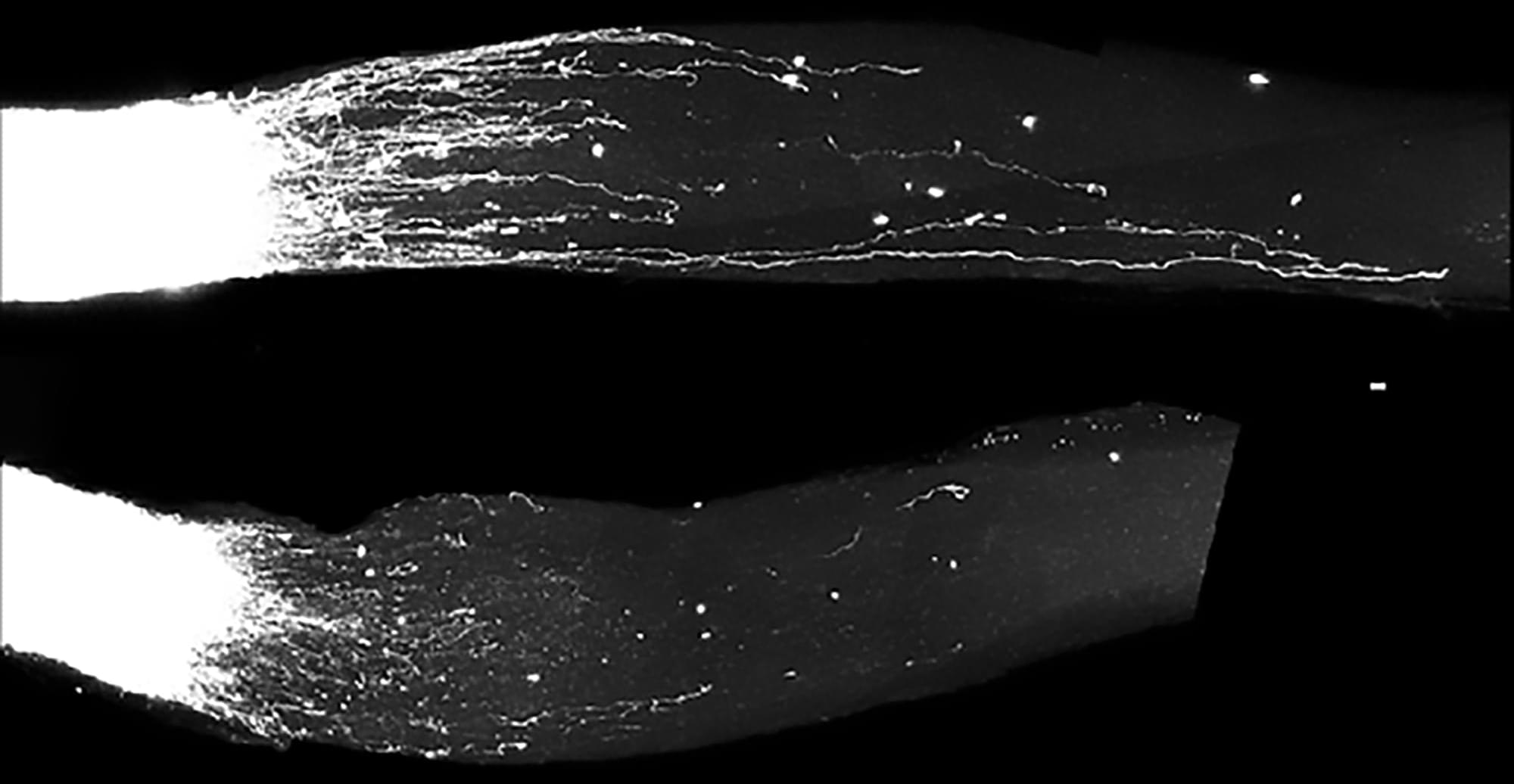
Once dismissed as “junk,” a group of RNA molecules has been found to help regrow damaged nerves in mice in new research. The discovery could unlock new ways to treat nerve injuries and even restore growth in the brain and spinal cord.


