Can artificial intelligence provide careers for people with autism?
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

SpotMini Autonomous Navigation
SpotMini autonomously navigates a specified route through an office and lab facility. Before the test, the robot is manually driven through the space so it can build a map of the space using visual data from cameras mounted on the front, back and sides of the robot. During the autonomous run, SpotMini uses data from the cameras to localize itself in the map and to detect and avoid obstacles. Once the operator presses ‘GO’ at the beginning of the video, the robot is on its own. Total walk time for this route is just over 6 minutes. (The QR codes visible in the video are used to measure performance, not for navigation.)
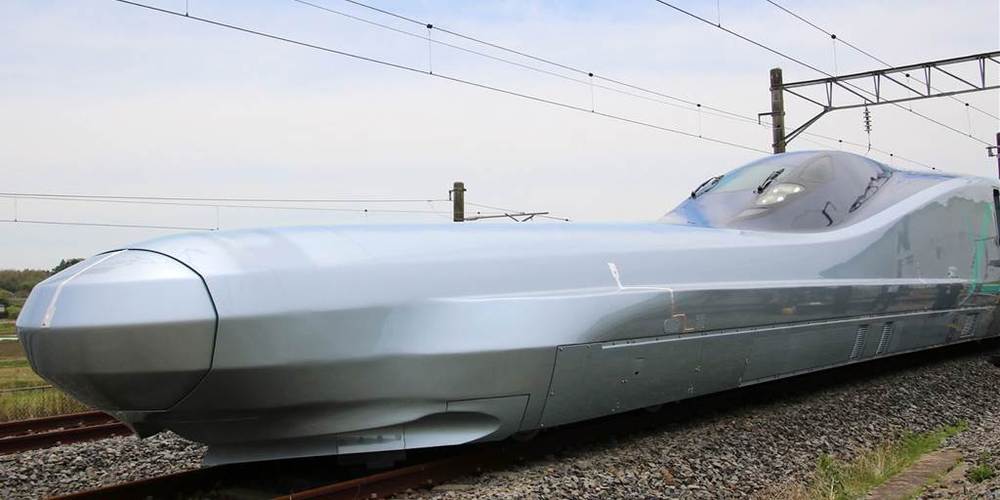


Superfast bullet train that rivals airplane flying times set to debut in Japan
The picture of a “bullet train” speeding past Mount Fuji is an iconic image of modern Japan.
In recent years, however, Japan has lost the “world’s fastest train” title to China — if only by a few miles per hour. But now, Japan plans to reclaim that crown, with a new bullet train that will whisk between cities with journey times that rival passenger jets.
The Alfa-X train, unveiled by rail company JR East, will carry passengers at up to 224 miles per hour, outpacing the fastest Japanese bullet trains in commercial service today by almost 25 miles per hour.

Mathematicians revive abandoned approach to the Riemann Hypothesis
Many ways to approach the Riemann Hypothesis have been proposed during the past 150 years, but none of them have led to conquering the most famous open problem in mathematics. A new paper in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) suggests that one of these old approaches is more practical than previously realized.
“In a surprisingly short proof, we’ve shown that an old, abandoned approach to the Riemann Hypothesis should not have been forgotten,” says Ken Ono, a number theorist at Emory University and co-author of the paper. “By simply formulating a proper framework for an old approach we’ve proven some new theorems, including a large chunk of a criterion which implies the Riemann Hypothesis. And our general framework also opens approaches to other basic unanswered questions.”
The paper builds on the work of Johan Jensen and George Pólya, two of the most important mathematicians of the 20th century. It reveals a method to calculate the Jensen-Pólya polynomials—a formulation of the Riemann Hypothesis—not one at a time, but all at once.
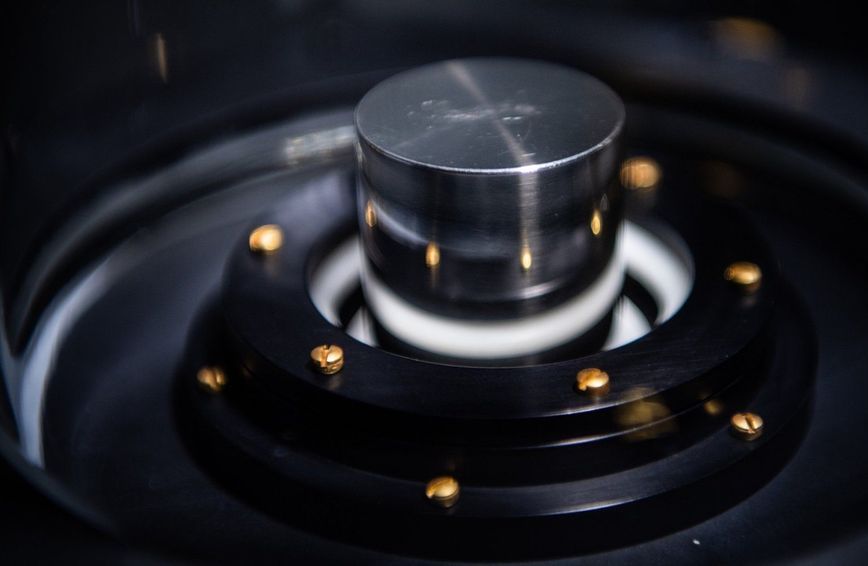

