Machine learning is everywhere these days, but it’s usually more or less invisible: it sits in the background, optimizing audio or picking out faces in images. But this new system is not only visible, but physical: it performs AI-type analysis not by crunching numbers, but by bending light. It’s weird and unique, but counter-intuitively, it’s an excellent demonstration of how deceptively simple these “artificial intelligence” systems are.
Machine learning systems, which we frequently refer to as a form of artificial intelligence, at their heart are just a series of calculations made on a set of data, each building on the last or feeding back into a loop. The calculations themselves aren’t particularly complex — though they aren’t the kind of math you’d want to do with a pen and paper. Ultimately all that simple math produces a probability that the data going in is a match for various patterns it has “learned” to recognize.
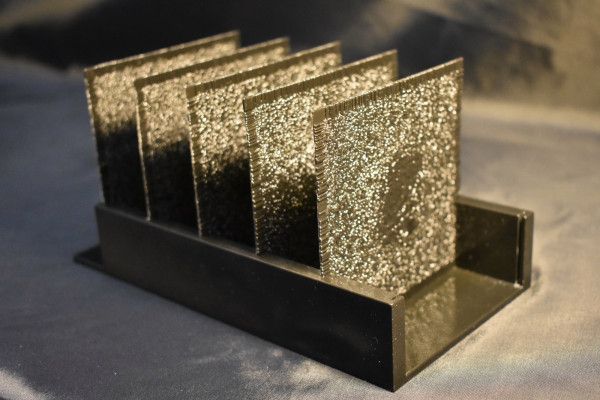
The thing is, though, that once these “layers” have been “trained” and the math finalized, in many ways it’s performing the same calculations over and over again. Usually that just means it can be optimized and won’t take up that much space or CPU power. But researchers from UCLA show that it can literally be solidified, the layers themselves actual 3D-printed layers of transparent material, imprinted with complex diffraction patterns that do to light going through them what the math would have done to numbers.