On the morning of April 26, Tsinghua University held an inauguration ceremony for Tsinghua AI Agent Hospital and the 2025 Tsinghua Medicine Townhall Meeting at the Main Building Reception Hall. Tsinghua President Li Luming and Vice President Wang Hongwei attended the event.
President Li Luming reviewed the progress of Tsinghua University’s medical programs over the past year, emphasizing the University’s strong commitment to the development of medical disciplines. He highlighted Tsinghua’s strength in fundamental research in Artificial intelligence, which has already led to a series of high-level innovations at the intersection of AI and medicine. The establishment of the Tsinghua AI Agent Hospital represents a new initiative by Tsinghua to leverage its strengths in science and engineering to empower the advancement of medicine.
President Li encouraged Tsinghua Medicine to remain committed to fostering virtue and talent, cultivating a new generation of medical innovators with both a strong medical foundation and AI literacy. He also called for deeper integration across disciplines, particularly between engineering and medicine, as well as closer ties between clinical practice and technology. Finally, he urged Tsinghua Medicine to align its work with cutting-edge global trends and national strategic needs, driving medical advancement and contributing to the protection of public health.
Questions to inspire discussion.
Safety and Performance.
🛡️ Q: How does Tesla’s full self-driving system compare to human driving in terms of safety? A: According to Elon Musk, Tesla’s end-to-end neural networks trained on massive video datasets have been proven to be dramatically safer than average human driving.
⚡ Q: What recent hardware upgrade has improved Tesla’s full self-driving capabilities? A: Tesla’s AI4 hardware has been upgraded to 150–200 watts, enabling more complex neural networks and faster decision-making, achieving 36 frames per second processing.
Scalability and Efficiency.
📈 Q: Why is Tesla’s vision-only approach considered more scalable than competitors’ methods? A: Tesla’s vision-only approach is more scalable than competitors’ use of multiple sensors, sensor fusion, and high-definition maps, as stated by BU’s Robin Lee.
🚀 Q: When are the next Starship test flights scheduled? A: Flight 10 is targeting August 4th, while Flight 11 is set for September 1st, 2025, marking the final Block 2 Starship tests.
