Results showed the hippocampus experienced a boost both immediately after exercise and after continued habitual exercise following a 12-week regiment.
Getty Images


The ability to use organs from living HIV-positive individuals could increase the supply available for transplant.

This week I’m going to blow your mind, change your world and future with science, with current science, Quantum Mechanics. Seriously, this article/podcast can completely change your life and future. As well as, your view of the world.
Find out how to Change Your Life and Find Your Life’s Purpose using Quantum Mechanics. Sounds weird and unbelievable but it works…Check it out!
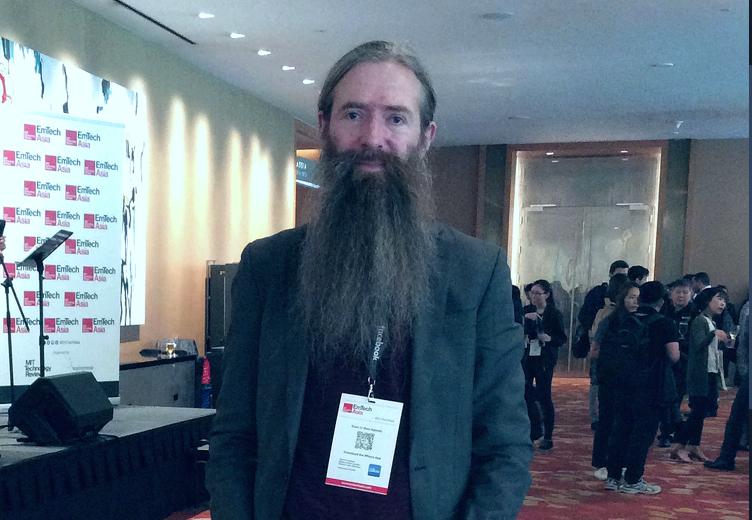


“If I can bring forward the defeat of aging even one day, I would have saved the lives of 110,000 people.” – Dr. Aubrey de Grey at EmTech Asia 2019.
The age-old quest for immortality was largely confined to the myths and legends of past civilizations until about just two decades back when telomerase, the active component for the gene that confers immortality to cells was successfully isolated in a science laboratory. That turned the tide on the entire conversation from whether aging could be treated, to how it could be treated.
Since then it has spawned a whole new medical field – ‘healthspan’ – where scientific research is conducted with the aim of extending healthy human lives for as long as hundreds and thousands of years, if not outright immortality. It is not surprising that the intensive research into anti-aging technologies has attracted financial backing from those who are interested in technological progress – the tech community, the likes of Google and even cryptocurrency tycoons such as Ethereum Founder, Vitalik Buterin, who donated $2.4 million worth of ether to the nonprofit foundation SENS Research Foundation, of which Dr Aubrey de Grey is the Chief Science Officer.
My mission is to drastically improve your life by sharing how you can quickly break bad habits and build and keep new healthy habits. I read the books and do all the research and share my findings with you in my YouTube videos! Not a bad deal, eh?
This video is a book review of Telomere Lengthening: Curing all diseases including cancer & aging by Dr. Bill Andrews and Jon Cornell.
- Dr. Bill Andrew’s Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/telomere.bill.andrews
- Dr. Bill Andrew’s LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/william-h-andrews-5455b45/
- Sierra Sciences website: http://www.cure-aging-or-die-trying.com/
- Defy Time’s website where you can buy TAM-818 products: https://defytime.com/
- Watch the documentary “The Immortalists” about Dr. Bill Andrews & Aubrey de Grey: http://theimmortalists.com/watch/?fbclid=IwAR1qDvp7b1fsmN2FJ…8FYKWYT4IY
- Telomere Lengthening: Curing all diseases including cancer & aging by Dr. Bill Andrews and Jon Cornell — book on Amazon: https://www.amazon.com/Telomere-Lengthening-Curing-Disease-I…atfound-20
keywords=telomere+lengthening&qid=1553009067&s=gateway&sr=8–2
- Curing Aging: Bill Andrews on Telomere Basics book on Amazon: https://www.amazon.com/Bill-Andrews-Telomere-Basics-Curing/d…6SQ55SA5JP
- YouTube video- Bill Andrews speech at RAADfest 2018 (Sept 21, San Diego, CA): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Mqb1D8Bwkc4
- YouTube video- Human Longevity Project Dr Bill Andrews: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-B_nyf-gOu0
- YouTube video- Dr. Bill Andrews, “Telomere Lengthening Resetting the Clock of Aging”: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ccs7lXTmlyE
- Life Length’s website: https://lifelength.com/
Dr. Bill Andrews commented on this book review shorting after it was uploaded to YouTube. Here’s Dr. Andrews’ comment: Great Review Brent!!! And, yes, I would love to do an interview with you. And, yes, I am coming out with a new book soon.
The most potent telomerase inducer, TAM818 (www.defytime.com) produces 16% of the amount of telomerase to stop telomere shortening.
Gene Editing is different than Gene Therapy (also called Gene Delivery). In our Gene Therapy (www.libellagt.com) we are delivering (not editing) the telomerase gene to human cells. Liz Parrish did Gene Therapy, not Gene Editing, though she does have big plans of doing Gene Editing also in the future.
My books are also available in other languages at www.defytime.com.
The reason that I wrote both books is to answer all the questions that people ask me when I speak on stage. It’s not meant to be a matter of opinion that needs scientific support. That is because most of what I say is not controversial at all. It is all widely accepted by the scientific community. Adding references would have just made the book more technical than I wanted. Nevertheless, the one chapter on “Telomerase Does Not Cause Cancer” is controversial and so, not only did I provide references, I provided a link so readers could read the full text scientific peer reviewed studies. Other than that chapter both books should be considered just aids to help others explain the field.
The fact that I didn’t include a biography of myself is because the book isn’t about me. I am not trying to promote myself. I am just trying to make the world aware of the field so that more people would take an interest in supporting it; whether it is my lab or others. For those that want to know more about me my bio can be found at https://www.sierrasci.com/bill-andrews-bio.
I sure hope Warren Buffet, Warren Buffet’s friend, or Dr. Peter Attia hear this book review!!!
- Forever Labs 1 year free cryogenic storage discount code ($250 value): BN801
- Forever Labs website: https://foreverlabs.com
- Viome’s website: https://www.viome.com/
A second male birth control pill succeeded in preliminary testing, suggesting that a new form of contraception may eventually exist.
The new pill, which works similarly to female contraception, passed initial safety tests and produced hormone responses consistent with effective birth control in 30 men, according to research presented by the Los Angeles Biomedical Research Institute and the University of Washington at the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting. (The study has not yet been published in a peer-reviewed journal.) It’s early days for the drug — which has not yet been submitted for approval by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) — but co-principal investigator Dr. Christina Wang, lead researcher at LA BioMed, says it’s an important step toward effective, reversible male hormonal contraception.
“In females you have many, many methods. You have the pill, you have the patch, you have the vaginal ring, you have intrauterine devices, injections,” Wang says. “In men there is nothing that is like hormonal contraception. The standard is not equal for the genders.”