Circa 2017
Chinese scientists accomplish the feat of teleporting a photon to a satellite hundreds of miles above Earth.



We have known since the 19th century that young blood has surprising curative and rejuvenation abilities. It’s quite strange, but it happens to be true. In recent years, scientific efforts to understand what it is about young blood that causes rejuvenation have ramped up.
We now know that young and old mice with surgically connected circulatory systems will experience altered aging: the young mouse will prematurely grow old, and the old mouse will, in many cases, miraculously grow young. This is known as heterochronic parabiosis, and it is a large source of the legitimate excitement about the potential of young plasma to lead to human rejuvenation [1].
The challenge, of course, is how to achieve these benefits in more acceptable and less disturbing ways.

The cause of cancer is written into the DNA of tumours, scientists have discovered, in a breakthrough which could finally show how much disease is attributable to factors like air pollution or pesticides.
Until now the roots of many cancers have proved elusive, with doctors unable to tease out the impact of a myriad of carcinogenic causes which people encounter everyday.
Even with lung cancer, it is not known just how much can be attributed to smoking and how much could be linked to other factors, such as living by a busy road, or inhaling pollutants at work.
A recent survey by the IE University in Madrid reveals that one in four Europeans would be ready to put an artificial intelligence in power. Should we be concerned for democracy or, on the contrary, welcome Europeans’ confidence in technology?
Europeans ready to elect an AI?
According to the study in question, about one in four out of the 25,000 Europeans surveyed would be prepared to be governed by an AIt worth noting that there are significant variations between countries, because where the European average is around 30%, respondents in the Netherlands are much more open to having a government run by a supercomputer (+ 43%) than in France (+ 25%). “The idea of a pragmatic machine, impervious to fraud and corruption” is one of the reasons that seems most compelling to the interviewees. Added to this are the options that Machine Learning would enable: in fact, the AI described would be able to improve by studying and selecting the best political decisions in the world… It would then be able to make better decisions than existing politicians.

Many researchers see the move to relax the rules as a welcome change, yet some are worried the revisions don’t take public concerns enough into consideration.
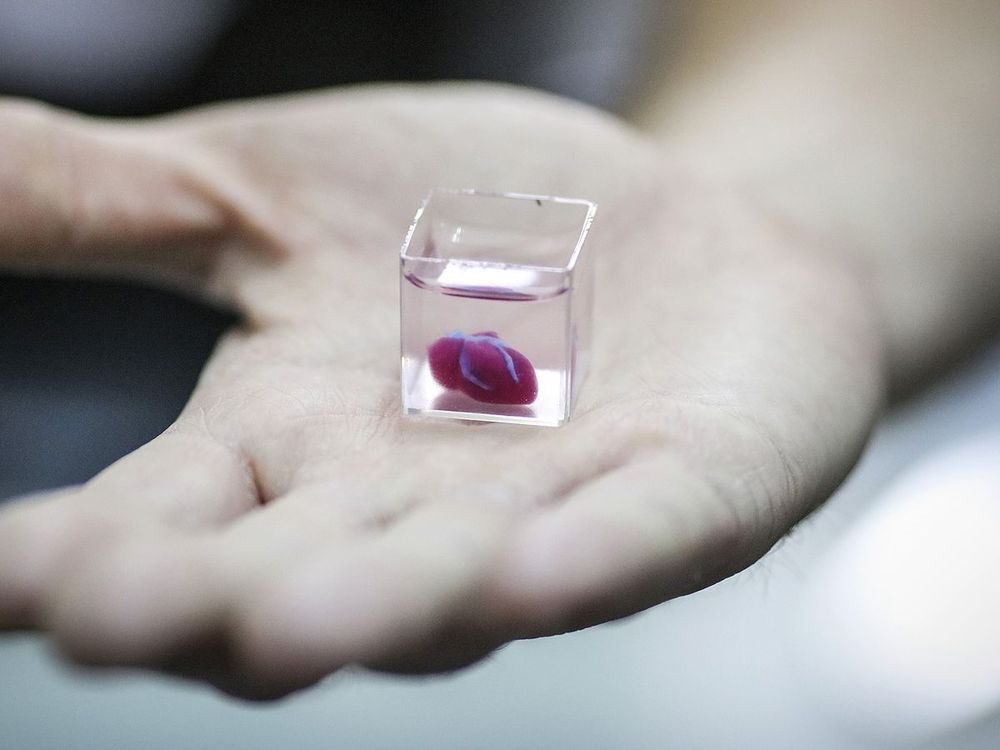
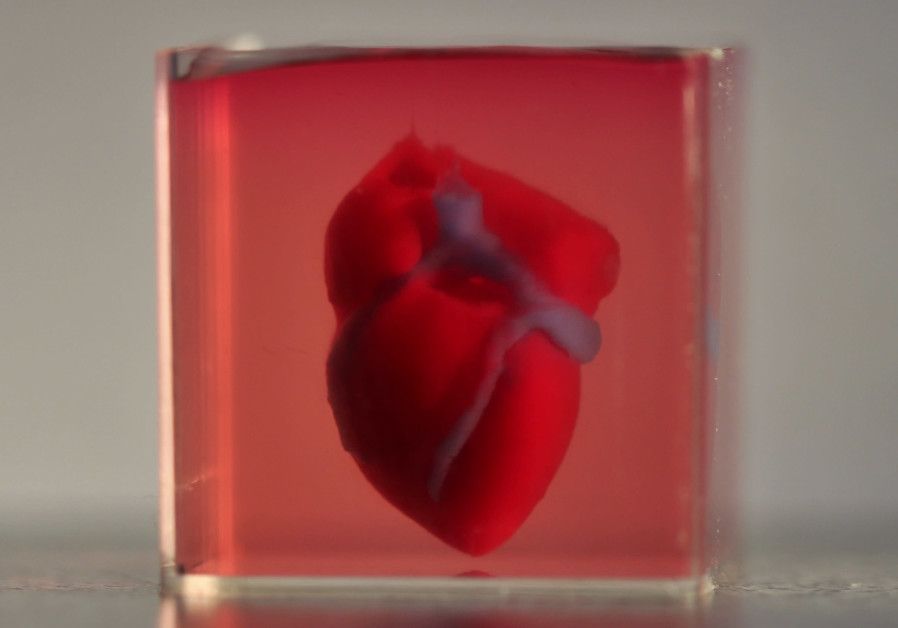

