© 2019 EPFL / Alain Herzog. OpticSELINE electrode array for intraneural stimulation of the optic nerve, developed in the Translational Neural Engineering Lab, and used in preliminary studies.
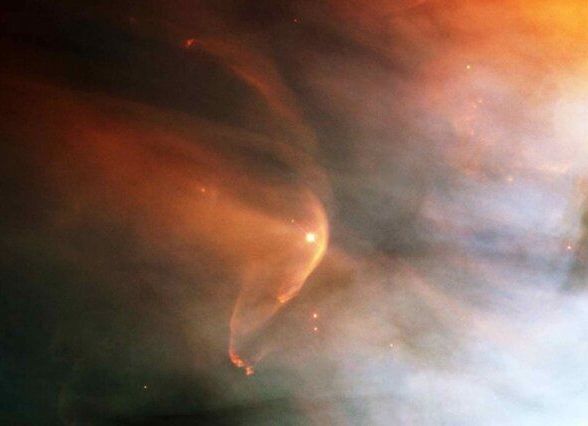



Vast interstellar events where clouds of charged matter hurtle into each other and spew out high-energy particles have now been reproduced in the lab with high fidelity. The work, by MIT researchers and an international team of colleagues, should help resolve longstanding disputes over exactly what takes place in these gigantic shocks.
Many of the largest-scale events, such as the expanding bubble of matter hurtling outward from a supernova, involve a phenomenon called collisionless shock. In these interactions, the clouds of gas or plasma are so rarefied that most of the particles involved actually miss each other, but they nevertheless interact electromagnetically or in other ways to produces visible shock waves and filaments. These high-energy events have so far been difficult to reproduce under laboratory conditions that mirror those in an astrophysical setting, leading to disagreements among physicists as to the mechanisms at work in these astrophysical phenomena.
Now, the researchers have succeeded in reproducing critical conditions of these collisionless shocks in the laboratory, allowing for detailed study of the processes taking place within these giant cosmic smashups. The new findings are described in the journal Physical Review Letters, in a paper by MIT Plasma Science and Fusion Center Senior Research Scientist Chikang Li, five others at MIT, and 14 others around the world.
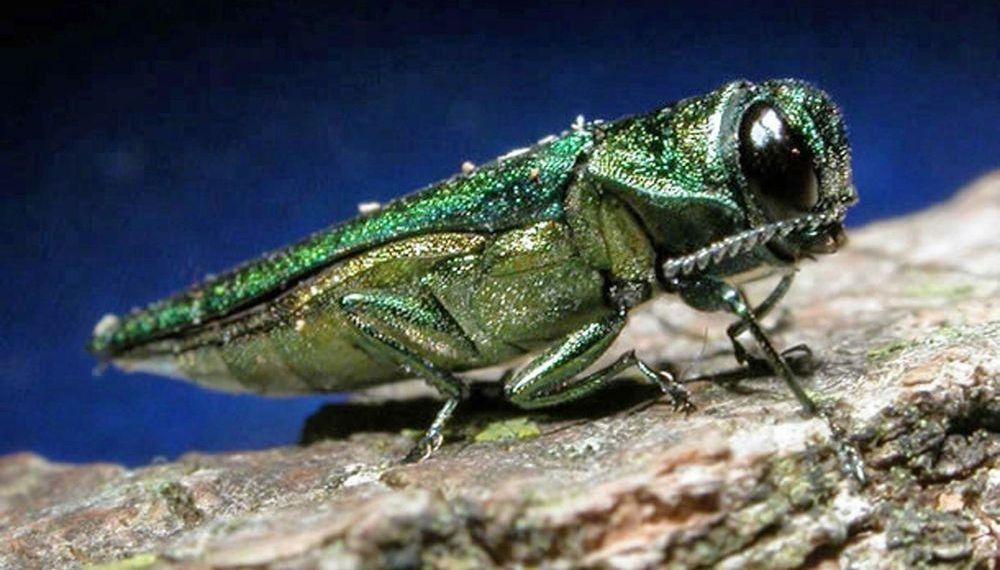

WASHINGTON — Several hundred million ash trees around the nation have fallen victim to a beetle known as the emerald ash borer. Thousands of doomed trees once stood tall in the D.C. area, according to bug guy Mike Raupp, an entomologist at the University of Maryland.
“This is a devastating pest,” said Raupp.
