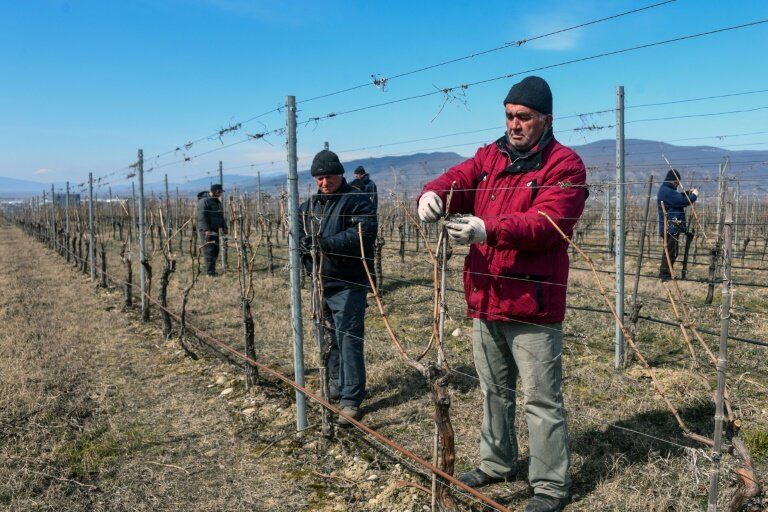


Georgia is immensely proud of its ancient wine-making tradition, claiming to have been the first nation to make wine. Now it wants to be the first to grow grapes on Mars.
Nestling between the Great Caucasus Mountains and the Black Sea, Georgia has a mild climate that is perfect for vineyards and has developed a thriving wine tourism industry.
Now Nikoloz Doborjginidze has co-founded a project to develop grape varieties that can be grown on Mars.