Microsoft is still deeply tied to OpenAI, but who knows what the future holds.


Ann Johnson became paralyzed after a brainstem stroke at age 30. As a participant in a clinical trial led by researchers at UC Berkeley and UC San Francisco, she finally heard her voice again.


Srinivasa Ramanujan Aiyangar [ a ] FRS (22 December 1887 – 26 April 1920) was an Indian mathematician. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest mathematicians of all time, despite having almost no formal training in pure mathematics. He made substantial contributions to mathematical analysis, number theory, infinite series, and continued fractions, including solutions to mathematical problems then considered unsolvable.
Ramanujan initially developed his own mathematical research in isolation. According to Hans Eysenck, “he tried to interest the leading professional mathematicians in his work, but failed for the most part. What he had to show them was too novel, too unfamiliar, and additionally presented in unusual ways; they could not be bothered”. [ 4 ] Seeking mathematicians who could better understand his work, in 1913 he began a mail correspondence with the English mathematician G. H. Hardy at the University of Cambridge, England. Recognising Ramanujan’s work as extraordinary, Hardy arranged for him to travel to Cambridge. In his notes, Hardy commented that Ramanujan had produced groundbreaking new theorems, including some that “defeated me completely; I had never seen anything in the least like them before”, [ 5 ] and some recently proven but highly advanced results.
During his short life, Ramanujan independently compiled nearly 3,900 results (mostly identities and equations). [ 6 ] Many were completely novel; his original and highly unconventional results, such as the Ramanujan prime, the Ramanujan theta function, partition formulae and mock theta functions, have opened entire new areas of work and inspired further research. [ 7 ] Of his thousands of results, most have been proven correct. [ 8 ] The Ramanujan Journal, a scientific journal, was established to publish work in all areas of mathematics influenced by Ramanujan, [ 9 ] and his notebooks—containing summaries of his published and unpublished results—have been analysed and studied for decades since his death as a source of new mathematical ideas.
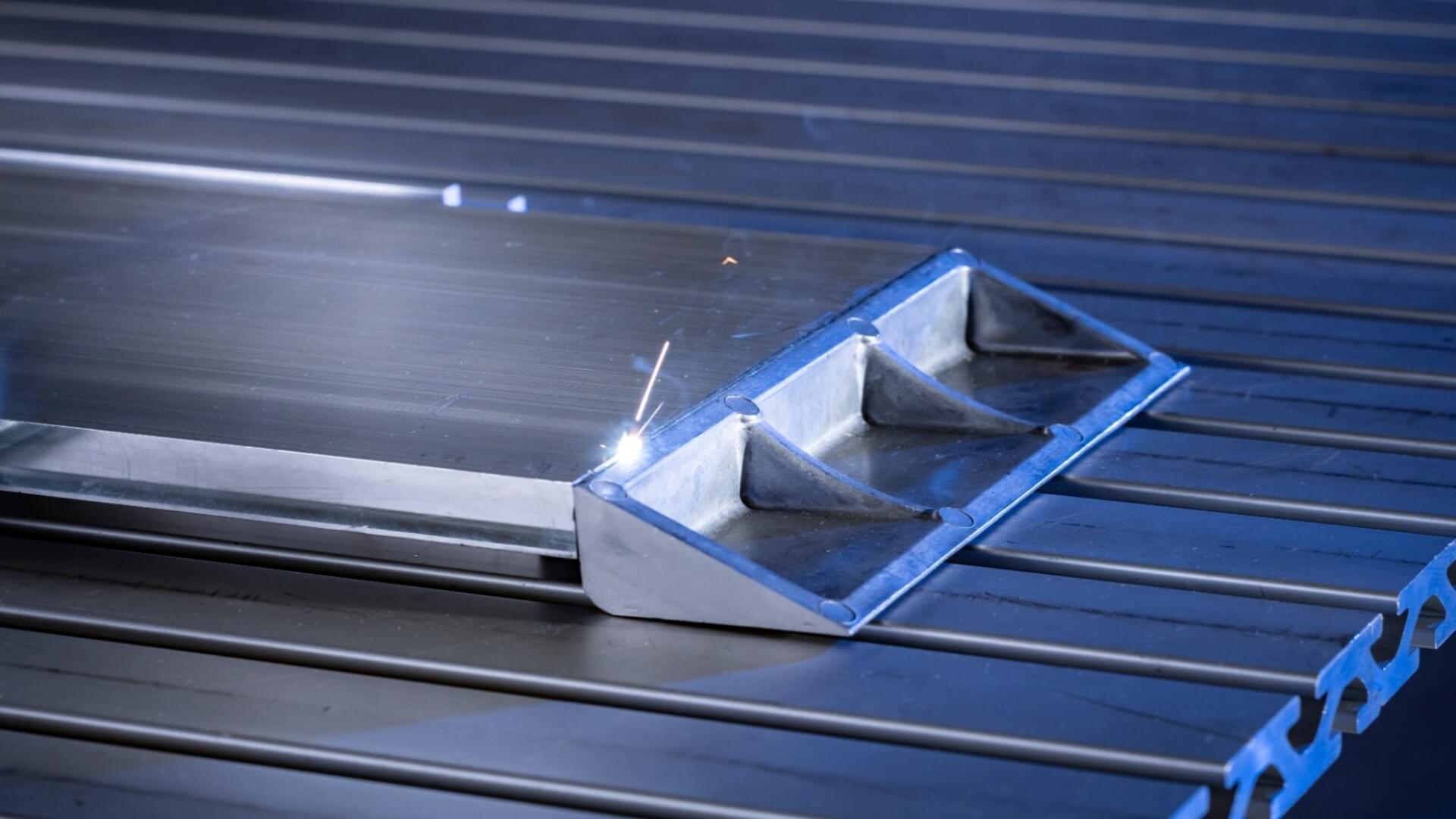

