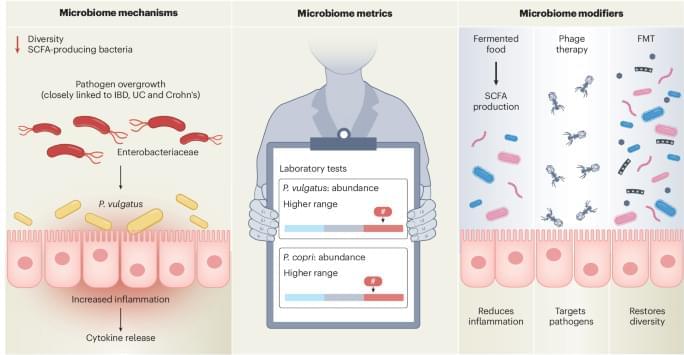
Brain scans analyzed with AI reveal how narcissistic and Machiavellian traits align with different brain networks.

Learn data science using real world examples on Brilliant! First 30 days are free and 20% off the annual premium subscription when you use our link ➜ https://brilliant.org/sabine.
We still don’t know what “consciousness” actually means. But in a new study, researchers have used the equations of quantum mechanics to determine a brain’s “criticality,” a measure which allows them to separate waking brains from sleeping ones. I think they’re onto something. Let’s take a look.
Paper: https://journals.aps.org/pre/abstract… Check out my new quiz app ➜ http://quizwithit.com/ 💌 Support me on Donorbox ➜ https://donorbox.org/swtg 📝 Transcripts and written news on Substack ➜ https://sciencewtg.substack.com/ 👉 Transcript with links to references on Patreon ➜ / sabine 📩 Free weekly science newsletter ➜ https://sabinehossenfelder.com/newsle… 👂 Audio only podcast ➜ https://open.spotify.com/show/0MkNfXl… 🔗 Join this channel to get access to perks ➜
/ @sabinehossenfelder 🖼️ On instagram ➜
/ sciencewtg #science #sciencenews #consciousness.
🤓 Check out my new quiz app ➜ http://quizwithit.com/
💌 Support me on Donorbox ➜ https://donorbox.org/swtg.
📝 Transcripts and written news on Substack ➜ https://sciencewtg.substack.com/
👉 Transcript with links to references on Patreon ➜ / sabine.
📩 Free weekly science newsletter ➜ https://sabinehossenfelder.com/newsle…
👂 Audio only podcast ➜ https://open.spotify.com/show/0MkNfXl…
🔗 Join this channel to get access to perks ➜
/ @sabinehossenfelder.
🖼️ On instagram ➜ / sciencewtg.
#science #sciencenews #consciousness
Tissue from other organs, such as rat hearts and livers, has also been successfully cryopreserved and revived before. Whether this could eventually translate to putting an entire organ—or even an entire organism—in a state of suspended animation requires future research. Some animals produce their own cryoprotectants as they transition to a state of torpor to avoid harsh winters. This is something else scientists could learn from in the pursuit of artificial suspended animation. Alien and Foundation are onto something. Putting humans into a state of suspended animation during spaceflight would drastically reduce the risk of tissue damage caused by microgravity and extreme radiation. No one is trekking to Mars—at least not yet—so we still have time. But even just the thought is no less tantalizing.
Joscha Bach and John Vervaeke explore the nature of the mind, idealism, and computation. Sponsors: The Anagoge Podcast can be found https://www.youtube.com/An…
Joscha Bach, cognitive scientist & AI researcher, talks about philosophy in computation, East Germany, AI, ChatGPT, AlphaZero, human intelligence, consciousn…

A new study in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society by researchers including István Szapudi of the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Institute for Astronomy suggests the universe may rotate —just extremely slowly. The finding could help solve one of astronomy’s biggest puzzles.
“To paraphrase the Greek philosopher Heraclitus of Ephesus, who famously said ‘panta rhei’ (everything moves), we thought that perhaps panta kykloutai—everything turns,” said Szapudi.
Current models say the universe expands evenly in all directions, with no sign of rotation. This idea fits most of what astronomers observe. But it doesn’t explain the so-called Hubble tension—a long-standing disagreement between two ways of measuring how fast the universe is expanding.
Supported by the U.S. National Science Foundation, physicists have revealed the presence of a previously unobserved type of subatomic phenomenon called a fractional exciton. Their findings confirm theoretical predictions of a quasiparticle with unique quantum properties that behaves as though it is made of equal fractions of opposite electric charges bound together by mutual attraction.
The discovery was supported by NSF through multiple grants and laboratory work performed at the NSF National High Magnetic Field Laboratory in Tallahassee, Florida. The results are published in Nature and show potential for developing new ways to improve how information is stored and manipulated at the quantum level, which could lead to faster and more reliable quantum computers.
