NASA enlists some machine learning help to boost the search for other worlds.
Dec. 14 (UPI) — NASA scientists have found a planetary system with as many planets as our own.
“Scientists have found for the first time eight planets in a distant planetary system,” Paul Hertz, astrophysics division director at NASA Headquarters, said during a teleconference on Thursday that was live-streamed on NASA TV.
Astronomers were aware of seven of the eight planets orbiting the Kepler 90 star. The discovery of the new planet, Kepler-90i, was made possible by machine learning.
The SRF Summer Scholars Program offers undergraduate students the opportunity to conduct biomedical research to combat diseases of aging, such as cancer, atherosclerosis, and Parkinson’s Disease. Under the guidance of a scientific mentor, each Summer Scholar is responsible for his or her own research project in such areas as genetic engineering and stem cell research. The Summer Scholars Program emphasizes development of both laboratory and communication skills to develop well-rounded future scientists, healthcare professionals, and policy makers.
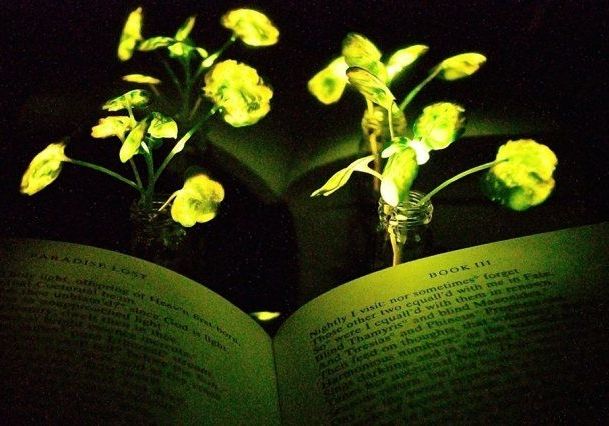
The humble house plant could soon start earning its keep by lighting up a room, if new research from MIT pans out. Engineers have hacked watercress plants to make them glow for a few hours at a time, and while it’s currently only about as bright as those old stars you might have stuck to your ceiling as a kid, the long-term plan is to develop plants that you could read by to reduce the need for electric lighting.
The idea of a glowing plant is not particularly new. They’ve been promised by Kickstarter campaigns for years, including the likes of Bioglow and Glowing Plants, but those startups have since gone bust. Although we’re not going to pretend that this new project is immune from meeting the same fate, having the backing of MIT scientists gives us a little more hope that the glowing plants might eventually bear fruit.
The work comes from the same “plant nanobionics” team that recently designed explosive-detecting spinach and leaf sensors that can alert farmers at the first sign of thirsty crops. In this case, the researchers wanted to tackle lighting, which accounts for about 20 percent of energy consumption worldwide.
A new story on my work out from Bodyhacks. (Please remember I don’t write these stories nor pick the photos, but I’m honored people I don’t know choose to cover my work and #libertairan governor campaign however they wish): http://bodyhacks.com/zoltan-istvan-libertarian-transhumanist…alifornia/ #transhumanism
On the 2018 California ballot, the good people of California will have a chance to vote not only for a candidate who stands for a unique political agenda but one who stands for an equally unique non-political ideology. Zoltan Istvan [real name] will run on the Libertarian party’s platform, but with a transhumanist agenda.
He’s not the first transhumanist to run. In Australia, Meow Meow Ludo Disco Gamma [also real name] ran for office on a science platform last year, but that was way down under. This is ‘Merica, and it’s not the first time Istvan has run either. He put his name in the hat with Hilary and Donald in the last presidential election. [Psst, he didn’t win.]
Zoltan is not only a transhumanist in philosophy, he’s a practicing preacher. He even wrote a best-selling book, The Transhumanist Wager, to back up his beliefs.
Istvan believes humanity stands on the precipice of transhumanism as a normal state of affairs. Technology, he sees as a way to level the playing field of inequality. But, does anyone take him seriously?
This is the third part of our ongoing series of articles that discuss the Hallmarks of Aging. Published in 2013, the paper divides aging into distinct categories (“hallmarks”) of damage to explain how the aging process works and how it causes age-related diseases[1].
Today, we will be looking at one of the primary hallmarks, telomere attrition.
Imagine that instead of switching on a lamp when it gets dark, you could read by the light of a glowing plant on your desk.
MIT engineers have taken a critical first step toward making that vision a reality. By embedding specialized nanoparticles into the leaves of a watercress plant, they induced the plants to give off dim light for nearly four hours. They believe that, with further optimization, such plants will one day be bright enough to illuminate a workspace.
“The vision is to make a plant that will function as a desk lamp—a lamp that you don’t have to plug in. The light is ultimately powered by the energy metabolism of the plant itself,” says Michael Strano, the Carbon P. Dubbs Professor of Chemical Engineering at MIT and the senior author of the study.
A number of studies in different countries show that when people are asked “how long would you like to live?”, they respond with a figure equal to or slightly higher than the current life expectancy in a given country[1–4]. So, why does the public often lack enthusiasm for longevity?
These studies have shown that, generally, the public is uninterested in living longer than normal because they believe that these extra years will be spent suffering from the illnesses of old age. This is why the public often reacts to words like ‘longevity’ this way; to them, ten extra years likely means a decade spent in a wheelchair or some other decrepit state robbed of independence and health.