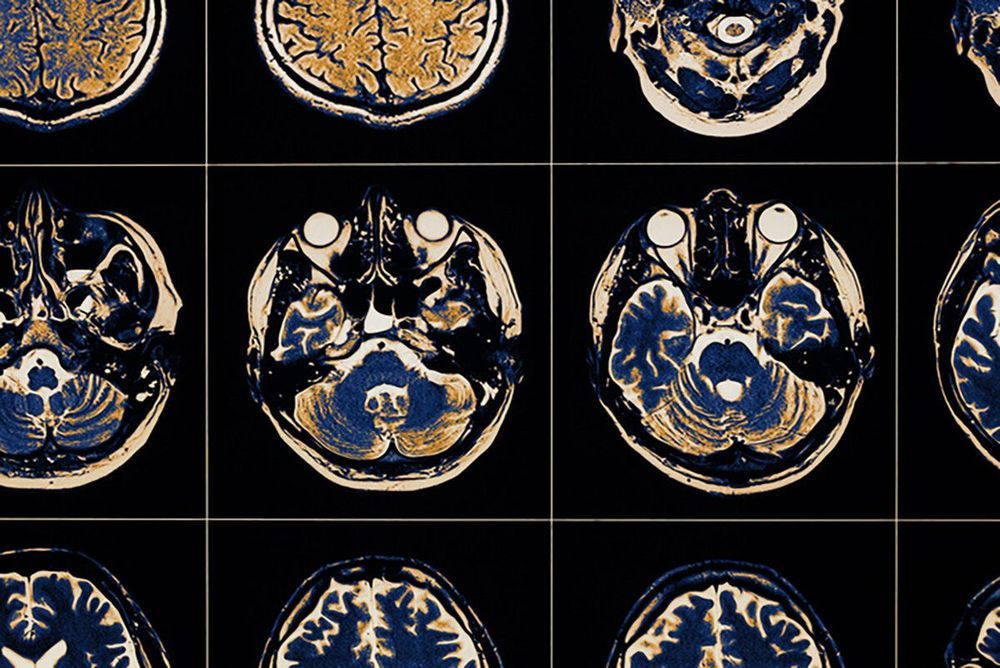
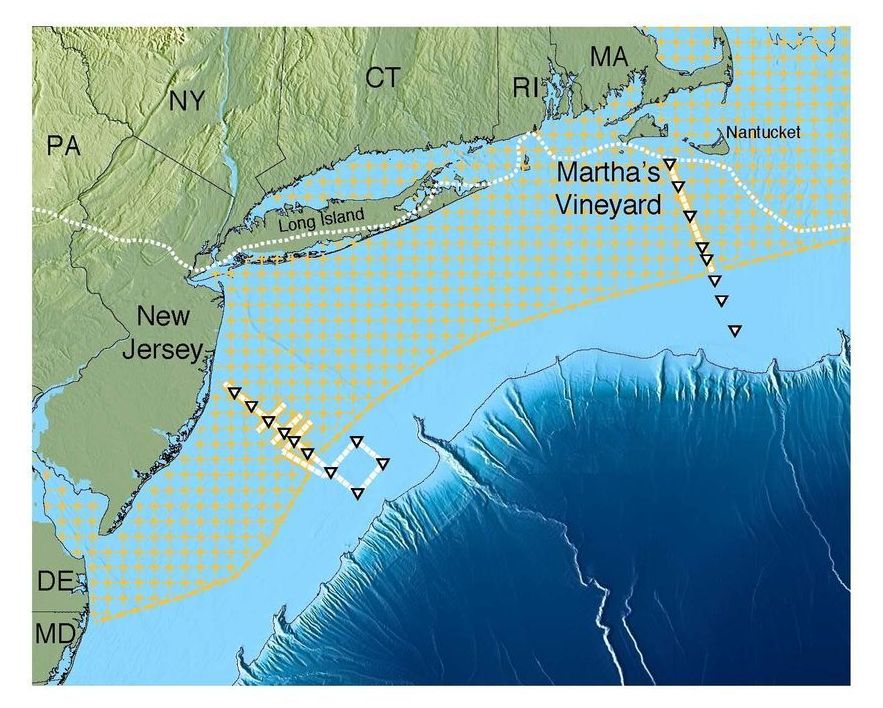
In a new survey of the sub-seafloor off the U.S. Northeast coast, scientists have made a surprising discovery: a gigantic aquifer of relatively fresh water trapped in porous sediments lying below the salty ocean. It appears to be the largest such formation yet found in the world. The aquifer stretches from the shore at least from Massachusetts to New Jersey, extending more or less continuously out about 50 miles to the edge of the continental shelf. If found on the surface, it would create a lake covering some 15,000 square miles. The study suggests that such aquifers probably lie off many other coasts worldwide, and could provide desperately needed water for arid areas that are now in danger of running out.
The researchers employed innovative measurements of electromagnetic waves to map the water, which remained invisible to other technologies. “We knew there was fresh water down there in isolated places, but we did not know the extent or geometry,” said lead author Chloe Gustafson, a Ph.D. candidate at Columbia University’s Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory. “It could turn out to be an important resource in other parts of the world.” The study appears this week in the journal Scientific Reports.
The first hints of the aquifer came in the 1970s, when companies drilled off the coastline for oil, but sometimes instead hit fresh water. Drill holes are just pinpricks in the seafloor, and scientists debated whether the water deposits were just isolated pockets or something bigger. Starting about 20 years ago, study coauthor Kerry Key, now a Lamont-Doherty geophysicist, helped oil companies develop techniques to use electromagnetic imaging of the sub-seafloor to look for oil. More recently, Key decided to see if some form of the technology could also be used also to find fresh-water deposits. In 2015, he and Rob L. Evans of Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution spent 10 days on the Lamont-Doherty research vessel Marcus G. Langseth making measurements off southern New Jersey and the Massachusetts island of Martha’s Vineyard, where scattered drill holes had hit fresh-water-rich sediments.