This could be bad news for some companies.
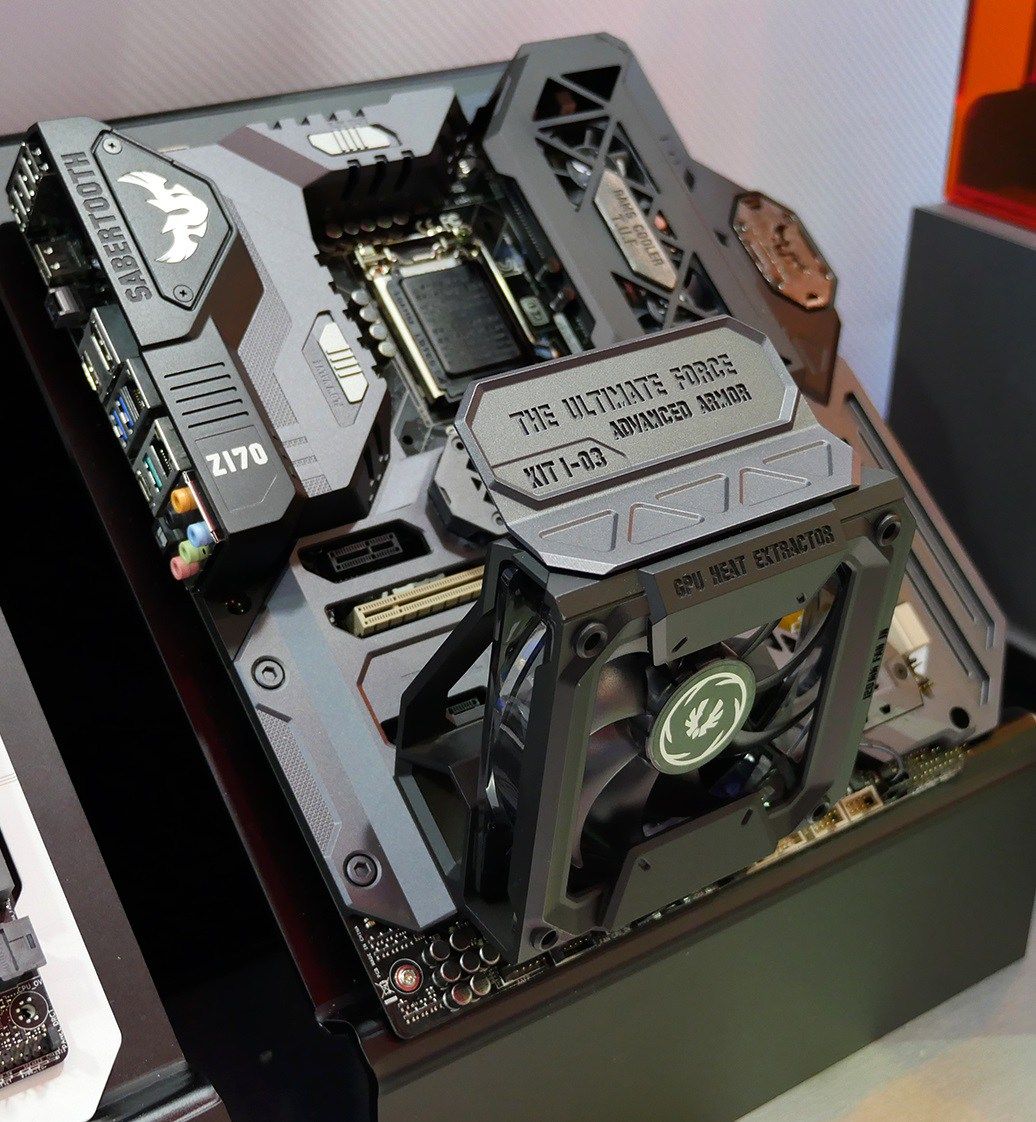
Many people love the flexibility of building their PC. They know that they can say what they want, how they want it. Each individual component in the PC can be customized to how the user wants it. Some people build them to achieve the top specifications while others will build them as cheaply as possible as are on a budget. Whatever the reason for building a PC, a little help has now been offered by ASUS, which will allow you to use 3D printing to print simply the components you need.
What ASUS plans to do is provide CAD files to customers to use their 3D printer to print their very own motherboard components. But, the printing is more for aesthetic reasons rather than anything else. The idea behind it is that consumers will be able to create a personalized look for their motherboard, or print other components in a particular color. Some suggestions also include being able to print company logo’s on parts also.