We’re gonna need something better than “There’s no evidence this is not true.”


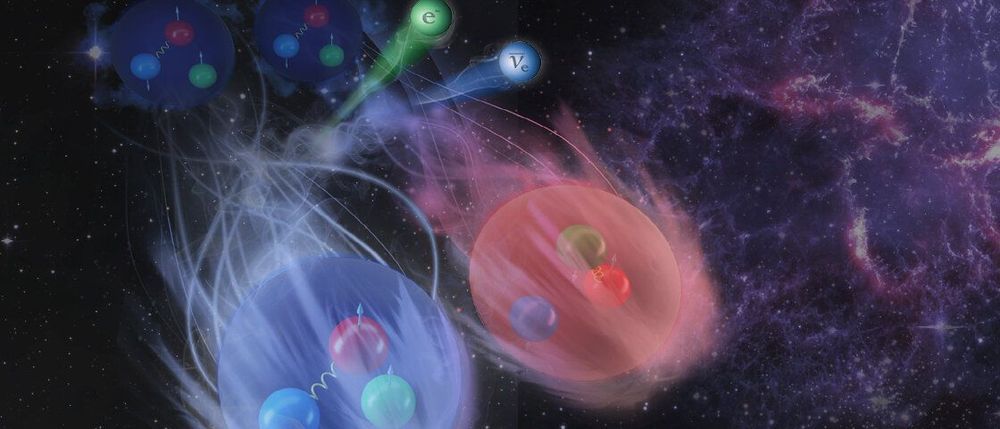
An international collaboration including scientists at the Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) solved a 50-year-old puzzle that explains why beta decays of atomic nuclei are slower than what is expected based on the beta decays of free neutrons.
The findings, published in Nature Physics, fill a long-standing gap in physicists’ understanding of beta decay, an important process stars use to create heavier elements, and emphasize the need to include subtle effects—or more realistic physics—when predicting certain nuclear processes.
“For decades, scientists have lacked a first-principles understanding of nuclear beta decay, in which protons convert into neutrons, or vice versa, to form other elements,” said ORNL staff scientist Gaute Hagen, who led the study. “Our team demonstrated that theoretical models and computation have progressed to the point where it is possible to calculate some decay properties with enough precision to allow for direct comparison to experiment.”
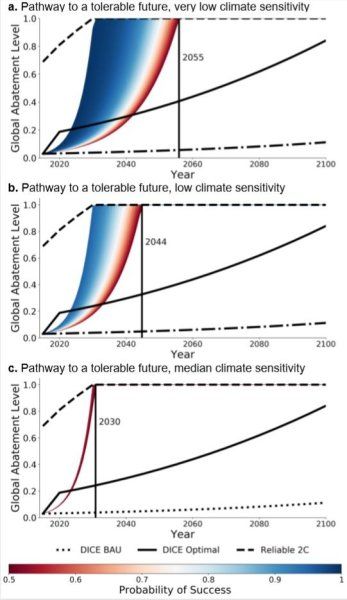
A new comprehensive study of climate change has painted over 5 million pictures of humanity’s potential future, and few foretell an Earth that has not severely warmed. But with immediate action and some luck, there are pathways to a tolerable climate future, according to a research team led by Tufts University.
A Kickstarter campaign is launching on Tuesday for a drone you control with your mind.
The mind-controlled drone is the work EEGSmart, a Chinese company focused on the development of brain-machine interface (BMI) technology — and according to New Atlas writer Loz Blain, who got a chance to test the device, “It’s not perfect, but it does give a glimpse of a mind-controlled future.”
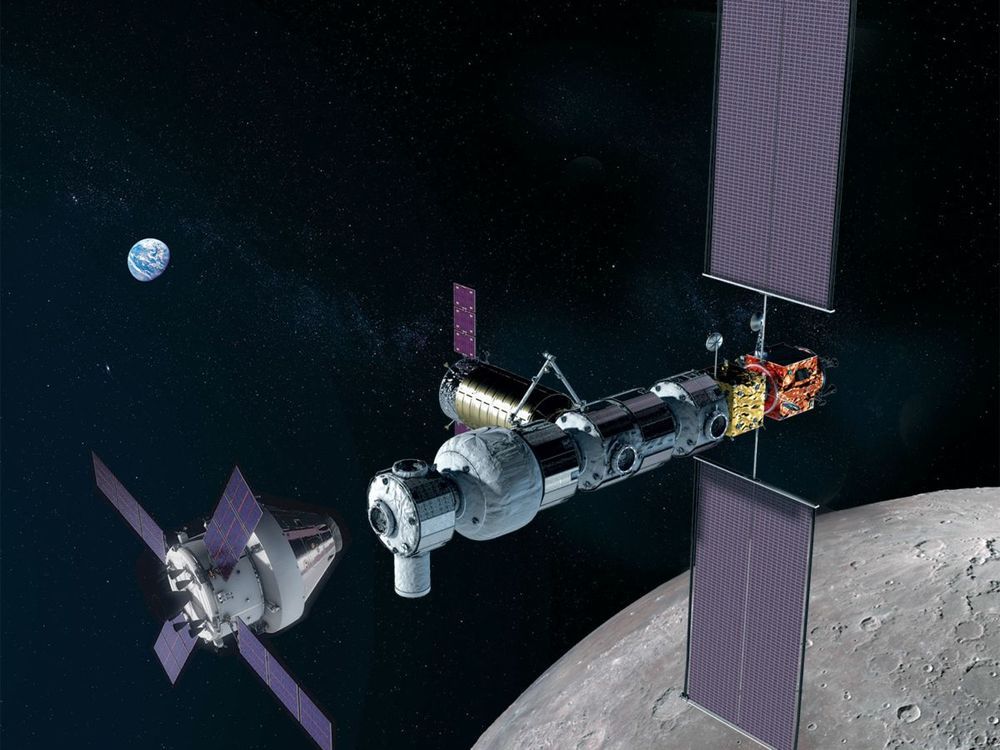

