Tune in beginning at 6:30 a.m. EDT on Monday, as Anne McClain of NASA and David Saint-Jacques of the Canadian Space Agency set up a redundant power supply for the station’s robotic arm. Watch live coverage here:
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

China’s NewSpace: Mapping of its 60+ Start-ups
Chinese space has been a very hot topic in recent years. Other than the impressive space exploration missions (Tiangong, Chang’e…), the interest for China is also due to the recent opening up of this industry to private investments, which has led to a leap in the number of space start-ups. These start-ups, supported by venture capital heavy-weights are covering the entire space industrial chain: launchers, satellite platforms, satellite subsystems, satellite services, ground segment, etc.
The number of space start-ups on the other hand, is a debated question. Chen Lan estimated in November 2018 that there were over 100 Chinese space start-ups [1]. FutureAerospace, a Beijing-based think-tank, sets the number at around 60, at the same period [2]. Other space watchers have suggested 80 such as in [3]. However, how this count is made is rarely detailed (how do we define a “NewSpace company”?), and very few lists are available at the time of writing, if any. Up to now, only Disrupt Space, a start-up which plans to build a global space entrepreneurial community, has undertaken the establishment of a list, which sets the count at 35 Chinese space start-ups (see map below).
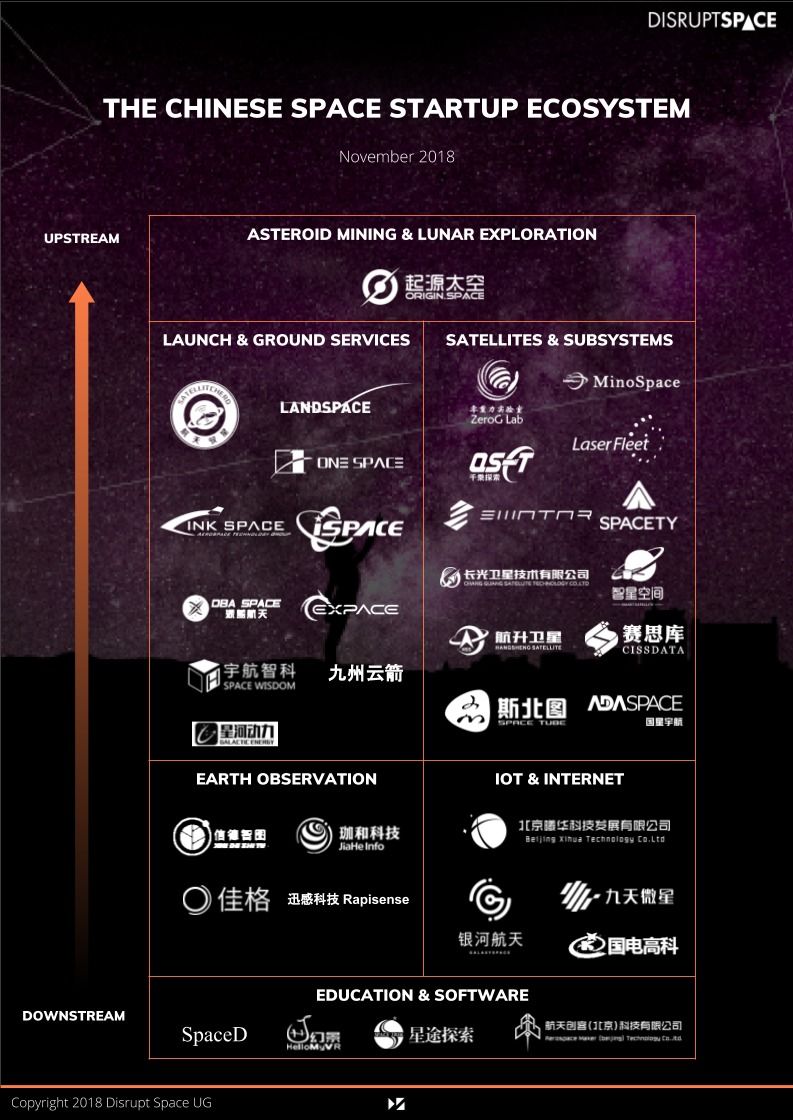
Fig. 1 – Disrupt Space’s Chinese Space Start-up Mapping in November 2018 [4]


Forever young: study uncovers protein that keeps skin youthful
Beauty might only be skin deep, but for those wondering how to keep that skin young, scientists may have found an answer in the form of a protein that encourages cell competition.
The prosaically named COL17A1 might not sound like a fountain of youth, but the new study suggests it does the heavy lifting when it comes to keeping skin intact and unimpaired.
The protein works by encouraging cell competition, a key process to maintain tissue fitness. That effectively “drives out” weaker cells while encouraging replication of stronger ones.

Finally, rejuvenation is a thing!
Fresh interview with Aubrey de Grey
What is ageing? We can define ageing as a process of accumulation of the damage which is just a side-effect of normal metabolism. While researchers still poorly understand how metabolic processes cause damage accumulation, and how accumulated damage causes pathology, the damage itself — the structural difference between old tissue and young tissue — is categorized and understood pretty well. By repairing damage and restoring the previous undamaged — young — state of an organism, we can really rejuvenate it! It sounds very promising, and so it is. And for some types of damage (for example, for senescent cells) it is already proved to work!
Today in our virtual studio, somewhere between cold, rainy Saint-Petersburg and warm, sunny Mountain View, we meet Aubrey de Grey, again! For those of you who are not familiar with him, here is a brief introduction.
500,000 Pieces of Space Junk Are Traveling at 17,500 MPH Around Earth [VIDEOS]
More than 500,000 pieces of debris, or “space junk,” are tracked as they orbit the Earth. They all travel at speeds up to 17,500 mph, fast enough for a relatively small piece of orbital debris to damage a satellite or a spacecraft. If that sounds dangerous, that’s because it it is. The rising population of space debris increases the potential danger to all space vehicles, but especially to the International Space Station, space shuttles and manned spacecraft. NASA takes the threat of collisions with space debris seriously and has a long-standing set of guidelines on how to deal with each potential collision threat.