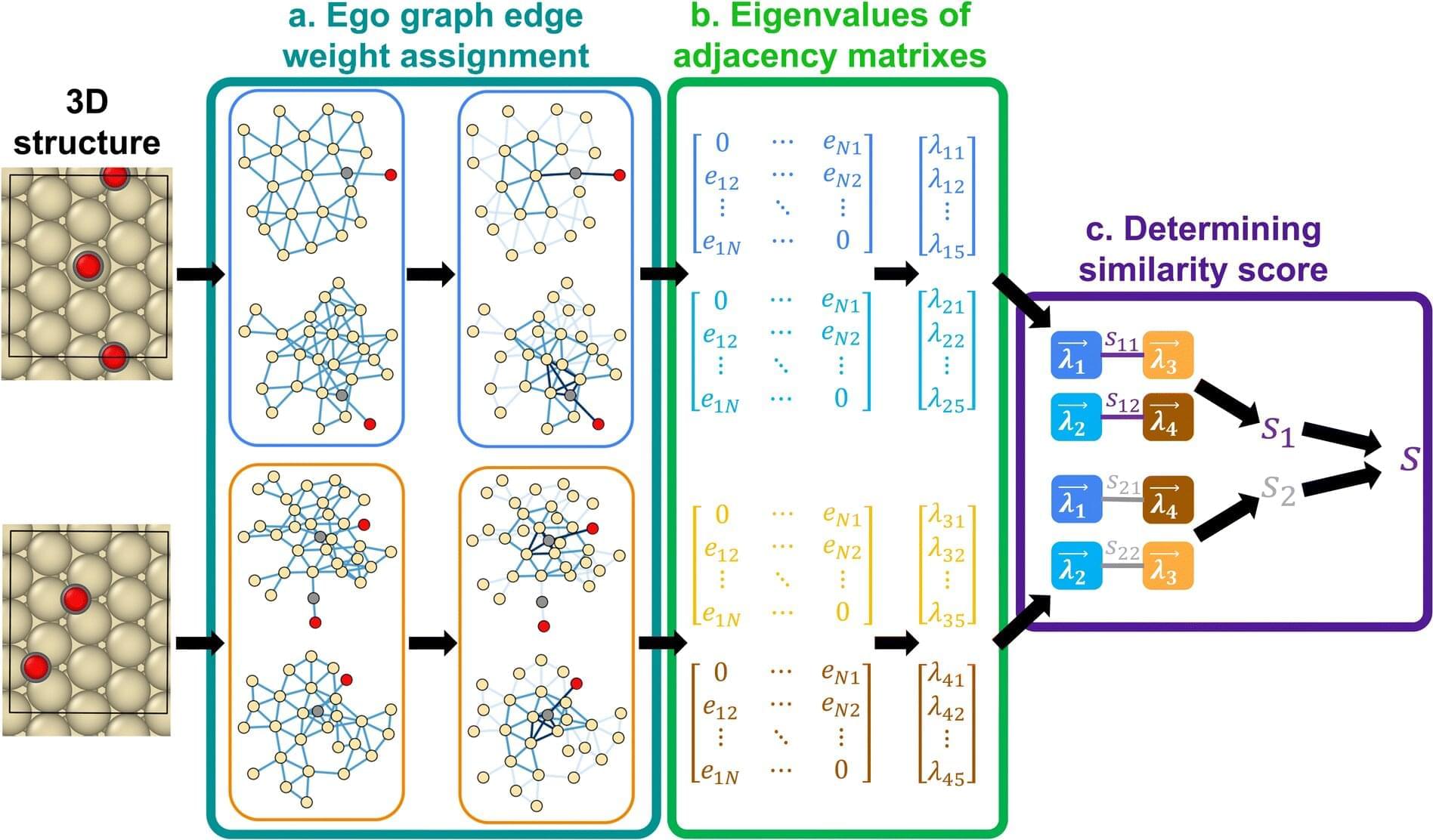
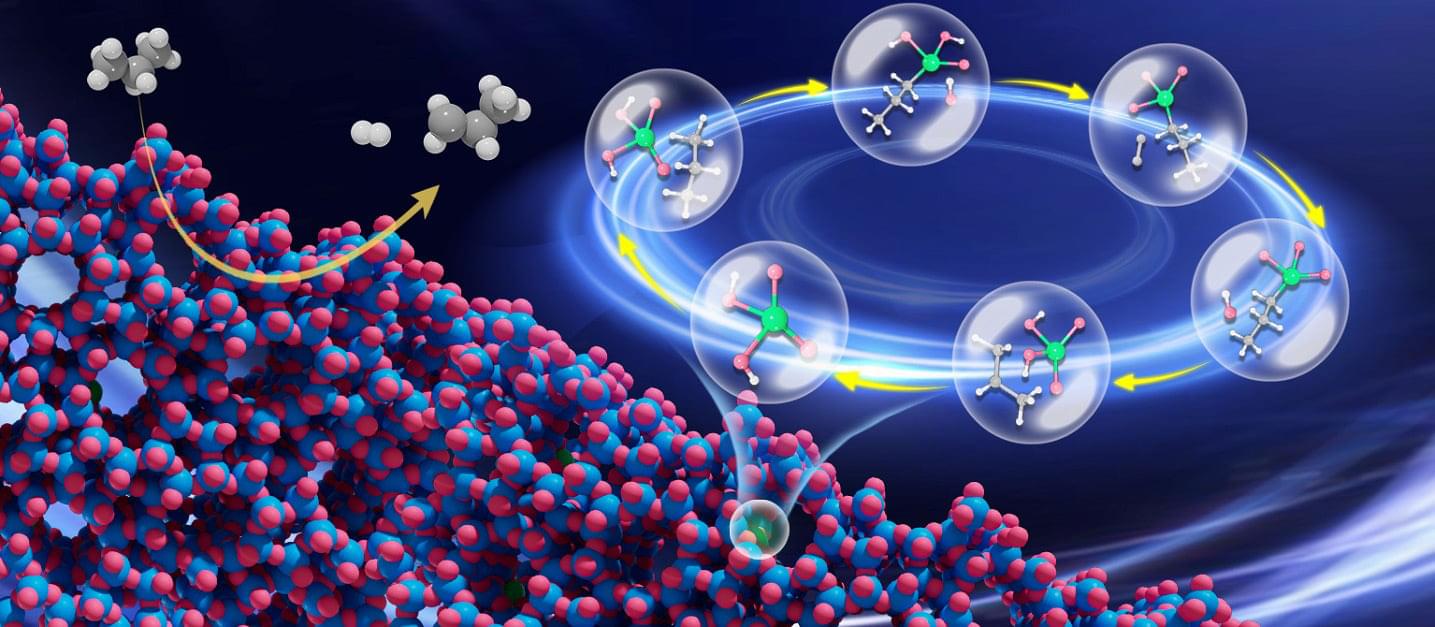
A new algorithm opens the door for using artificial intelligence and machine learning to study the interactions that happen on the surface of materials.
Scientists and engineers study the atomic interactions that happen on the surface of materials to develop more energy efficient batteries, capacitors, and other devices. But accurately simulating these fundamental interactions requires immense computing power to fully capture the geometrical and chemical intricacies involved, and current methods are just scratching the surface.
“Currently it’s prohibitive and there’s no supercomputer in the world that can do an analysis like that,” says Siddharth Deshpande, an assistant professor in the University of Rochester’s Department of Chemical Engineering. “We need clever ways to manage that large data set, use intuition to understand the most important interactions on the surface, and apply data-driven methods to reduce the sample space.”