There’s a Brand-New Kilogram, And It’s Based on Quantum Physics
The kilogram isn’t a thing anymore. Instead, it’s an abstract idea about light and energy.
As of today (May 20), physicists have replaced the old kilogram — a 130-year-old, platinum-iridium cylinder weighing 2.2 pounds (1 kilogram) sitting in a room in France — with an abstract, unchanging measurement based on quadrillions of light particles and Planck’s constant (a fundamental feature of our universe).
In one sense, this is a grand (and surprisingly difficult) achievement. The kilogram is fixed forever now. It can’t change over time as the cylinder loses an atom here or an atom there. That means humans could communicate this unit of mass, in terms of raw science, to space aliens. The kilogram is now a simple truth, an idea that can be carried anywhere in the universe without bothering to bring a cylinder with you.
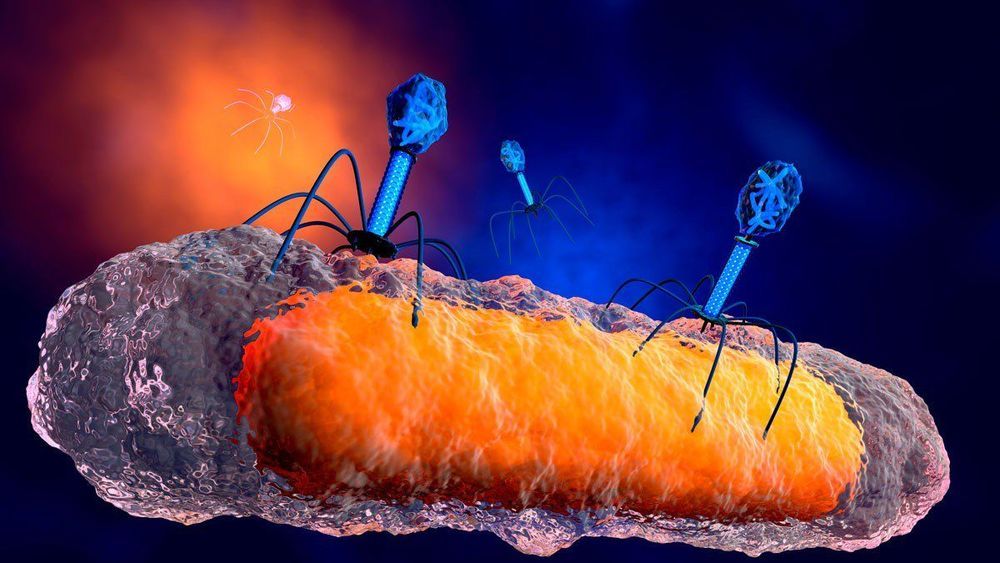
Genetically engineered phage therapy has rescued a teenager on the brink of death
It’s a remarkable story of recovery, but it’s unclear how useful this sort of therapy could become.
The background: Isabelle Holdaway had been given less than a 1% chance of survival after a lung transplant, carried out to combat the symptoms of cystic fibrosis, left her with an antibiotic-resistant infection. She had been sent home and was in a terrible physical condition: underweight, with liver failure, and with lesions on her skin from the infection.
A breakthrough: Her consultant at Great Ormond Street Hospital in London worked with a team at the University of Pittsburgh to develop an untested phage therapy. This treatment used a cocktail of three phages, which are viruses that solely attack and kill bacteria. Two of the three phages, selected from a library of more more than 10,000 kept at the University of Pittsburgh, had been genetically engineered to be better at attacking the bacteria. The therapy was injected into her bloodstream twice daily and applied to the lesions on her skin, according to Nature Medicine.
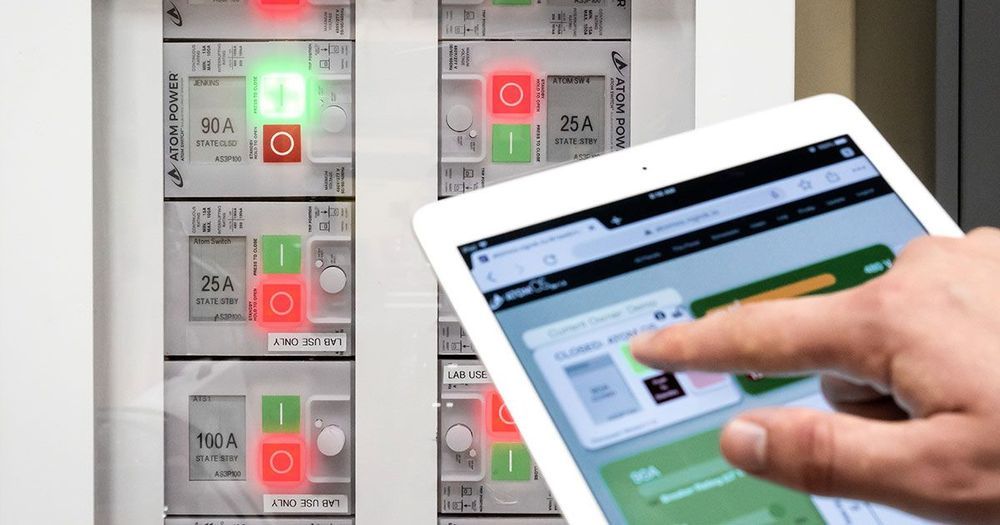

Atom Power Is Launching the Era of Digital Circuit Breakers
In the dark, dank depths of your home basement hangs a drab gray box that guards the building’s electrical circuits. The circuit breakers inside switch off current flow when there is risk of an overload or short circuit, keeping you safe from fires or electrocution. It’s a critical job, and one that breakers have been doing with a fairly simple, 140-year-old electromechanical technology.
But circuit breakers are about to get a digital overhaul. New semiconductor breakers that combine computing power and wireless connectivity could become the hub of smart, energy-efficient buildings of the future.
“It’s like going from a telephone that just makes calls to a smartphone with capabilities we’d never imagined before,” says Ryan Kennedy, CEO and co-founder of Atom Power in Charlotte, North Carolina. “This is a platform that changes everything in power systems.”