I was just telling someone today this very message. Of course they believe borders keep things from happening. Maybe physically; but not in an online retail and consumer world. Who are the most advance and real time responsive in meeting the interests and demands of consumers; will be the winners.
From time to time, the Singularity Hub editorial team unearths a gem from the archives and wants to share it all over again. It’s usually a piece that was popular back then and we think is still relevant now. This is one of those articles. It was originally published October 7, 2015. We hope you enjoy it!
You’ve heard the chatter: Robots and AI want your job. One famous study predicted 47% of today’s jobs may be automated by 2034. And if you want to know how likely it is you’ll be replaced by a robot, check out this BBC tool. (Writer = 33%. Yay?)
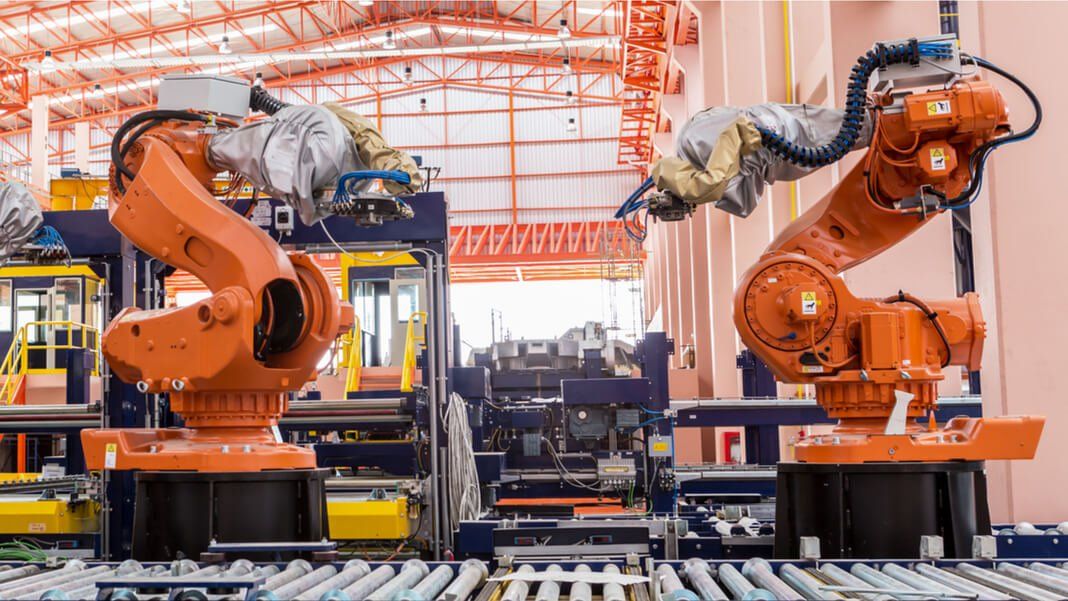
But nowhere is automation as immediately evident as it is in manufacturing. It’s been going on for decades, most obviously in automotive assembly and heavy machinery. Increasingly, however, more advanced robot factory workers are branching out.