Much like a tongue freezes to a frigid metal pole, ice can cause speed up the adsorption, or stickiness, of molecules. An icy surface can also cause molecules to degrade in the presence of light, releasing trace gases. Before researchers can measure these reactions and incorporate their impacts in global atmospheric models, researchers first need to understand the structure of ice itself.
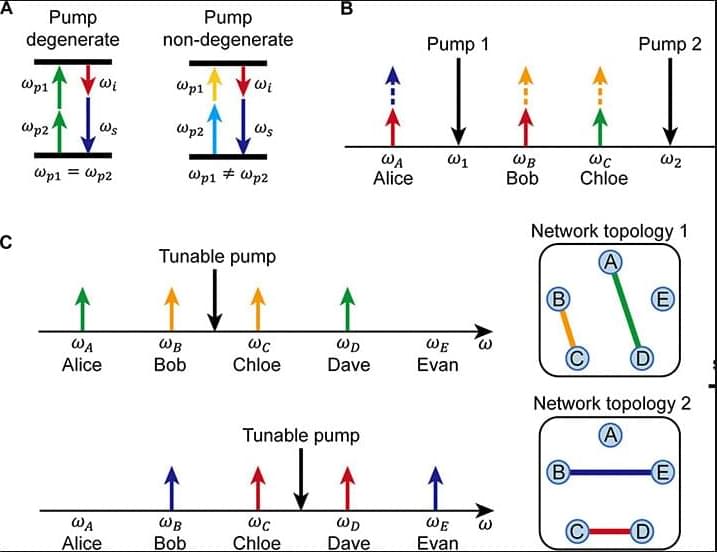
InnovativeTsinghua researchers proposed a reconfigurable quantum entanglement distribution network using siliconphotonics, reducing the required wavelength channels to O(N) and improving the scalability, reconfigurability, and performance of quantum technology.
More: bit.ly/3W9PvNx
💫 Meet the area of science that even Albert Einstein himself called “spooky”: quantum entanglement! 🤯
Classical physics is the force governing an extremely predictable world, where an apple set on a table stays there until something causes it to move again.
In the quantum world, not only can the apple end up on Mars, but, hypothetically, it could exist both on the table and on Mars at the same time. It could even be inextricably tied to another apple in some other part of the universe through entanglement. Thus, “reality” as we know it is much more uncertain, with the possibility for many solutions or outcomes to exist, rather than just one.
Quantum entanglement remains a spooky part of our world. Check out the resources below to learn more about how NASA scientists are working to unravel the mysteries of our quantum universe.
Transfer RNAs (called tRNAs for short) are small RNA molecules that play an important role in protein synthesis! Each tRNA corresponds to one of the 20 possible protein building blocks in humans called amino acids. As the ribosome reads each codon along an mRNA, the tRNA bring the correct amino acid, which is then added to the growing protein molecule!
Many types of RNA, including tRNAs, fold into specific shapes that help them function and keep them stable. Complementary sequences at different positions along the length of an RNA fold the molecule into loops and other complex structures.
TRNAs are folded into a distinct L-shape that helps them carry out their function. One end of the tRNA has a specific sequence to match a codon on the mRNA, while the other end of the tRNA has a site to carry the amino acid that will be added to the new protein.
Learn more in our RNA fact sheet!
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is an essential molecule that performs many roles in the cell, from carrying the instructions to make proteins to regulating genes.
So far, 20 pipo don share ova $4m in rewards afta dem find $40m of di stolen money and call di crypto companies make dem block di transfer.
But sabi pipo no dey optimistic again say dem go fit recover di rest of di money becos of di North Korean knowledge for hacking and laundering of di money.
Dr Dorit Dor from cyber security company Check Point tok say, “North Korea na veri closed system and closed economy so dem don create successful industry of hacking and laundering and dem no care about di negative impression of cyber crime”
Quantum entanglement is a fundamental phenomenon in nature and one of the most intriguing aspects of quantum mechanics. It describes a correlation between two particles, such that measuring the properties of one instantly reveals those of the other, no matter how far apart they are. This unique property has been harnessed in applications such as quantum computing and quantum communication.
A common method for generating entanglement is through a nonlinear crystal, which produces photon pairs with entangled polarizations via spontaneous parametric down-conversion (SPDC): if one photon is measured to be horizontally polarized, the other will always be vertically polarized, and vice versa.
