Sure there’s lots of empty space within atoms, but that doesn’t mean there’s nothing there to see.
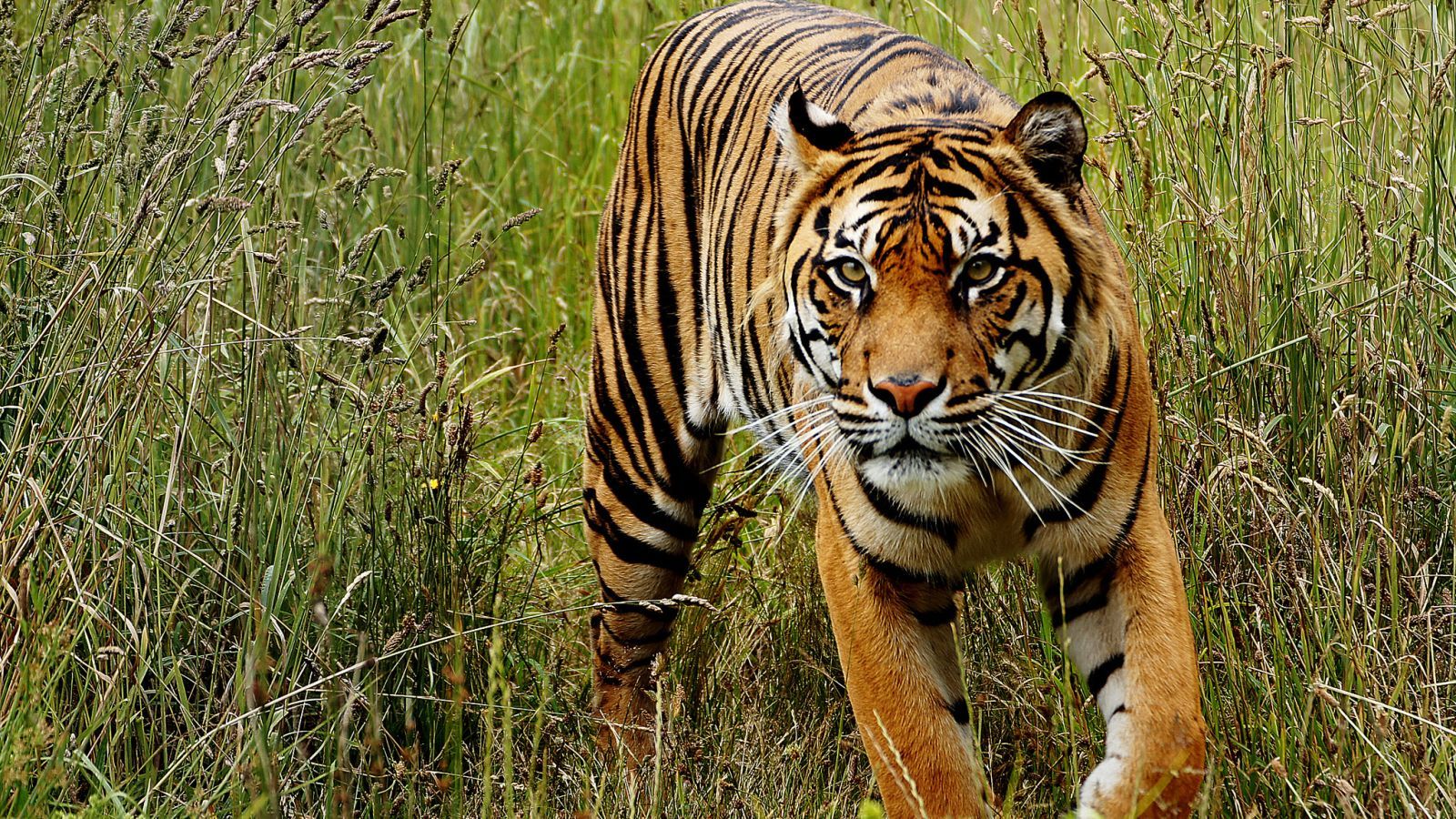






Tigers seem pretty straightforward: stripes, sharp claws, awe-inspiring grace wielded by hundreds of pounds of rippling muscle, fondness of sugary cereal, etc. But new research on the big cats’ DNA is the latest indication that underneath that striking orange and black pelage, not all tigers are the same. Scientists are now reporting that tigers are broken up into six distinct subspecies spread out across Asia.
In endangered species like tigers, pegging down the exact number of subspecies can be pretty important for conservation purposes. Being mindful of how the species is naturally divided up in the wild—and how populations may be evolving independently of one another—can allow conservationists to more effectively manage populations as cohesive units. Global tiger conservation has struggled with this since there’s been plenty of disagreement on how many subspecies even exist.
A recent discovery.

