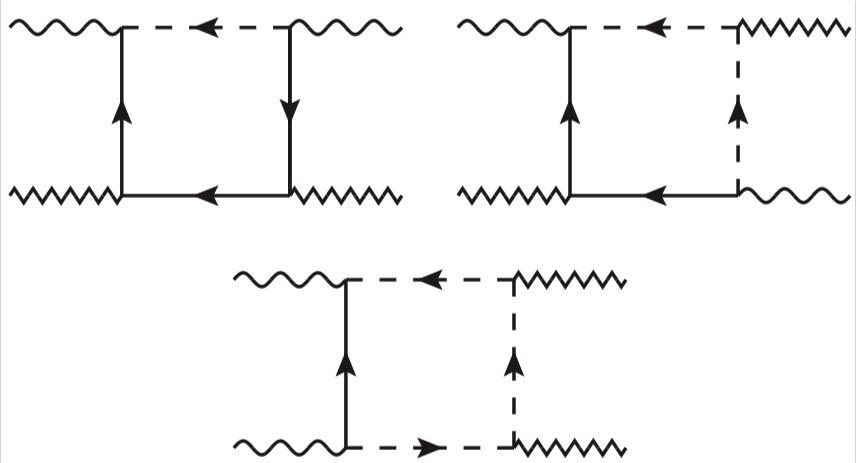
Researchers at the University of Southampton and the Korea Institute for Advanced Study have recently showed that supersymmetry is anomalous in N=1 superconformal quantum field theories (SCFTs) with an anomalous R symmetry. The anomaly described in their paper, published in Physical Review Letters, was previously observed in holographic SCFTs at strong coupling, yet their work confirms that it is already present in the simplest free STFCs.
“Supersymmetry is a symmetry that relates particles with integer and half-integer spin, and has played a central role in many advances in theoretical physics since its discovery,” Kostas Skenderis, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told Phys.org. “It has been used as a means to understand the behavior of strongly interacting quantum systems where our usual theoretical tools (perturbation theory) are not applicable, as well as in some of the main candidates for beyond the Standard Model physics.”
Supersymmetry underlies the mathematical consistency of string theory, which is the most complete theory of quantum gravity proposed so far. A quantum anomaly, such as that observed by the researchers, is essentially the failure of a symmetry to be preserved at a quantum level. These anomalies typically come in two types: “bad” ones, which render string theory mathematically inconsistent and “healthy” ones, which capture important quantum properties of the theory.