Local governments are fighting back against what Raupp says is a tsunami of the beetles, which chew their way into the tree and feed on what’s underneath the bark.
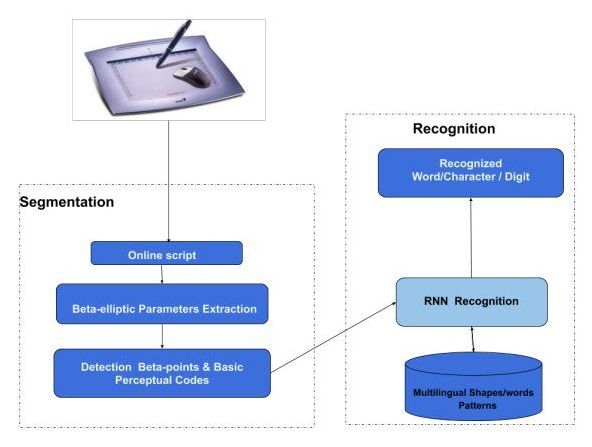
Researchers at the University of Sfax, in Tunisia, have recently developed a new method to recognize handwritten characters and symbols in online scripts. Their technique, presented in a paper pre-published on arXiv, has already achieved remarkable performance on texts written in both the Latin and Arabic alphabet.
In recent years, researchers have created neural network-based architectures that can tackle a variety of tasks, including image classification, face recognition, natural language processing (NLP), and many more. Handwriting recognition systems are computer tools that are specifically designed to recognize characters and other hand-written symbols in a similar way to humans.
In their early years of life, in fact, human beings innately develop the ability to understand different types of handwriting by identifying specific characters both individually and when grouped together. Over the past decade or so, many studies have tried to replicate this ability in computer systems, as this would ultimately enable more advanced and automatic analyses of handwritten texts.
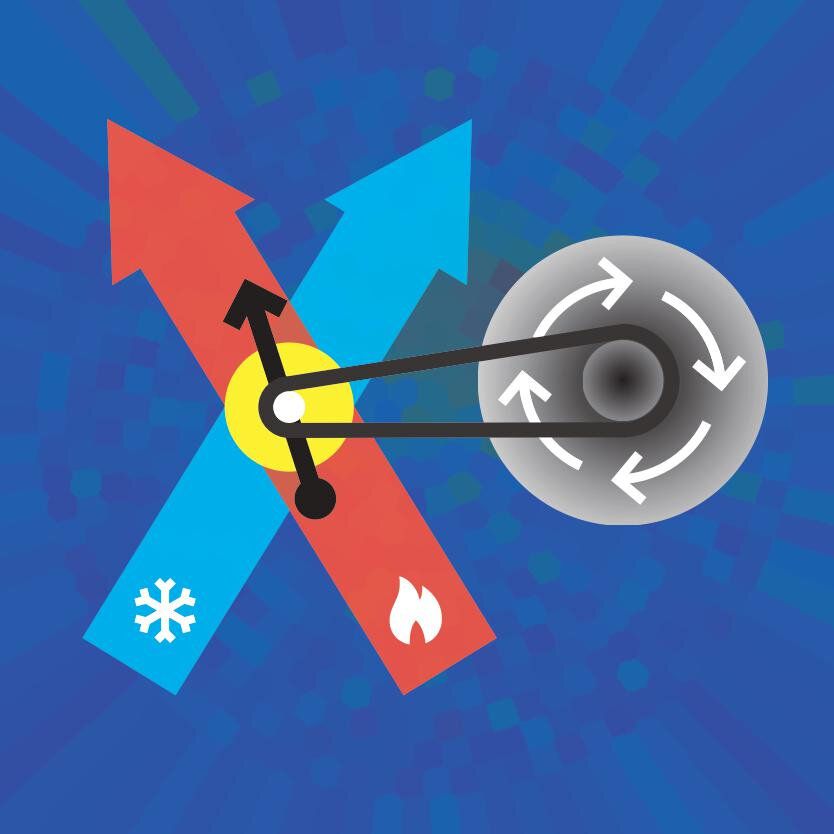

Theoretical physicists at Trinity College Dublin are among an international collaboration that has built the world’s smallest engine—which, as a single calcium ion, is approximately ten billion times smaller than a car engine.
Work performed by Professor John Goold’s QuSys group in Trinity’s School of Physics describes the science behind this tiny motor. The research, published today in international journal Physical Review Letters, explains how random fluctuations affect the operation of microscopic machines. In the future, such devices could be incorporated into other technologies in order to recycle waste heat and thus improve energy efficiency.
