A wonderfully written, very friendly essay on the discoveries, carrier and life of Prof Dr David Sinclair and of course on sirtuins, the epigenetic theory of aging, resveratrol, nicotinamide dinucleotide NAD+ and healthy aging.
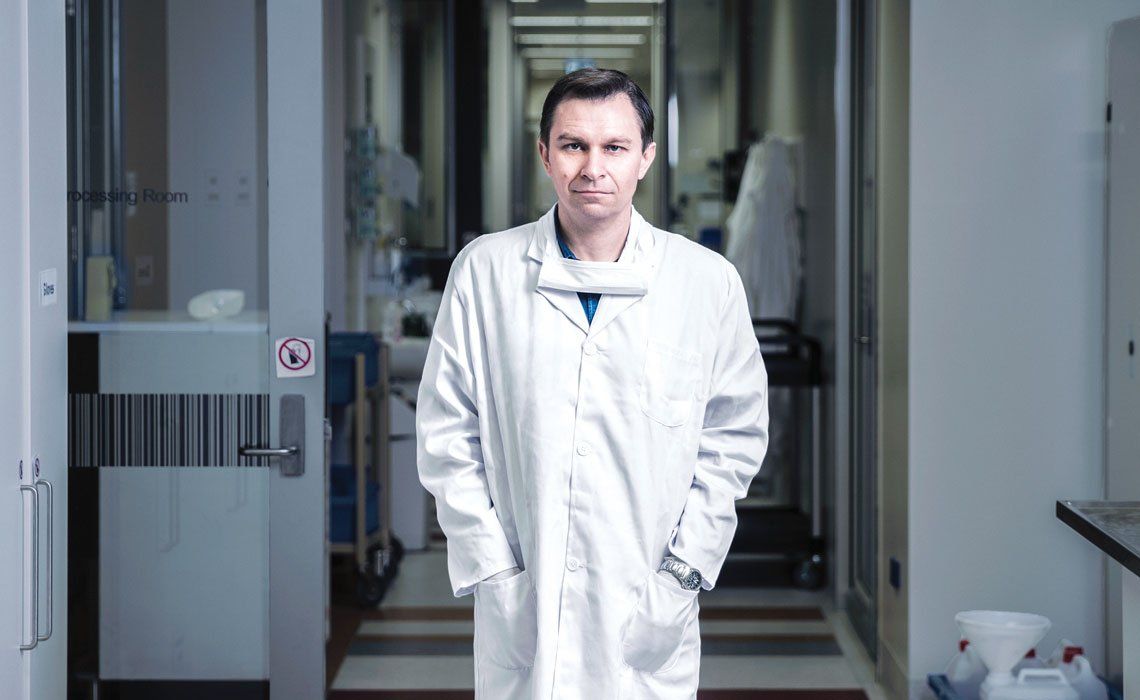
Since my recent visit to the Harvard Medical School laboratory run by Australian geneticist David Sinclair, I’ve been struggling with a shamefully greedy impulse. How can I get my hands on the wonder molecules that Sinclair is trialling to amazing effect in mice, not only slowing down their ageing but reversing it? My fear of missing out has flared up since I learnt from Sinclair that he estimates at least a third of his scientific colleagues are taking some version of these “anti-ageing” molecules, just as he does, in the belief it will increase their health spans by as much as 10 years. This means not just having a chance at living an extra decade, but living it in good health, avoiding the age-related diseases and general frailty that can make those years harrowing.
It becomes difficult to remain impartial when a respected scientist tells you he will soon turn 50, does not have a single grey hair and, according to regular blood and genetic tests, has the biological age of 31.4, even though he’s a workaholic and doesn’t exercise much. Or that he likes to think his mother prolonged her life – post lung cancer, with only one lung – for 20 years by taking the molecules he gave her, and that his 79-year-old father, who has taken several different kinds of them for years, currently lists whitewater rafting and mountaineering among his hobbies. Sinclair’s wife, Sandra Luikenhuis, even gives these molecules to the family dogs. (Luikenhuis, who has a PhD in genetics from Massachusetts Institute of Technology, only began taking the molecules herself after she noticed the irrefutably positive effect they’d had on their pets.)
If all goes well, and these anti-ageing molecules live up to their promise, Sinclair and his family will be proof it’s still possible to be going strong on the other side of the private apocalypse each of us has to face, what Philip Roth famously called the “massacre” of ageing. Imagine if you could still be standing tall after the dust clears, not one of the walking wounded, not just surviving, but thriving.