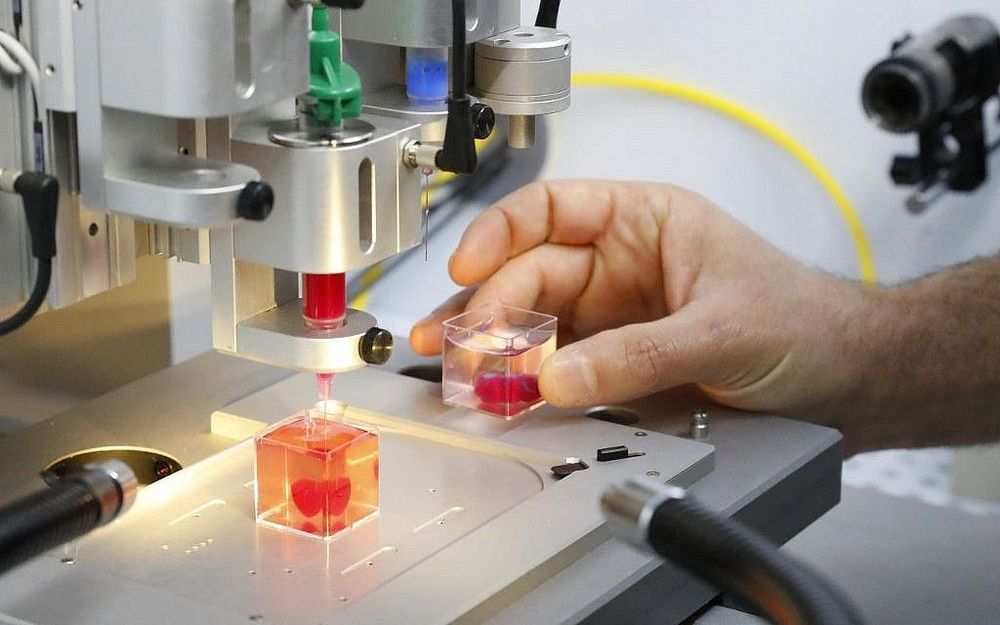
Israeli researchers have printed a 3D heart using a patient’s own cells, something they say could be used to patch diseased hearts — and possibly, full transplants.
The heart the Tel Aviv University team printed in about three hours is too small for humans — about 2.5 centimeters, or the size of a rabbit’s heart. But it’s the first to be printed with all blood vessels, ventricles and chambers, using an ink made from the patient’s own biological materials.