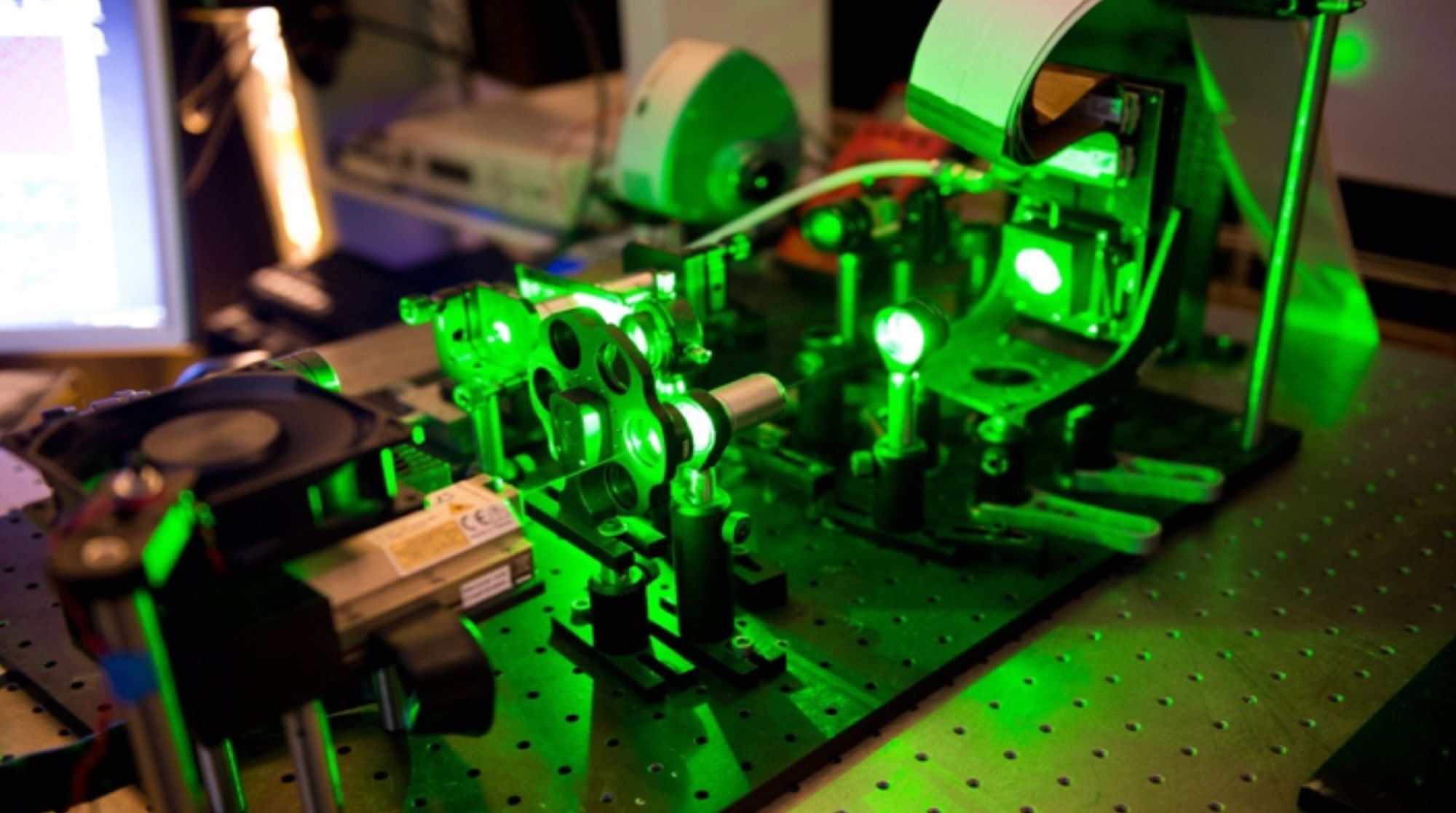
The pace at which conventional chips improve is slowing, and these startups say optical computers are the answer.
AI good for internal back office and some limited front office activities; however, still need to see more adoption of QC in the Net and infrastructure in companies to expose their services and information to the public net & infrastructure.