🛰️ Q: What new AI initiative is SpaceX undertaking? A: SpaceX is hiring AI software engineers to integrate artificial intelligence into engineering workflows supporting Falcon, Starship, and satellite operations.

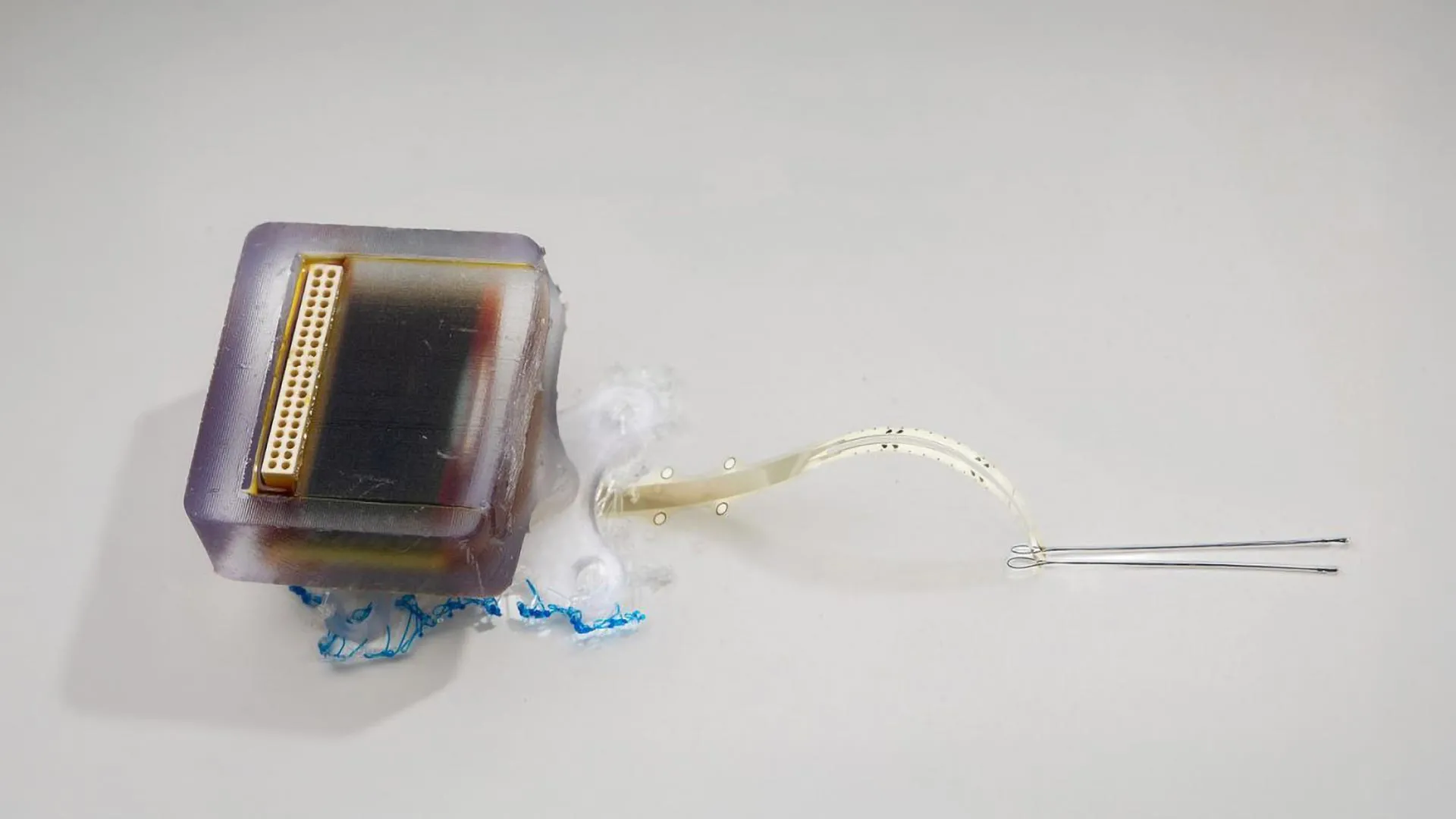
A groundbreaking study from the University of Auckland and Chalmers University of Technology is offering new hope for spinal cord injury patients. Researchers have developed an ultra-thin implant that delivers gentle electric currents directly to the injured spinal cord. This device mimics natural developmental signals to stimulate nerve healing, and in animal trials, it restored movement and touch sensation in rats—without causing inflammation or damage.
Yellowstone, a popular tourist destination and namesake of an equally popular TV show, was the first-ever national park in the United States. And bubbling beneath it—to this day—is one of Earth’s most seismically active networks of volcanic activity.
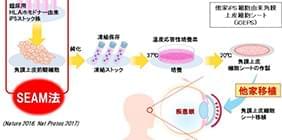
A group of researchers led by Prof. NISHIDA Kohji of Osaka University transplanted iPS cells-derived corneal epithelial cell sheets into a patient with corneal disorders in July 2019.
This is the first clinical study of cornea regeneration using iPS to examine the safety and effects of sheet-shaped corneal epithelial cells, which are cultivated by inducing corneal epithelial cells using iPS cells from others (provided by the Center for iPS Cell Research and Application (CiRA), Kyoto University), with their own method. The status of the patient, who was discharged from hospital on August 23, 2019, will be continually monitored.
Corneal epithelial stem cell deficiency caused by damage to the corneal epithelium has challenges, such as donor shortage and rejection in recipients of transplants using donor corneas. In order to ultimately solve these challenges, the research group has advanced the development of regenerative therapies using hiPS-derived corneal cells.
A gene called SDR42E1 has been identified as a key player in how our bodies absorb and process vitamin D. Researchers found that disabling this gene in colorectal cancer cells not only crippled their survival but also disrupted thousands of other genes tied to cancer and metabolism. This opens the door to highly targeted cancer therapies—by either cutting off vitamin D supply to tumors or enhancing the gene’s activity to boost health. The findings hint at vast possibilities in treating diseases influenced by vitamin D, though long-term impacts remain uncertain.