Some people object we shouldn’t cure ageing because it is natural. Well, so is malaria, for example…
You know, I may even agree ageing is ‘natural’. If we define natural as something that happens spontaneously, without external intervention, as a consequence of chemical and physical interactions, then yes, ageing is natural. This is not a great argument in favour of ageing, though, because there are very many perfectly natural things that are really bad for you, ranging on the badness spectrum pretty much anywhere from ‘mildly upsetting’ to ‘catastrophically apocalyptic’: mosquito bites, genetic diseases, viral diseses, earthquakes, tsunamis, stars going nova, being eaten by lions, cancer, a pidgeon pooing on the fancy suit you rented for your wedding precisely when you say ‘I do’, bacterial infections, and so on. So, okay, maybe ageing is natural. So what? It is also the number one cause of suffering and diseases in the western world. Frankly, I don’t give a damn if it is natural or not. It’s still pretty bad.
Speaking of rejuvenation being not natural, I could nitpick a lot. I could ask, what is ‘not natural’? Is it anything human made? Then what about things made by animals? For example, if a building is ‘not natural’, what about a beehive then? Natural or not? Given we humans have a natural tendency to tweak things around to make them work the way we want, wouldn’t rejuvenation be our natural response to the problem of ageing, just like medicines are our natural response to the problem of diseases?
I really could nitpick a lot, but it won’t be necessary. Whatever definition of ‘not natural’ one may want to give, the real issue here is that there’s a hidden meaning to ‘not natural’ which is always subtly implied, even though not stated explicitly: Things that are ‘not natural’ must be somehow bad, not good for you, dangerous for the environment, immoral, evil. Maybe they bring bad luck as well. Needless to say, this is just as wrong as claiming everything natural is good for you. Medicines are good for you. Vaccines are good for you. In a broader sense, electrical installations are good for you (if you don’t stick your fingers into the power outlet); technology, transportation, anti-seismic buildings, toothbrushes, and so on, are good for you. All ‘not natural’ stuff that is still good and you’d hardly give it up. So, okay, let’s say rejuvenation is ‘not natural’. Who cares? It’d prevent you from getting crippled by a number of nasty diseases.



Test Your Sperm in The Comfort of Your Phone
Check your swimmers with YO the first FDA cleared Smartphone based solution for testing your motile sperm.
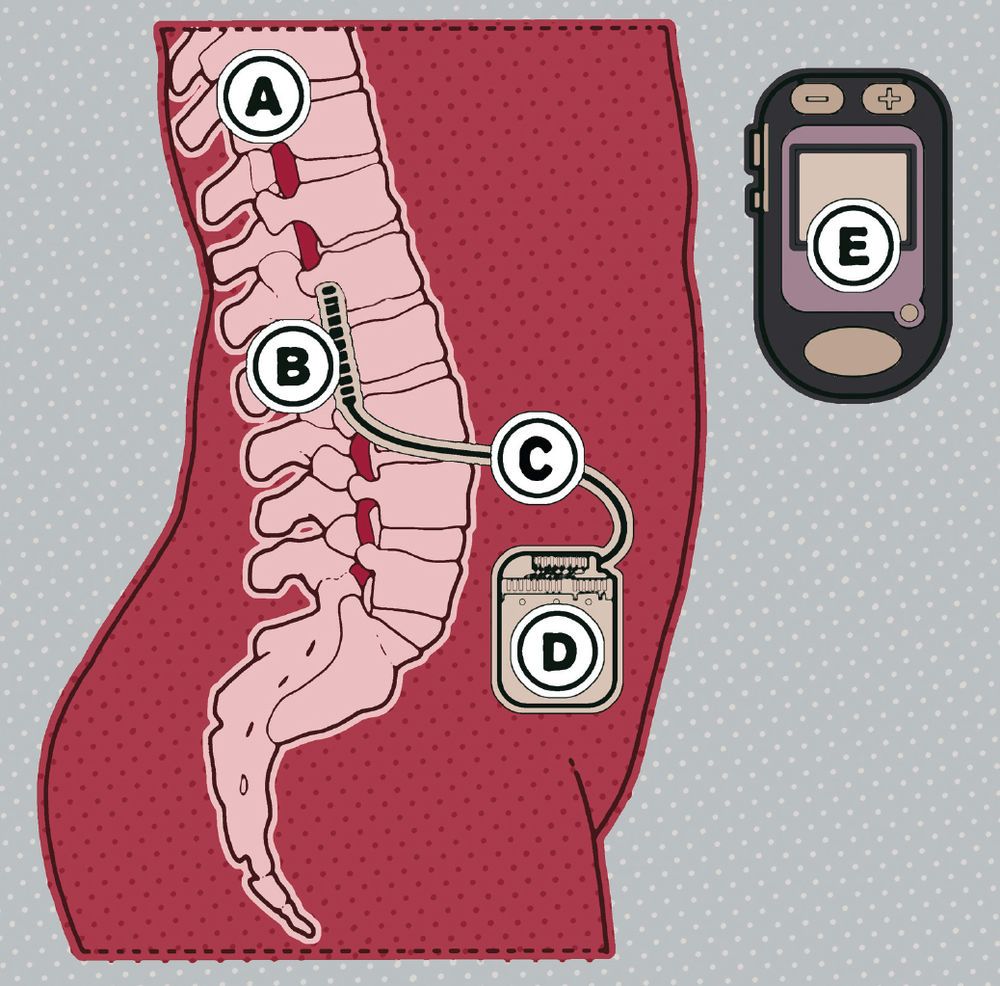
For decades, researchers have been seeking ways to help the millions of people with spinal cord injuries regain control of their limbs, with frustratingly little success. The new device provides a rare glimmer of hope. Scientists at the University of Louisville’s Kentucky Spinal Cord Injury Research Center, where Meas and three other patients received their implants, speculate that the stimulation may be reawakening connections between the brain and the body. “There’s residual circuitry that we can recover that no one realized was possible to do,” says Reggie Edgerton, director of the Neuromuscular Research Laboratory at the University of California, Los Angeles. “We were shocked.”