Meanwhile, metasurfaces—ultrathin optical devices—are known for their ability to encode vast amounts of information, allowing the creation of high-resolution holograms. By combining metasurfaces with nonlinear crystals, researchers can explore a promising approach to enhancing the generation and control of entangled photon states.
Mathematicians from New York University and the University of British Columbia have resolved a decades-old geometric problem, the Kakeya conjecture in 3D, which studies the shape left behind by a needle moving in multiple directions.
The research is published on the arXiv preprint server.
The Kakeya conjecture was inspired by a problem asked in 1917 by Japanese mathematician Sōichi Kakeya: What is the region of smallest possible area in which it is possible to rotate a needle 180 degrees in the plane? Such regions are called Kakeya needle sets.
The one advantage combat pilots had over artificial intelligence was unpredictability. Now a new study has put that in jeopardy.
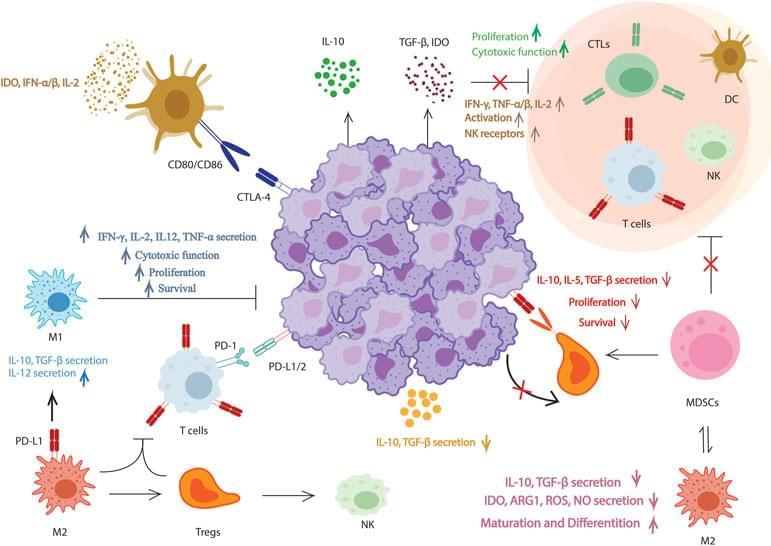
Lung cancer is the major cause of cancer death worldwide. Cancer immunotherapy has been introduced as a promising and effective treatment that can improve the immune system’s ability to eliminate cancer cells and help establish immunological memory. Nanoparticles can contribute to the rapidly evolving field of immunotherapy by simultaneously delivering a variety of immunological agents to the target site and tumor microenvironment. Nano drug delivery systems can precisely target biological pathways and be implemented to reprogram or regulate immune responses. Numerous investigations have been conducted to employ different types of nanoparticles for immunotherapy of lung cancer. Nano-based immunotherapy adds a strong tool to the diverse collection of cancer therapies. This review briefly summarizes the remarkable potential opportunities for nanoparticles in lung cancer immunotherapy and its challenges.
Humankind’s quest to defeat cancer continues by developing targeted treatments. Among the frequently used cancer treatments with significant improvements are chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery, and combinations of them. However, these strategies have various limitations; for instance, although surgery offers the best outcome for cancers detected at early stages, this approach often falls short for cancers detected at late stages which have already spread throughout the body. Furthermore, chemotherapy has low specificity, drug-induced side effects, and drug resistance, and has shown higher cancer relapse rates similar to radiation therapy (Velpurisiva et al., 2017; Doroudian et al., 2020; Niloy et al., 2021; Anconina et al., 2022; Hosseinkazemi et al., 2022). As a result, researchers were encouraged to make use of the human body’s own defense system as a tool to fight cancer.
Chinese firm Xpeng announced its plans to mass-produce flying cars and humanoid robots by next year.
He Xiaopeng, XPeng Motors’ chairman and CEO, stated that if the project remains on track, XPeng could be the first company to mass-produce flying cars globally, reports a Chinese online daily.
The company’s Iron humanoid robot is now in use at the EV maker’s Guangzhou factory, and it plans to start mass-production. By 2026, humanoid robots with entry-level Level 3 capabilities in the country are expected to enter moderate-scale commercial production, Xiapeng added.
Chinese EV maker XPeng aims to mass-produce flying cars and humanoid robots, with Level 3 robots set for commercial production by 2026.