“Our findings point toward an entirely new class of quantum particles that carry no overall charge but follow unique quantum statistics,” says Jia Li, leader of the research team and associate professor of physics at Brown University. “The most exciting part is that this discovery unlocks a range of novel quantum phases of matter, presenting a new frontier for future research, deepening our understanding of fundamental physics and even opening up new possibilities in quantum computation.”
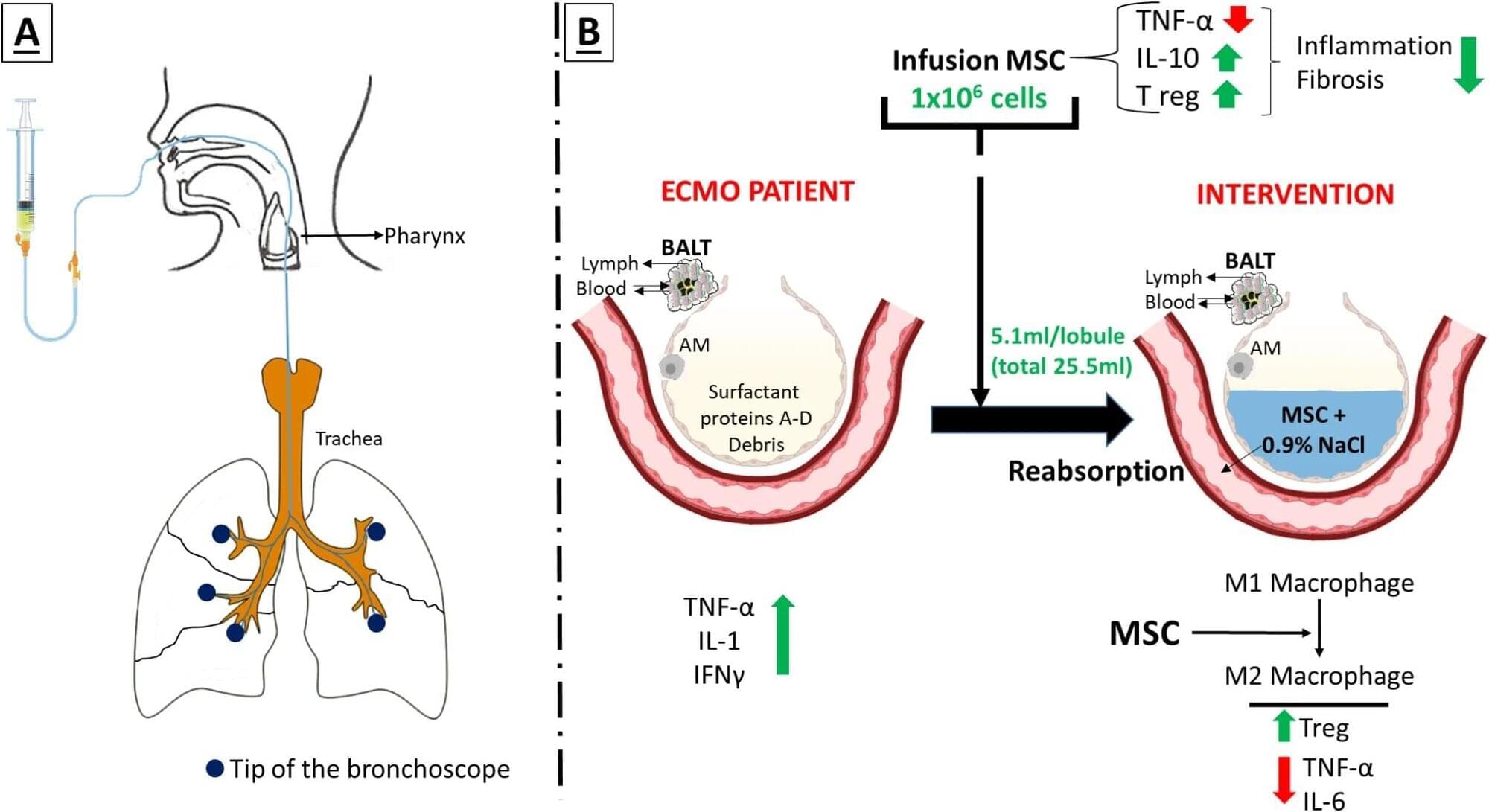
A multidisciplinary clinical team led by Professor Bernat Soria from the Institute of Bioengineering at the Miguel Hernández University of Elche (UMH, Spain) has developed a new method to deliver cell therapies in patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), a life support system used in cases of severe lung failure.
The advance has been published in Stem Cell Research & Therapy. The team has opted not to patent the technique in order to encourage its use in public health systems once further clinical testing is completed.
The method—named CIBA, for “Consecutive Intrabronchial Administration”—enables the delivery of stem-cell-based treatments directly into the alveoli of critically ill patients who cannot receive standard intravenous cell therapy due to the ECMO system’s constraints.