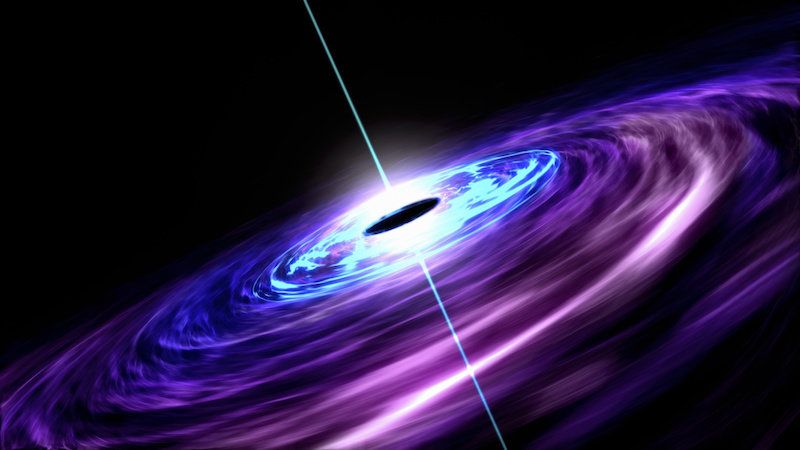
Astrophysicists at Western University have found evidence for the direct formation of black holes that do not need to emerge from a star remnant. The production of black holes in the early universe, formed in this manner, may provide scientists with an explanation for the presence of extremely massive black holes at a very early stage in the history of our universe.
Shantanu Basu and Arpan Das from Western’s Department of Physics & Astronomy have developed an explanation for the observed distribution of supermassive black hole masses and luminosities, for which there was previously no scientific explanation. The findings were published today by Astrophysical Journal Letters.
The model is based on a very simple assumption: supermassive black holes form very, very quickly over very, very short periods of time and then suddenly, they stop. This explanation contrasts with the current understanding of how stellar-mass black holes are formed, which is they emerge when the centre of a very massive star collapses in upon itself.