The engine itself—a single calcium ion—is electrically charged, which makes it easy to trap using electric fields. The working substance of the engine is the ion’s “intrinsic spin” (its angular momentum). This spin is used to convert heat absorbed from laser beams into oscillations, or vibrations, of the trapped ion.
A group of researchers led by Skoltech Professor Pavel Troshin studied coordination polymers, a class of compounds with scarcely explored applications in metal-ion batteries, and demonstrated their possible future use in energy storage devices with a high charging/discharging rate and stability. The results of their study were published in the journal Chemistry of Materials.
The charging/discharging rate is one of the key characteristics of lithium-ion batteries. Most modern commercial batteries need at least an hour to get fully charged, which certainly limits the scope of their application, in particular, for electric vehicles. The trouble with active materials, such as the most popular anode material, graphite, is that their capacity decays significantly, as their charging rate increases. To retain the battery capacity at high charging rates, the active electrode materials must have high electronic and ionic conductivity, which is the case with the newly-discovered coordination polymers that are derived from aromatic amines and salts of transition metals, such as nickel or copper. Although these compounds hold a great promise, their application in lithium-ion batteries remains virtually unexplored.
A recent study undertaken by a group of scientists from Skoltech and the Institute for Problems of Chemical Physics of RAS led by Professor P. Troshin in collaboration with the University of Cologne (Germany) and the Ural Federal University, focused on tetraaminobenzene-based linear polymers of nickel and copper. Although the linear polymers exhibited much lower initial electronic conductivity as compared to their two-dimensional counterparts, it transpired that they can be used as anode materials that get charged/discharged in less than a minute, because their conductivity increases dramatically after the first discharge due to lithium doping.
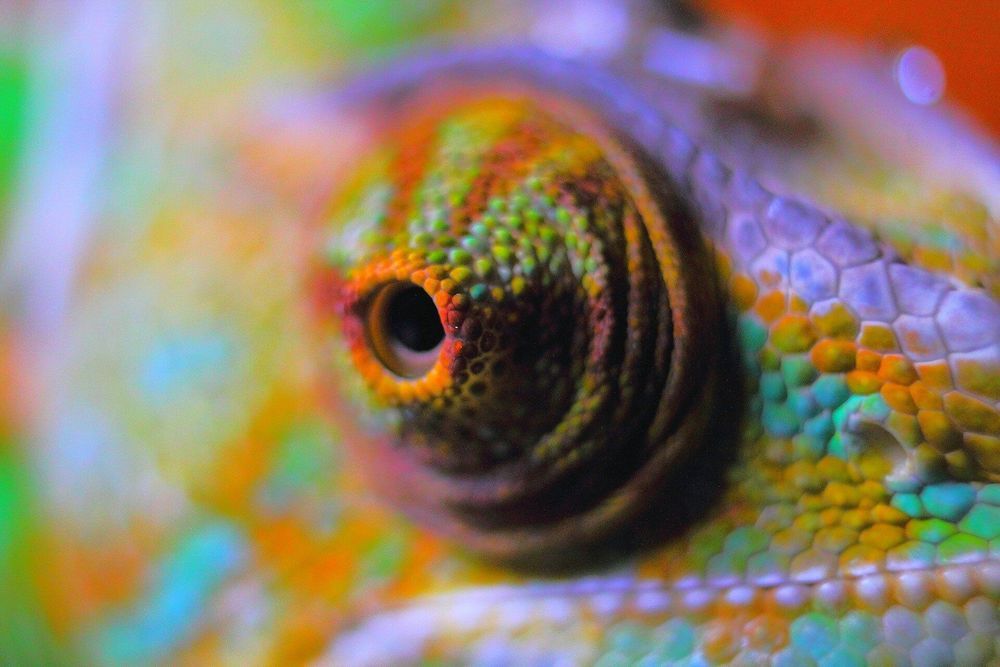

Researchers have developed artificial ‘chameleon skin’ that changes color when exposed to light and could be used in applications such as active camouflage and large-scale dynamic displays.
The material, developed by researchers from the University of Cambridge, is made of tiny particles of gold coated in a polymer shell, and then squeezed into microdroplets of water in oil. When exposed to heat or light, the particles stick together, changing the color of the material. The results are reported in the journal Advanced Optical Materials.