That will require widening of the locations where AI is done. The vast majority of experts are in North America, Europe and Asia. Africa, in particular, is barely represented. Such lack of diversity can entrench unintended algorithmic biases and build discrimination into AI products. And that’s not the only gap: fewer African AI researchers and engineers means fewer opportunities to use AI to improve the lives of Africans. The research community is also missing out on talented individuals simply because they have not received the right education.
If AI is to improve lives and reduce inequalities, we must build expertise beyond the present-day centres of innovation, says Moustapha Cisse.
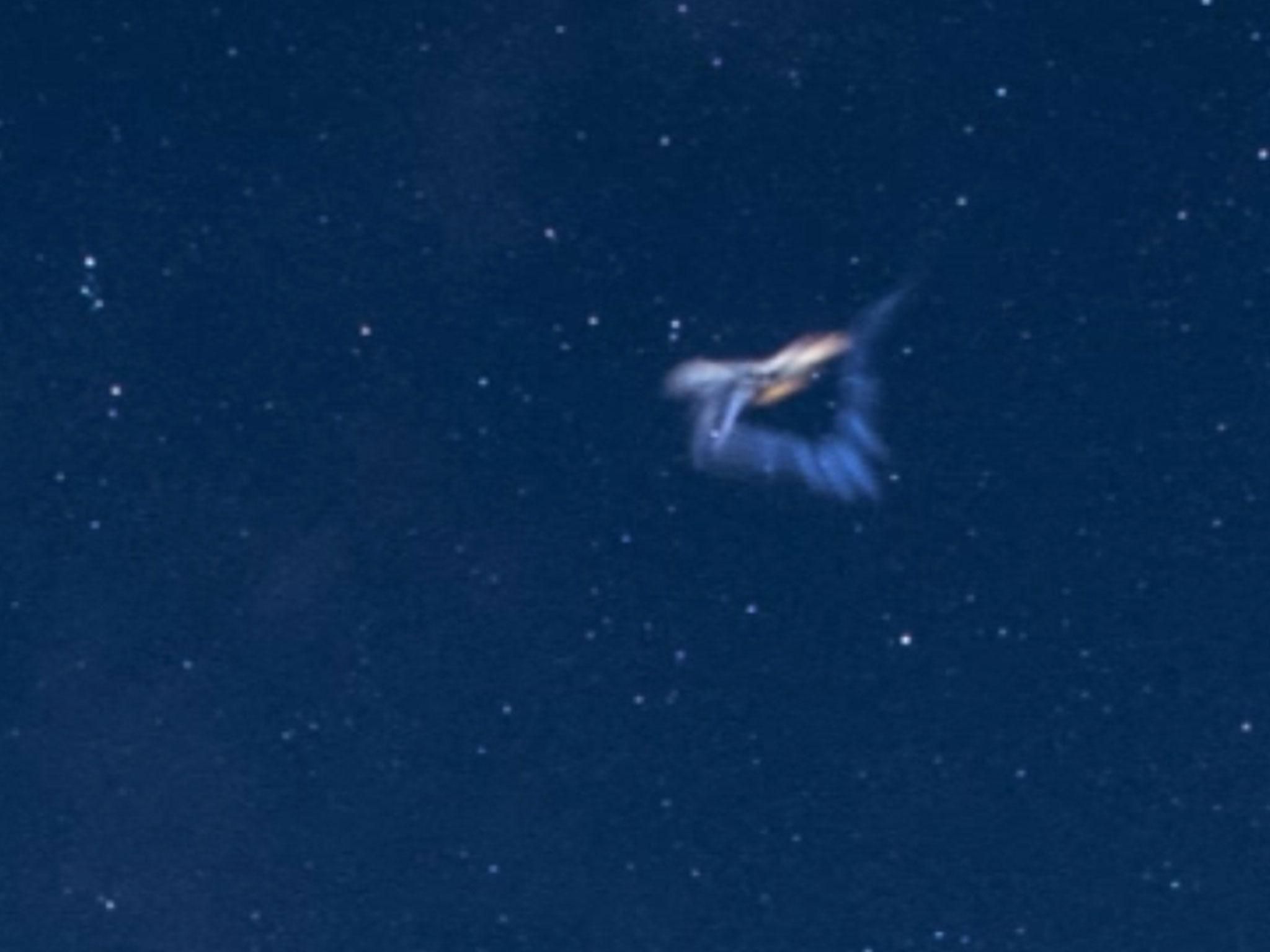

But halfway through the shoot, Nick saw the meteor fly across the sky behind the castle.
He said: “I immediately thought, ‘I hope that was caught in the frame’. It’s very unusual to see a meteor that big. Because I was shooting the star trail, I couldn’t check the footage immediately.”
When he got home and reviewed his pictures, he realised he had caught the moment.

A massive sinkhole recently collapsed nearby Mulberry, Florida, draining approximately 215 million gallons of radioactive and contaminated water into Florida’s aquifer. The sinkhole was located directly below a wastewater storage pond used by Mosaic, the largest phosphate fertilizer producer in the world.
There is local outcry that the event in fact took place three weeks before the local community was notified, despite the fact that this is Florida’s largest and primary aquifer for potable water. The fertilizer company is currently working on pumping out the contaminated water and believes the wastewater is slow moving in the aquifer and has yet to reach public households. Mosaic’s phosphate fertilizer plant was storing its “gypsum stack” containing sulfate, gypsum, sodium and radioactive phosphogypsum in a pond nearby the plant.
Florida is known for sinkholes, this one however was larger than normal at 45 feet in diameter. The ground collapsed down to the aquifer below, a source of fresh water for most of Florida. Mosaic diverted the wastewater pond but not until 215 million gallons were lost down the sinkhole.