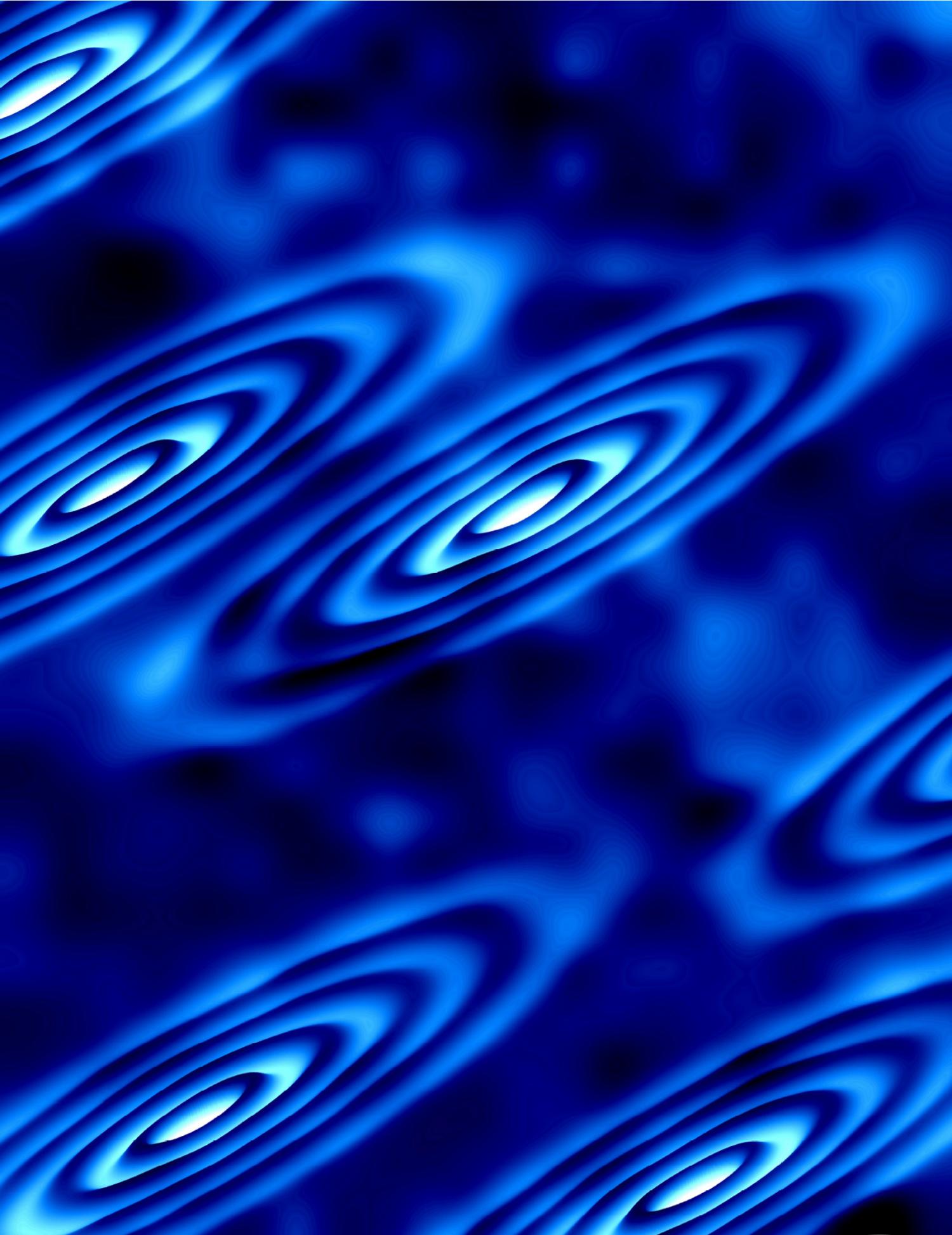
For the first time, an experiment has directly imaged electron orbits in a high-magnetic field, illuminating an unusual collective behavior in electrons and suggesting new ways of manipulating the charged particles.
The study, conducted by researchers at Princeton University and the University of Texas-Austin was published Oct. 21, in the journal Science. The study demonstrates that the electrons, when kept at very low temperatures where their quantum behaviors emerge, can spontaneously begin to travel in identical elliptical paths on the surface of a crystal of bismuth, forming a quantum fluid state. This behavior was anticipated theoretically during the past two decades by researchers from Princeton and other universities.
“This is the first visualization of a quantum fluid of electrons in which interactions between the electrons make them collectively choose orbits with these unusual shapes,” said Ali Yazdani, the Class of 1909 Professor of Physics at Princeton, who led the research.