In nature, animals such as chameleons and cuttlefish are able to change color thanks to chromatophores: skin cells with contractile fibers that move pigments around. The pigments are spread out to show their color, or squeezed together to make the cell clear.
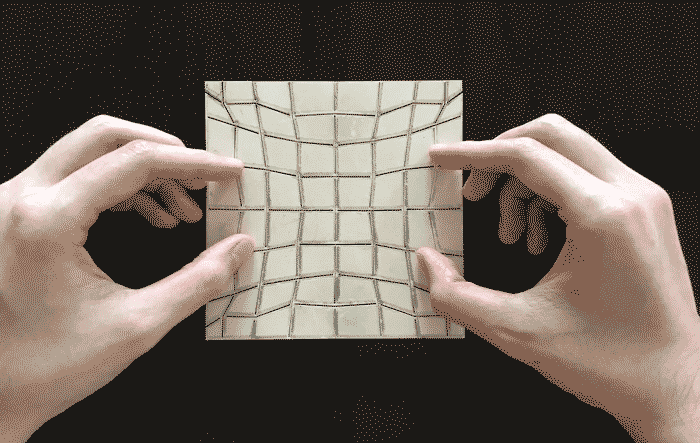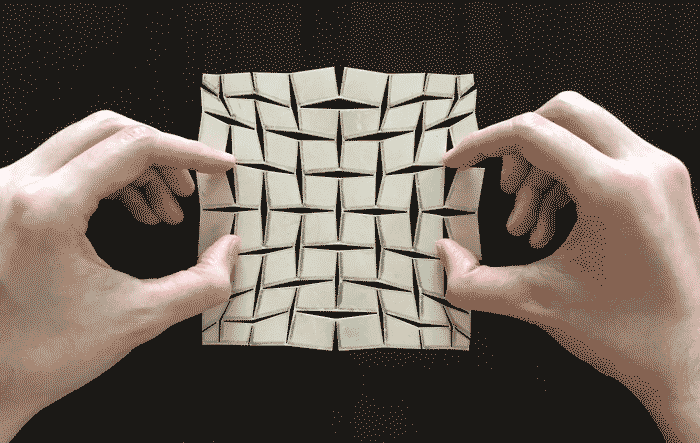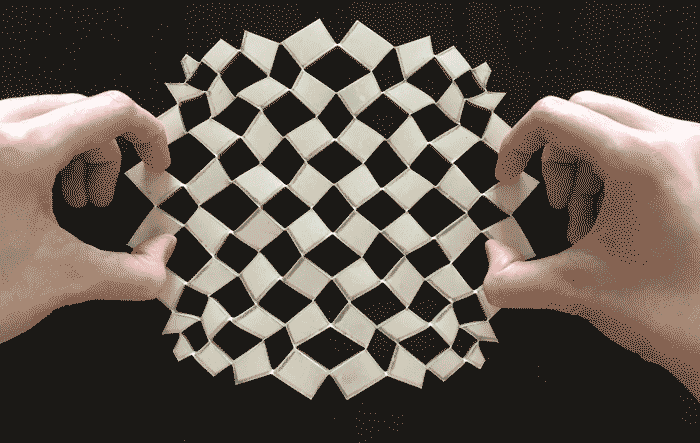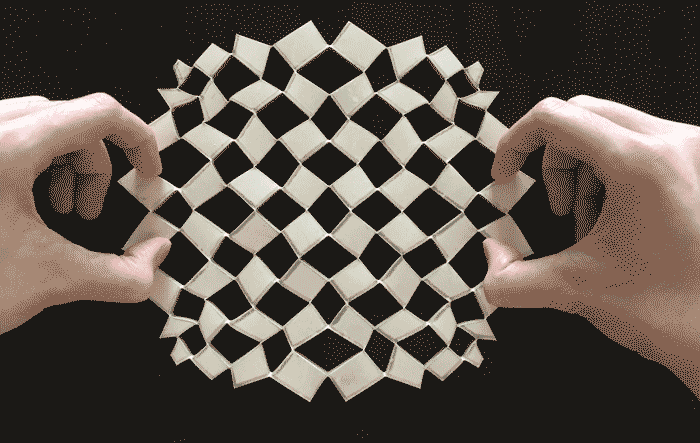
This could lead to self-healing cars.
