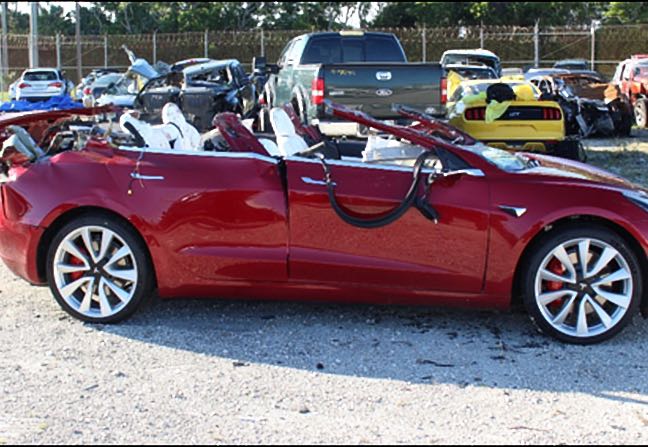
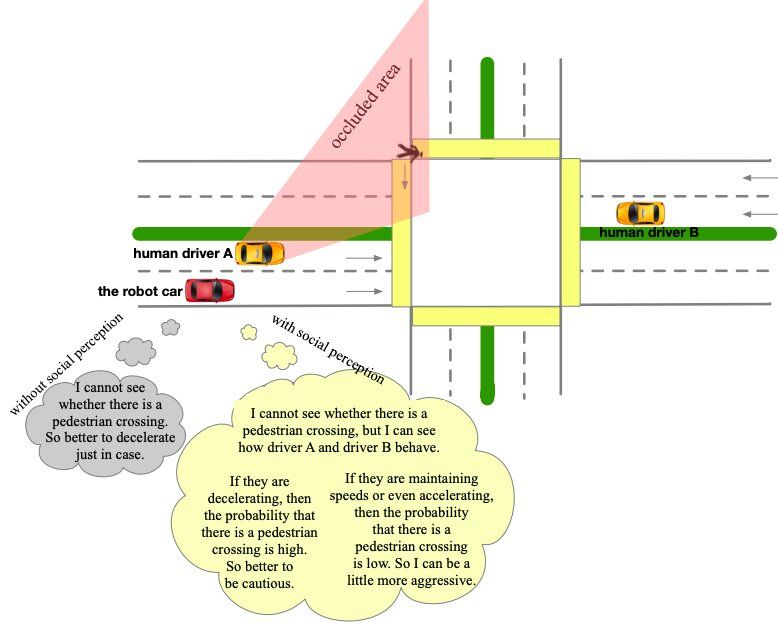
A.I. is yet to prove the safety of self-driving cars.
“Shortly following the accident, we informed the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration and the National Transportation Safety Board that the vehicle’s logs showed that Autopilot was first engaged by the driver just 10 seconds prior to the accident, and then the driver immediately removed his hands from the wheel,” a Tesla spokesperson told The Register in an emailed statement. “Autopilot had not been used at any other time during that drive. We are deeply saddened by this accident and our thoughts are with everyone affected by this tragedy.”