Some of the benefits, such as better bowel and bladder control and improved blood pressure, remain even when the device is switched off. Electrical stimulation isn’t a cure, of course. The patients still can’t walk. And the stimulation must be customized for each individual, a time-consuming process. But it’s an enormous advance nonetheless. Says Edgerton, “It opens up a whole new mechanism of recovery.”
Robots are cloning again.
Robots can evolve. Robots can reproduce. All hail our robot overlords.
The design, evolution and manufacture of robots, by robots, is called “Generative Designâ€. As reported by Global Futurist, generative design will see a future where products and services delivered by robots are designed by the robots themselves. It’s practical artificial intelligence with results you can touch and hold.
Watch for yourself.
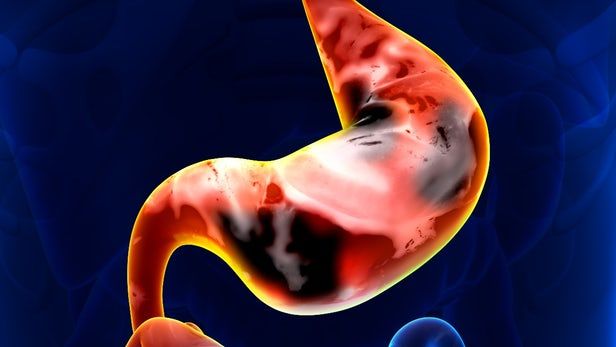
For several years, Professor George Hanna from Imperial College London has been directing work toward the development of a test that can detect cancers of the esophagus and stomach by measuring the levels of five chemicals in a patient’s breath. These chemicals are butyric, pentanoic and hexanoic acids, butanal, and decanal, which previous research has identified as pointers to the presence of stomach or esophageal cancer.
In 2015, Professor Hanna announced the results of the first clinical study analyzing the breath samples of 210 patients. The patents exhaled into a breathalyzer-like device, which used a selected ion flow tube mass spectrometer to detect the presence of any of the five aforementioned chemicals in the breath sample. The 2015 study achieved a 90 percent accuracy rate in correctly identifying the two cancers, and a recently completed, broader study has also proven successful.
The new study collected samples from 335 people across four London hospitals. Around half of the group had been diagnosed with stomach or esophageal cancer and the other half had shown no evidence of cancer after having an endoscopy. After analyzing all the samples, the new breath test achieved an 85 percent accuracy rate, correctly identifying those both with and without cancer.
Looking for that perfect gift for the medical student in your life? Search no more.
Is it wise to make medical students feel like renegade fictional genius Tony Stark, magically waving human bodies apart like the holographic diagrams in the Iron Man basement lab? Should we use technology to make millennials feel like superheroes? Stop asking difficult philosophical questions and look at how cool this is.
This augmented reality app is called Project Esper. It uses hand gestures to allow the users move and study anatomy. Users can pull the human body apart and investigate the organs and limbs piece by piece. Look—just look at this magical Star Trek karate:
Luv this.
Archaeology isn’t an easy job, but it becomes easier in virtual reality, if you can walk around ancient buildings as if they were still there.
Lithodomos VR, an Australian virtual reality archaeological startup, knows this and has raised $900,000 in Australian dollars ($679,000 in U.S. dollars) in a seed funding round.
Melbourne-based Lithodomos VR creates what it calls breathtaking, archaeologically accurate reconstructions of the ancient world in VR for use in the tourism, education and entertainment industries. It has contracts for content in Spain, museum installations, a video in the Berlin Film Festival (VR category), an app in Jerusalem, and that is just a start.