Researchers from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have developed a mathematical framework that can turn any sheet of material into any prescribed shape, inspired by the paper craft termed kirigami (from the Japanese, kiri, meaning to cut and kami, meaning paper).
Unlike its better-known cousin origami, which uses folds to shape paper, kirigami relies on a pattern of cuts in a flat paper sheet to change its flexibility and allow it to morph into 3D shapes. Artists have long used this artform to create everything from pop-up cards to castles and dragons.
“We asked if it is possible to uncover the basic mathematical principles underlying kirigami and use them to create algorithms that would allow us to design the number, size and orientation of the cuts in a flat sheet so that it can morph into any given shape,” said L. Mahadevan, de Valpine Professor of Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Organismic and Evolutionary Biology, the senior author on the paper.
Nearly one year ago to the day, we first revealed Curtiss Motorcycle’s upcoming Zeus V8 electric motorcycle. And now we’re learning that the innovative electric motorcycle has already begun production, thanks to a recently announced partnership.
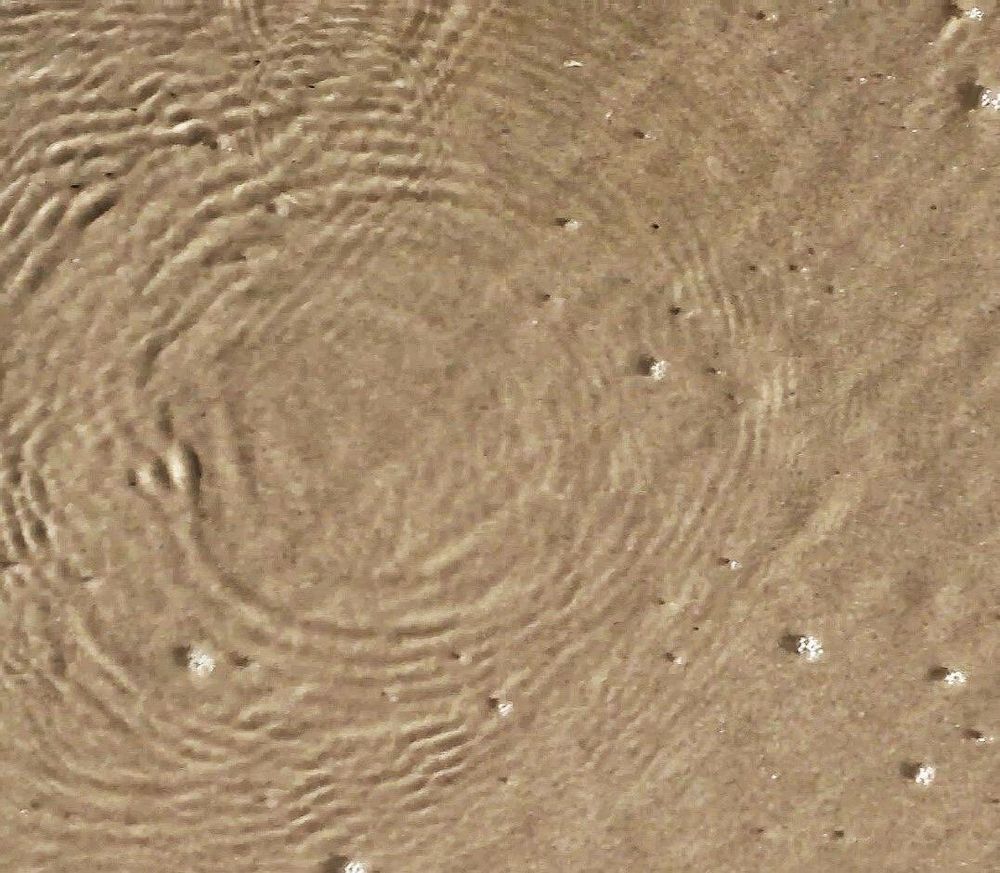
He solved a 127-year-old physics problem on paper and proved that off-centered boat wakes could exist. Five years later, practical experiments proved him right.
“Seeing the pictures appear on the computer screen was the best day at work I’ve ever had,” says Simen Ådnøy Ellingsen, an associate professor at NTNU’s Department of Energy and Process Engineering.
That was the day that Ph.D. candidate Benjamin Keeler Smeltzer and master’s student Eirik Æsøy had shown in the lab that Ellingsen was right and sent him the photos from the experiment. Five years ago, Ellingsen had challenged accepted knowledge from 1887, armed with a pen and paper, and won.