Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
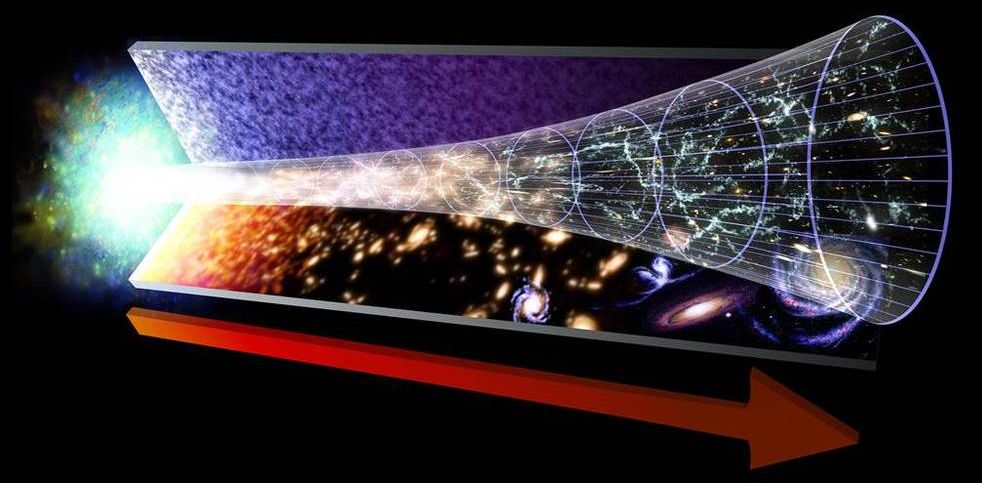
What happened before the Big Bang?
In trying to answer such questions, scientists bump up against the limits of the laws of physics. Existing theories can account for the evolution of the universe from its earliest moments — from a fraction of a second after the Big Bang — but the question of what came before has been among the most vexing in all of science.
“It’s my life’s work to try to answer that question,” University of Toronto physicist Renée Hložek says.
This image represents the evolution of the universe, starting with the Big Bang. The red arrow marks the flow of time.
How Epic & ILM’s John Knoll Tried to Recreate the Moon Landing for Microsoft’s Build 2019 Keynote
In the end, it wasn’t meant to be. Microsoft had pulled out all the stops for its Build 2019 developer conference keynote on Monday morning. The company had partnered with Epic Games and Industrial Light & Magic chief creative officer John Knoll for a hugely ambitious demo of its Hololens 2 headset that aimed to recreate the Apollo 11 moon landing, 50 years after the fact, in mixed reality.
All had worked out well during multiple rehearsals over the last few days. But when Knoll and science journalist and “Man on the Moon” author Andrew Chaikin were set to go on stage on Monday, the demo just didn’t run. Microsoft stalled by extending its pre-show ImagineCup competition until the show’s moderator couldn’t think of any more questions to ask. Then Knoll and Chaikin went on stage, giving it one more go — and the mixed-reality overlays simply refused to appear.

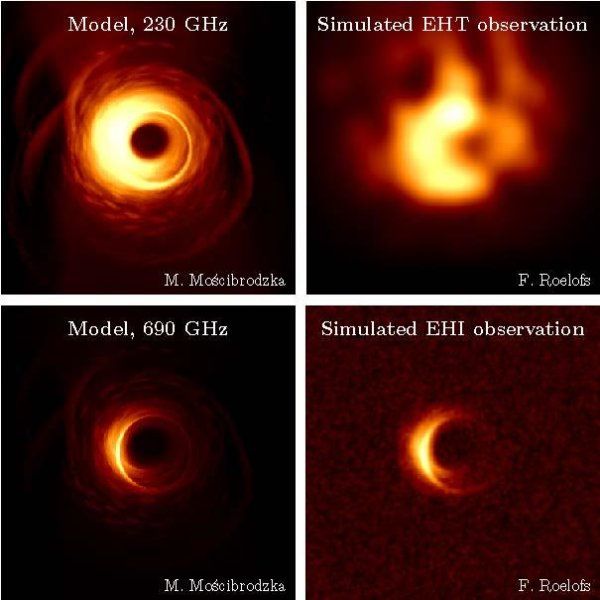
Telescopes in space for even sharper images of black holes
The idea is to place two or three satellites in circular orbit around the Earth to observe black holes. The concept goes by the name Event Horizon Imager (EHI). In their new study, the scientists present simulations of what images of the black hole Sagittarius A would look if they were taken by satellites like these.
More than five times as sharp
“There are lots of advantages to using satellites instead of permanent radio telescopes on Earth, as with the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT),” says Freek Roelofs, a PhD candidate at Radboud University and the lead author of the article. “In space, you can make observations at higher radio frequencies, because the frequencies from Earth are filtered out by the atmosphere. The distances between the telescopes in space are also larger. This allows us to take a big step forward. We would be able to take images with a resolution more than five times what is possible with the EHT.”
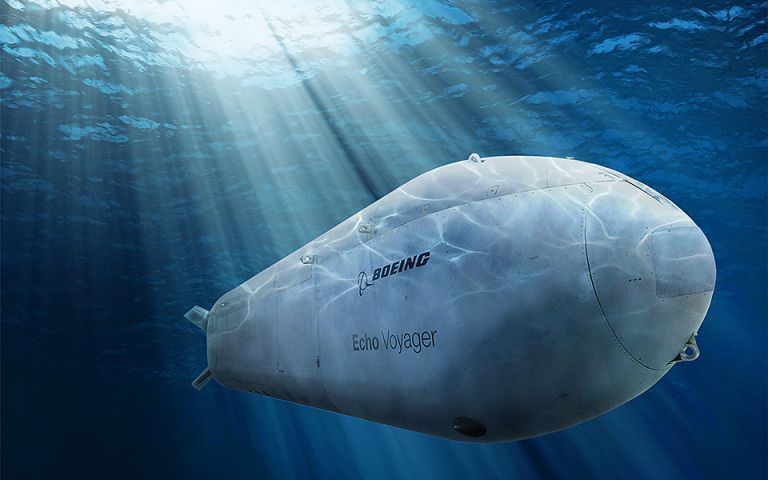


Navy’s Giant New Robot Sub Will Prowl Ocean For Months Autonomously
The Navy just awarded Boeing a contract to build a giant robot submarine, called the Orca Extra-Large Unmanned Undersea Vehicle, which it says will prowl the depths of the ocean autonomously for months at a time.
The U.S. Naval Institute says the sub will be used for “mine countermeasures, anti-submarine warfare, anti-surface warfare, electronic warfare and strike missions.”

