Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
MIT Has Invented Slightly Eerie Lasers That Transmit Whispers Only You Can Hear
New technology being developed by the MIT’s Lincoln Laboratory uses laser light to excite moisture in the air surrounding a target’s ear, causing it to quietly whisper a personal message from several metres away.
“Our system can be used from some distance away to beam information directly to someone’s ear,” says MIT team leader and physicist Charles M. Wynn.
You probably don’t need us to count off potential applications for such a device, which range from military applications to targeted advertising.

Cambridge University releases a brain-training app that improves concentration akin to Ritalin
Decoder, developed in collaboration with a games developer, gets users to assume the role of an intelligence officer tasked with breaking up global criminal gangs (users are able to select a character and their backstory).
To meet the objective, users have to identify different combinations of number strings in missions littered with distraction.
Winning each mission means users unlock letters of the next criminal location (the higher the score, the more letters revealed).
Paralyzed Individuals Operate Tablets Using Brain Waves
Paralyzed individuals can now operate tablets using brain waves.
High-Speed & High-Definition Book Scanner
This is how they digitize books 📚.

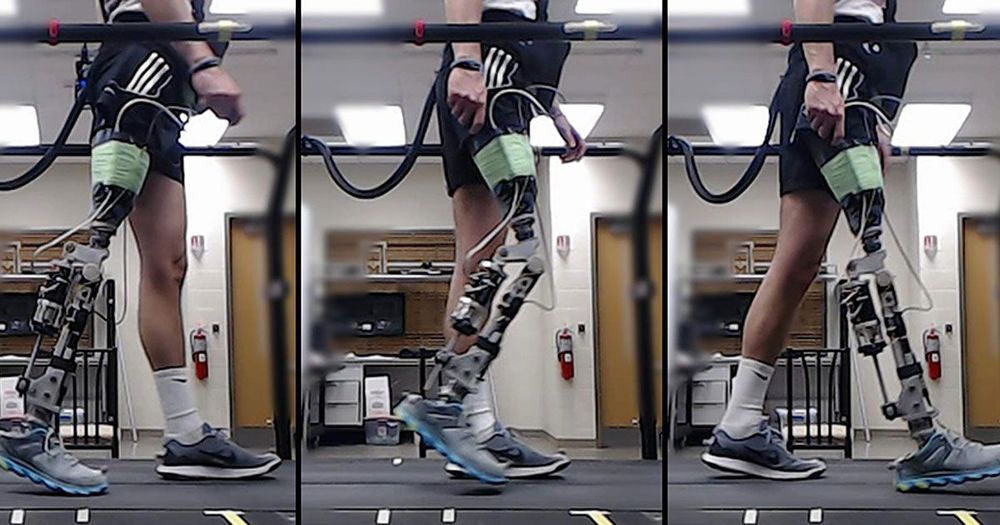
AI Helps Amputees Walk With a Robotic Knee
A movie montage for modern artificial intelligence might show a computer playing millions of games of chess or Go against itself to learn how to win. Now, researchers are exploring how the reinforcement learning technique that helped DeepMind’s AlphaZero conquer chess and Go could tackle an even more complex task—training a robotic knee to help amputees walk smoothly.
Computer algorithms help prosthetics wearers walk within minutes rather than requiring hours of training.

AI technology accelerates and augments legal work
Law firms are under tremendous pressure to innovate to provide better value to their clients, who demand more value for their legal dollars. Providing higher-value services in turn boosts firms’ competitiveness.
However, much of the day-to-day work of any legal office – whether it’s in-house counsel, a boutique firm or one of the largest legal power houses – is the tedious, repetitive work of reading and preparing answers to complaints. Larger firms may have armies of junior associates do much of this necessary but mundane case-preparation work. At smaller firms, partners and senior associates are often involved in all stages of litigation. Preparing responses is time-consuming. It can take several hours to a full day to complete. Those are hours that both attorneys and firms would prefer to use tackling more strategic legal work.
We asked ourselves, what if, instead of taking hours, those high-volume, repetitive tasks could take a couple of minutes?