Deep learning, as explained by tech journalist Michael Copeland on Blogs.nvidia.com, is the newest and most powerful computational development thus far. It combines all prior research in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. At its most fundamental level, Copeland explains, deep learning uses algorithms to peruse massive amounts of data, and then learn from that data to make decisions or predictions. The Defense Agency Advanced Project Research (DARPA), as Wired reports, calls this method “probabilistic programming.”
Mimicking the human brain’s billions of neural connections by creating artificial neural networks was thought to be the path to AI in the early days, but it was too “computationally intensive.” It was the invention of Nvidia’s powerful graphics processing unit (GPU), that allowed Andre Ng, a scientist at Google, to create algorithms by “building massive artificial neural networks” loosely inspired by connections in the human brain. This was the breakthrough that changed everything. Now, according to Thenextweb.com, Google’s Deep Mind platform has been proven to teach itself, without any human input.
This is what scares me; autonomous warfare.
WASHINGTON: DARPA is taking another step toward building autonomous electronic warfare systems with a small contract award to BAE Systems.
Artificial intelligence and autonomy loom large in the Pentagon these days. And electronic warfare, much more quietly, dominates a great deal of thinking across the services these days after we’ve watched how the Russians operate against Ukraine and in Syria. So DARPA’s additional $13.3 million award announced today is worth noting.
Why does all this matter? One of the biggest challenges facing the F-35 program, for example, is the creation of a huge digital threat library (known as mission data files) for the airplane. It includes electronic spectrum information for a wide array of emitters — radar, radio and other sources.
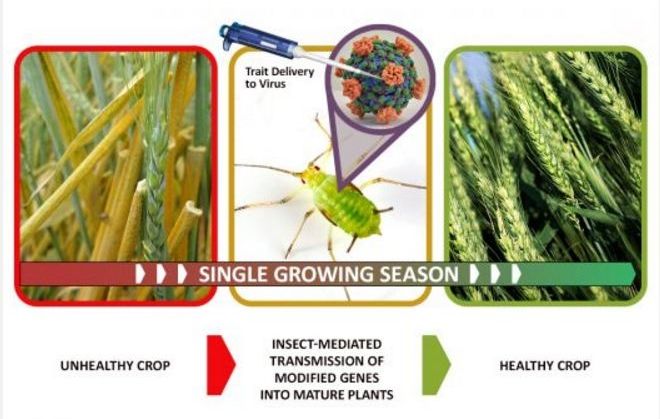
A new DARPA program is poised to provide an alternative to traditional agricultural threat response, using targeted gene therapy to protect mature plants within a single growing season.
DARPA proposes to use a natural and very efficient two-step delivery system to transfer modified genes to plants; insect vectors and the plant viruses they transmit.
In the process, DARPA aims to transform certain insect pests into “Insect Allies,” the name of the new program.
This story may sound like the plot of a science-fiction movie.
Next year, a team of top scientists will hunker down inside a classified facility in the Nevada desert so they can experiment with a piece of advanced technology.
The test will focus on a small nuclear reactor and if it works as planned, it could be a huge step toward putting humans on Mars.
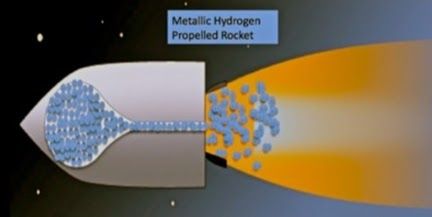
On October 5th 2016, Ranga Dias and Isaac F. Silvera of Lyman Laboratory of Physics, Harvard University released the first experimental evidence that solid metallic hydrogen has been synthesized in the laboratory.
It took 495 GPa pressure to create. The sample is being held in the cryostat in liquid nitrogen.
Atomic metallic hydrogen, if metastable at ambient pressure and temperature could be used as the most powerful chemical rocket fuel, as the atoms recombine to form molecular hydrogen. This light-weight high-energy density material would revolutionize rocketry, allowing single-stage rockets to enter orbit and chemically fueled rockets to explore our solar system. To transform solid molecular hydrogen to metallic hydrogen requires extreme high pressures.