Neoliberalism slows down evolution! Just kidding…or am I? 🧐😁🤣🙈.
Like other organisms, bacteria constantly have to fight to survive in hostile living conditions. Together with colleagues in Finland, researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Biology in Plön have discovered that bacteria adapt to their environment more slowly and less efficiently as soon as they are exposed to two stress factors rather than one. This is due to mutations in different genes. The slower rate of evolution led to smaller population sizes. This means that evolution can take divergent paths if an organism is exposed to several stress factors.
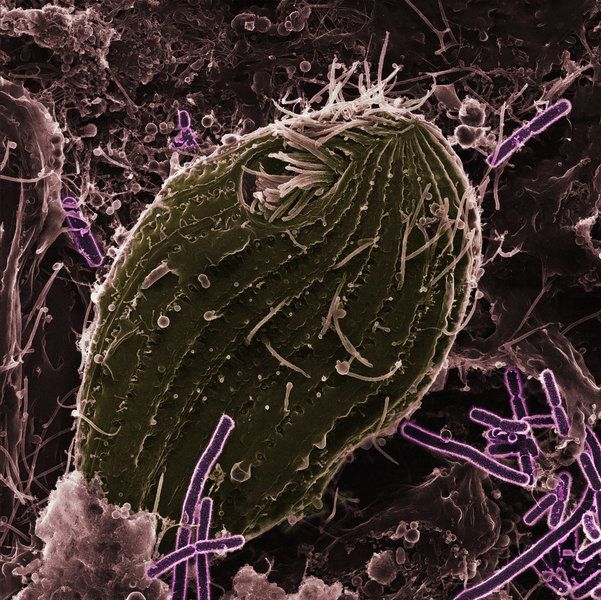
Bacteria rarely live alone; they are usually part of a community of species that is exposed to various stress factors. They can often react to these factors by adapting to new environmental conditions with astonishing speed. Antibiotics that enter soil and water via waste water and accumulate there in low concentrations can trigger the evolution of resistance in bacteria – even though these concentrations are so low that they inhibit bacterial growth only slightly or not at all. However, bacteria do not only have to fight antibiotics; they also have to deal with predators. This is why they often grow in large colonies that cannot be consumed by predatory organisms.
Typically, scientists investigate the effects that a single stress factor has on an organism. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Biology in Plön and the Universities of Helsinki and Jyväskylä, Finland, have now investigated the question of how microorganisms behave when they are confronted with more than one stress factor. “We simulated natural environmental conditions in the lab and exposed bacteria to both predators and antibiotics. This allows us to estimate how likely it is to find evolution of resistance to antibiotics outdoors,” explains study leader Lutz Becks.






![Shou-Cheng Zhang, Shanghai-born Chinese-American physicist at Stanford University, attends the 2016-2017 You Bring Charm to the World Award Ceremony held at Tsinghua University in Beijing, China, 31 March 2017.[Photo: IC]](https://lifeboat.com/blog.images/chinese-american-physicist-shou-cheng-zhang-dies-at-554.jpg)