I know some people don’t like it but the Lunar Gateway is getting more traction.
The International Space Station partners have endorsed plans to continue the development of the Gateway, an outpost around the Moon that will act as a base to support both robots and astronauts exploring the lunar surface.
The Multilateral Coordination Board, which oversees the management of the Space Station, stressed its common hope for the Gateway to open up a cost-effective and sustainable path to the Moon and beyond.

The fundamental idea of OpenAI LP is that investors and employees can get a capped return if we succeed at our mission, which allows us to raise investment capital and attract employees with startup-like equity. But any returns beyond that amount—and if we are successful, we expect to generate orders of magnitude more value than we’d owe to people who invest in or work at OpenAI LP—are owned by the original OpenAI Nonprofit entity.
We’ve created OpenAI LP, a new “capped-profit” company that allows us to rapidly increase our investments in compute and talent while including checks and balances to actualize our mission.

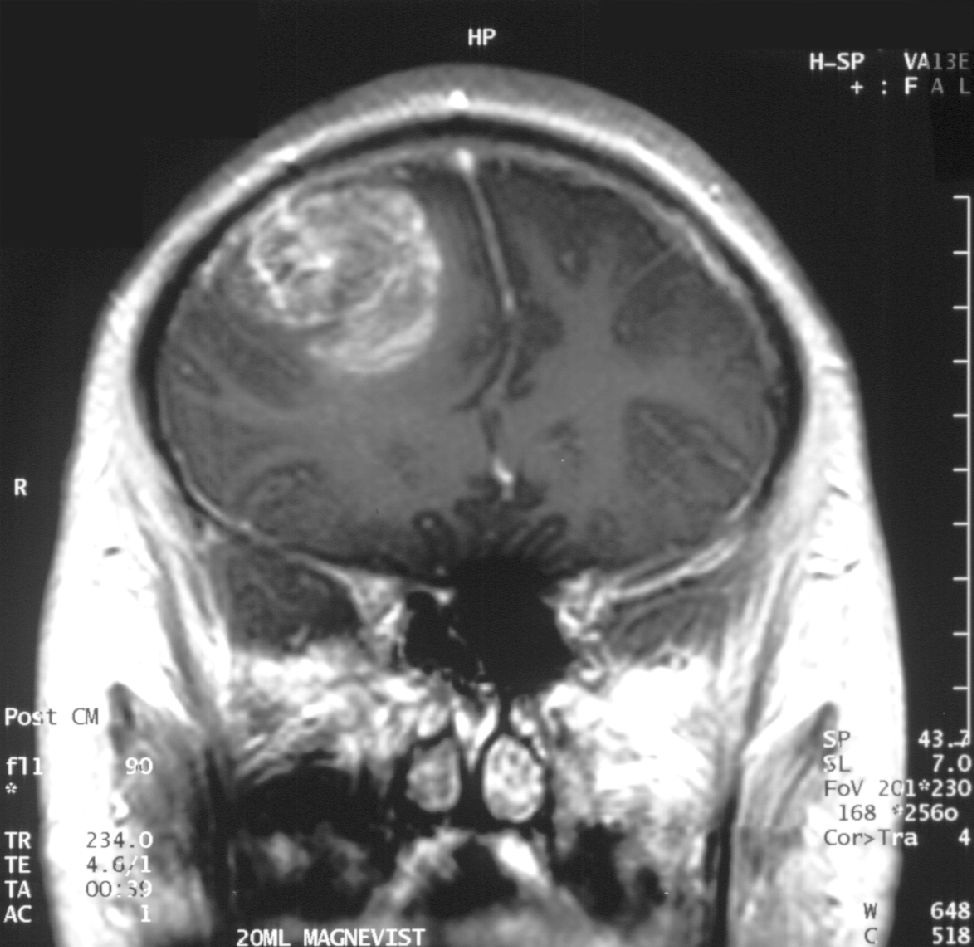
Scripps Research scientists have discovered a compound that potently and selectively kills the stem-like cells that make glioblastoma brain cancers so deadly.
In a study published this week in The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the Scripps Research scientists found that the new compound, which they dubbed RIPGBM, kills glioblastoma stem-like cells cultured from patients’ tumors with more than 40 times the potency of the standard GBM drug temozolomide. They found too that RIPGBM is highly selective, sparing other types of brain cells, and that it powerfully suppresses the growth of GBM tumors in a mouse model of the disease.
“Our discovery of this compound and the cellular pathways it affects offers a promising new strategy for treating glioblastoma,” says principal investigator Luke Lairson, PhD, an assistant professor of chemistry at Scripps Research.


Traditionally, welding has been limited to materials that share similar properties, so it’s tough to make even aluminum and steel join forces. But now, scientists from Heriot-Watt University are claiming a breakthrough method that can weld together materials as different as glass and metal, thanks to ultrafast laser pulses.