“We believe we will offer in a year’s time a complete cure for cancer,” said Dan Aridor, chairman of the board of Accelerated Evolution Biotechnologies Ltd. (AEBi).
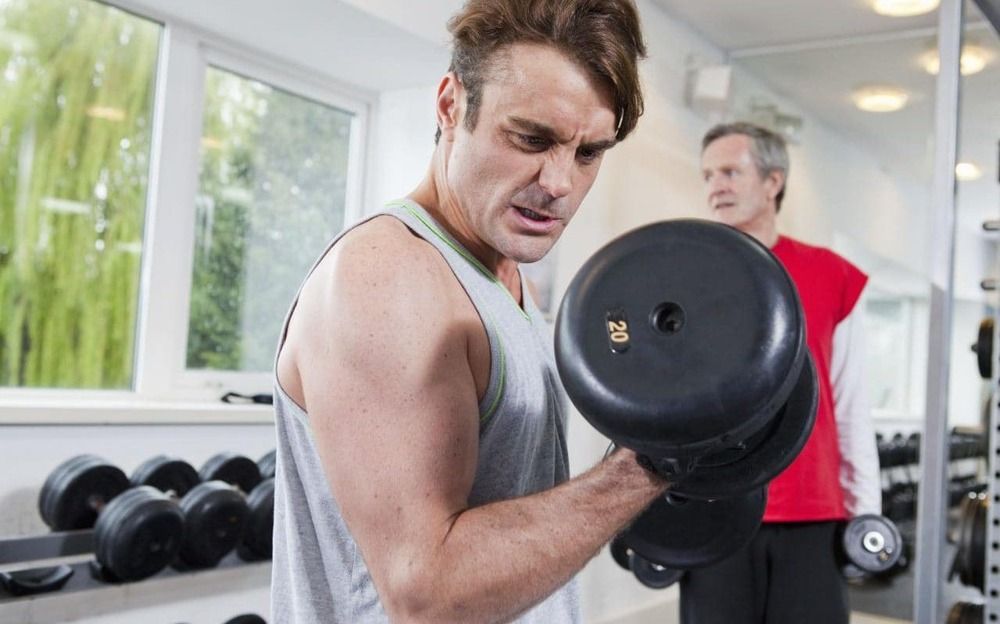


F ifteen-minute workouts could reverse diabetes in just six weeks, new research suggests. A trial of overweight men found that short, intense resistance training sessions three times a week significantly boosted their ability to manage insulin.
Previous research has indicated that 45-minute workouts could have this effect, but the new study has been greeted with particular excitement as experts believe type 2 diabetes patients will be more likely to commit to shorter sessions.
It is estimated that by 2025 there will be five million people with a diabetes diagnosis in the UK, 90 per cent of whom will have type 2, which is related to lifestyle.

The shutdown dragged on two weeks longer than any other in US history, and its effects on science have been profound. It has interrupted studies of everything from California’s coastal fisheries to clinical trials of experimental drugs, and key federal data sets have been pulled offline. Employees at many science agencies were forced to stay at home without pay for more than a month, and academic researchers have been deprived of key research funding.
Federal researchers head back to work after politicians approve deal to reopen government for three weeks. Federal researchers head back to work after politicians approve deal to re-open government for three weeks.
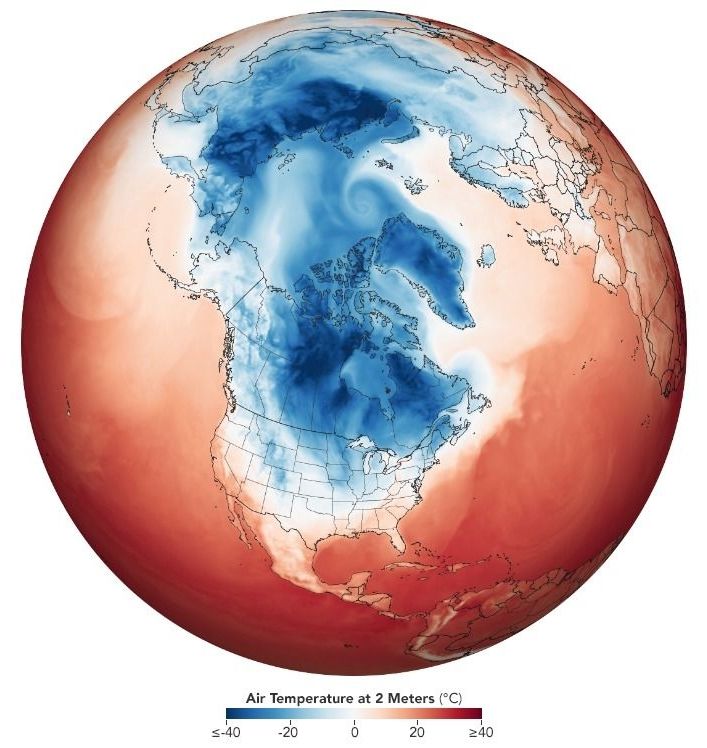
The culprit is a familiar one: the polar vortex.
Seen here is a model using NASA Earth science + other satellite measurements of temperature, moisture, wind speeds and directions, and other conditions: https://go.nasa.gov/2FXw5Gh



Researchers have created a new testing ground for quantum systems in which they can literally turn certain particle interactions on and off, potentially paving the way for advances in spintronics.
Spin transport electronics have the potential to revolutionize electronic devices as we know them, especially when it comes to computing. While standard electronics use an electron’s charge to encode information, spintronic devices rely on another intrinsic property of the electron: its spin.
Spintronics could be faster and more reliable than conventional electronics, as spin can be changed quickly and these devices use less power. However, the field is young and there are many questions researchers need to solve to improve their control of spin information. One of the most complex questions plaguing the field is how the signal carried by particles with spin, known as spin current, decays over time.
Using brain-scanning technology, artificial intelligence, and speech synthesizers, scientists have converted brain patterns into intelligible verbal speech—an advance that could eventually give voice to those without.
It’s a shame Stephen Hawking isn’t alive to see this, as he may have gotten a real kick out of it. The new speech system, developed by researchers at the Neural Acoustic Processing Lab at Columbia University in New York City, is something the late physicist might have benefited from.
Among many things I like here, at 112 min David mentions 20 top scientists in the field are working together.