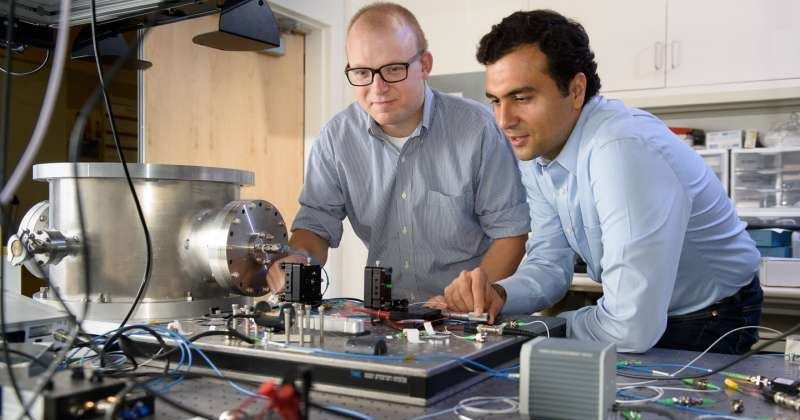
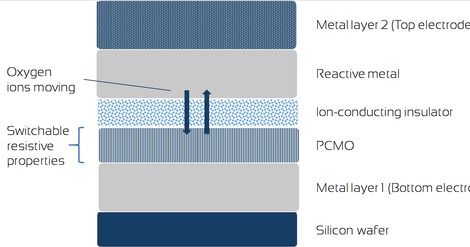
An entirely new type of computer that blends optical and electrical processing could get around this impending processing constraint and solve superlarge optimization problems. If it can be scaled up, this non-traditional computer could save costs by finding more optimal solutions to problems that have an incredibly high number of possible solutions.
There is a special type of problem – called a combinatorial optimization problem – that traditional computers find difficult to solve, even approximately. An example is what’s known as the “traveling salesman” problem, wherein a salesman has to visit a specific set of cities, each only once, and return to the first city, and the salesman wants to take the most efficient route possible. This problem may seem simple but the number of possible routes increases extremely rapidly as cities are added, and this underlies why the problem is difficult to solve.