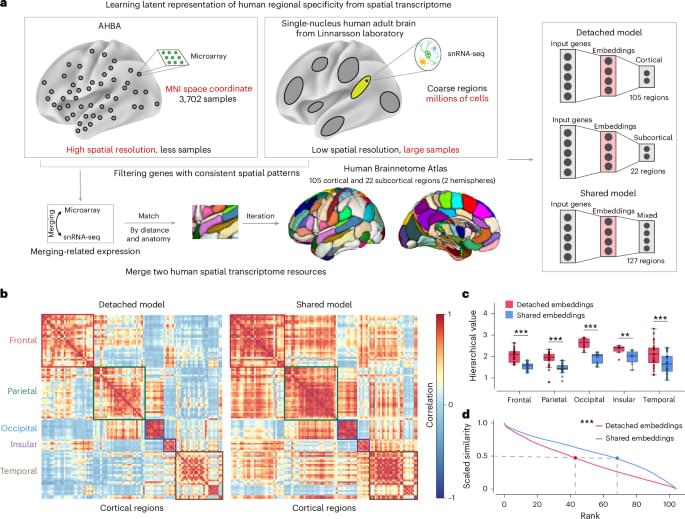
Researchers have created a protein that can detect the faint chemical signals neurons receive from other brain cells. By tracking glutamate in real time, scientists can finally see how neurons process incoming information before sending signals onward. This reveals a missing layer of brain communication that has been invisible until now. The discovery could reshape how scientists study learning, memory, and brain disease.