Laser welding tech enables crack-free EV battery housings without filler wire.
Researchers in Germany have recently unveiled a novel laser welding technology that eliminates the need for filler wire and delivers stronger, crack-free joints for electric vehicles, aerospace tanks, and heavy steel structures.
Developed by the Fraunhofer Institute for Material and Beam Technology IWS in Dresden, the process uses dynamic beam shaping to control the melt pool, reduce pores, and stabilize welds.
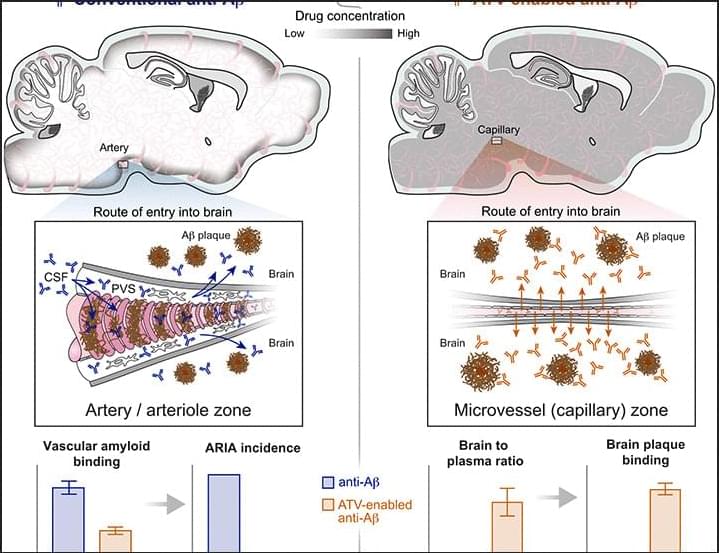
Paper on a promising Alzheimer’s immunotherapy: engineered asymmetric anti-amyloid-β antibody with a transferrin receptor binding domain for crossing the blood-brain-barrier and a mutation which mitigates harmful side effects seen in past versions of this type of treatment. #immunotherapy #alzheimers
Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA), side effects of anti-amyloid drugs seen in magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, are a major safety concern in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. We developed an antibody transport vehicle (ATV) targeting transferrin receptor (TfR) for brain delivery of anti-amyloid-β protein (anti-Aβ) using asymmetrical Fc mutations (ATVcisLALA) that mitigates TfR-related liabilities and retains effector function when bound to Aβ. Administration of ATVcisLALA:Aβ in mice exhibited broad brain distribution and enhanced parenchymal plaque target engagement. This biodistribution reduced ARIA-like lesions and vascular inflammation. Taken together, ATVcisLALA has the potential to improve the next generation of Aβ immunotherapy through enhanced biodistribution mediated by transport across the blood-brain barrier.
Peter H. Diamandis