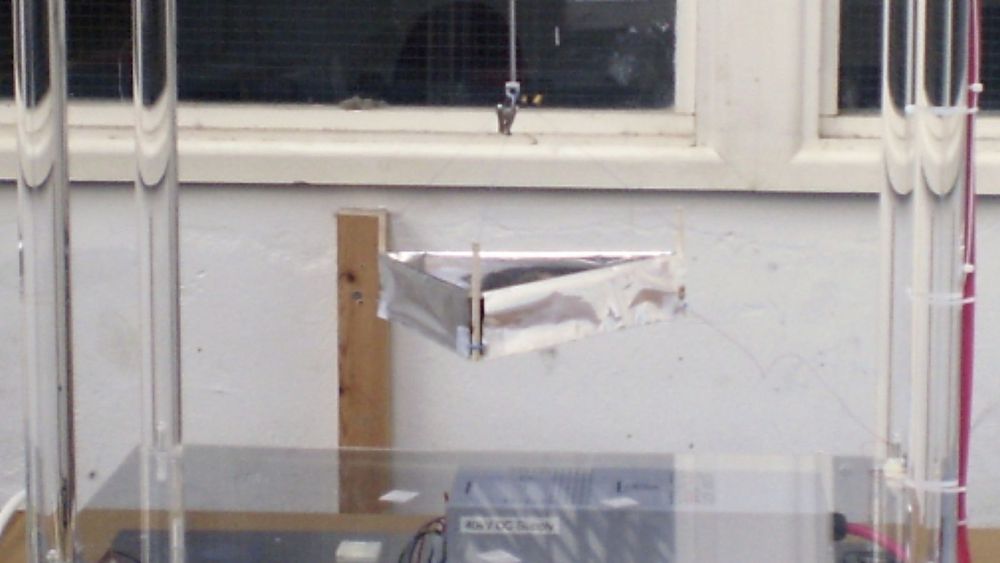
Stealth drones and other aircraft of the future could be powered by engines that don’t have any moving parts, can’t be detected by infrared, and are more efficient than what we have today. A new study by MIT researchers demonstrated all of these capacities and more for ionic thrusters and now at least one major aerospace company, Lockheed Martin, has said it’s investigating the technology.
“I think UAVs would be the most likely initial application if [ionic thrusters] work,” said the lead researcher in the study, MIT aerospace professor Steven Barrett, in an email to The Verge. Ionic thrusters for aircraft work by generating a high-voltage electrical field that strips electrons from air molecules, “ionizing” them and pushing them away behind an aircraft as ionic wind, to move the craft forward. Scientists and hobbyists have been tinkering with small, lightweight model planes using these kinds of propulsion systems since the 1960s. The technology uses no moving parts and is almost completely silent. It hasn’t come to full-size planes, though, due to power concerns.
Read more